Abstract
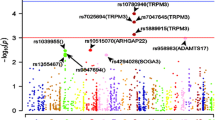
Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD) is a nonallergic clinical syndrome characterized by a severe decline in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) following the ingestion of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin. The effects of genetic variants have not fully explained all of the observed individual differences to an aspirin challenge despite previous attempts to identify AERD-related genes. In the present study, we performed genome-wide association study (GWAS) and targeted association study in Korean asthmatics to identify new genetic factors associated with AERD. A total of 685 asthmatic patients without AERD and 117 subjects with AERD were used for the GWAS of the first stage, and 996 asthmatics without AERD and 142 subjects with AERD were used for a follow-up study. A total of 702 SNPs were genotyped using the GoldenGate assay with the VeraCode microbead. GWAS revealed the top-ranked variants in 3′ regions of the HLA-DPB1 gene. To investigate the detailed genetic effects of an associated region with the risk of AERD, a follow-up targeted association study with the 702 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of 14 genes was performed on 802 Korean subjects. In a case–control analysis, HLA-DPB1 rs1042151 (Met105Val) shows the most significant association with the susceptibility of AERD (p = 5.11 × 10−7; OR = 2.40). Moreover, rs1042151 also shows a gene dose for the percent decline of FEV1 after an aspirin challenge (p = 2.82 × 10−7). Our findings show that the HLA-DPB1 gene polymorphism may be the most susceptible genetic factor for the risk of AERD in Korean asthmatics and confirm the importance of HLA-DPB1 in the genetic etiology of AERD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
(1995) Global Initiative for Asthma. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. NHLBI/WHO workshop report. Bethesda. National Institutes of Health
Akahoshi M, Obara K, Hirota T, Matsuda A, Hasegawa K, Takahashi N, Shimizu M, Nakashima K, Cheng L, Doi S, Fujiwara H, Miyatake A, Fujita K, Higashi N, Taniguchi M, Enomoto T, Mao XQ, Nakashima H, Adra CN, Nakamura Y, Tamari M, Shirakawa T (2005) Functional promoter polymorphism in the TBX21 gene associated with aspirin-induced asthma. Hum Genet 117:16–26
Babu KS, Salvi SS (2000) Aspirin and asthma. Chest 118:1470–1476
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21:263–265
Bennett A (2000) The importance of COX-2 inhibition for aspirin induced asthma. Thorax 55(Suppl 2):S54–S56
Bodmer JG, Marsh SG, Parham P, Erlich HA, Albert E, Bodmer WF, Dupont B, Mach B, Mayr WR, Sasazuki T et al (1990) Nomenclature for factors of the HLA system, 1989. Tissue Antigens 35:1–8
Chang HS, Park JS, Jang AS, Park SW, Uh ST, Kim YH, Park CS (2011) Diagnostic value of clinical parameters in the prediction of aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease in asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 3:256–264
Choi JH, Lee KW, Oh HB, Lee KJ, Suh YJ, Park CS, Park HS (2004a) HLA association in aspirin-intolerant asthma: DPB1*0301 as a strong marker in a Korean population. J Allergy Clin Immunol 113:562–564
Choi JH, Park HS, Oh HB, Lee JH, Suh YJ, Park CS, Shin HD (2004b) Leukotriene-related gene polymorphisms in ASA-intolerant asthma: an association with a haplotype of 5-lipoxygenase. Hum Genet 114:337–344
Dekker JW, Easteal S (1990) HLA-DP typing by amplified fragment length polymorphisms (AFLPs). Immunogenetics 32:56–59
Dekker JW, Nizankowska E, Schmitz-Schumann M, Pile K, Bochenek G, Dyczek A, Cookson WO, Szczeklik A (1997) Aspirin-induced asthma and HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DPB1 genotypes. Clin Exp Allergy 27:574–577
Delaney JC, Kay AB (1976) Complement components and IgE in patients with asthma and aspirin idiosyncrasy. Thorax 31:425–427
Gudbjartsson DF, Bjornsdottir US, Halapi E, Helgadottir A, Sulem P, Jonsdottir GM, Thorleifsson G, Helgadottir H, Steinthorsdottir V, Stefansson H, Williams C, Hui J, Beilby J, Warrington NM, James A, Palmer LJ, Koppelman GH, Heinzmann A, Krueger M, Boezen HM, Wheatley A, Altmuller J, Shin HD, Uh ST, Cheong HS, Jonsdottir B, Gislason D, Park CS, Rasmussen LM, Porsbjerg C, Hansen JW, Backer V, Werge T, Janson C, Jonsson UB, Ng MC, Chan J, So WY, Ma R, Shah SH, Granger CB, Quyyumi AA, Levey AI, Vaccarino V, Reilly MP, Rader DJ, Williams MJ, van Rij AM, Jones GT, Trabetti E, Malerba G, Pignatti PF, Boner A, Pescollderungg L, Girelli D, Olivieri O, Martinelli N, Ludviksson BR, Ludviksdottir D, Eyjolfsson GI, Arnar D, Thorgeirsson G, Deichmann K, Thompson PJ, Wjst M, Hall IP, Postma DS, Gislason T, Gulcher J, Kong A, Jonsdottir I, Thorsteinsdottir U, Stefansson K (2009) Sequence variants affecting eosinophil numbers associate with asthma and myocardial infarction. Nat Genet 41:342–347
Himes BE, Hunninghake GM, Baurley JW, Rafaels NM, Sleiman P, Strachan DP, Wilk JB, Willis-Owen SA, Klanderman B, Lasky-Su J, Lazarus R, Murphy AJ, Soto-Quiros ME, Avila L, Beaty T, Mathias RA, Ruczinski I, Barnes KC, Celedon JC, Cookson WO, Gauderman WJ, Gilliland FD, Hakonarson H, Lange C, Moffatt MF, O’Connor GT, Raby BA, Silverman EK, Weiss ST (2009) Genome-wide association analysis identifies PDE4D as an asthma-susceptibility gene. Am J Hum Genet 84:581–593
Hitomi Y, Ebisawa M, Tomikawa M, Imai T, Komata T, Hirota T, Harada M, Sakashita M, Suzuki Y, Shimojo N, Kohno Y, Fujita K, Miyatake A, Doi S, Enomoto T, Taniguchi M, Higashi N, Nakamura Y, Tamari M (2009) Associations of functional NLRP3 polymorphisms with susceptibility to food-induced anaphylaxis and aspirin-induced asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124(779-85):e6
Jinnai N, Sakagami T, Sekigawa T, Kakihara M, Nakajima T, Yoshida K, Goto S, Hasegawa T, Koshino T, Hasegawa Y, Inoue H, Suzuki N, Sano Y, Inoue I (2004) Polymorphisms in the prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype 2 gene confer susceptibility to aspirin-intolerant asthma: a candidate gene approach. Hum Mol Genet 13:3203–3217
Kim SH, Choi JH, Lee KW, Shin ES, Oh HB, Suh CH, Nahm DH, Park HS (2005a) The human leucocyte antigen-DRB1*1302-DQB1*0609-DPB1*0201 haplotype may be a strong genetic marker for aspirin-induced urticaria. Clin Exp Allergy 35:339–344
Kim SH, Choi JH, Park HS, Holloway JW, Lee SK, Park CS, Shin HD (2005b) Association of thromboxane A2 receptor gene polymorphism with the phenotype of acetyl salicylic acid-intolerant asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 35:585–590
Kim SH, Ye YM, Lee SK, Choi JH, Holloway JW, Park CS, Park HS (2006) Association of TNF-alpha genetic polymorphism with HLA DPB1*0301. Clin Exp Allergy 36:1247–1253
Kim SH, Ye YM, Hur GY, Lee SK, Sampson AP, Lee HY, Park HS (2007) CysLTR1 promoter polymorphism and requirement for leukotriene receptor antagonist in aspirin-intolerant asthma patients. Pharmacogenomics 8:1143–1150
Kim TH, Chang HS, Park SM, Nam BY, Park JS, Rhim T, Park HS, Kim MK, Choi IS, Cho SH, Chung IY, Park BL, Park CS, Shin HD (2008) Association of angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene polymorphisms with aspirin intolerance in asthmatics. Clin Exp Allergy 38:1727–1737
Kim JH, Park BL, Cheong HS, Bae JS, Park JS, Jang AS, Uh ST, Choi JS, Kim YH, Kim MK, Choi IS, Cho SH, Choi BW, Park CS, Shin HD (2010) Genome-wide and follow-up studies identify CEP68 gene variants associated with risk of aspirin-intolerant asthma. PLoS ONE 5:e13818
Lee SH, Rhim T, Choi YS, Min JW, Kim SH, Cho SY, Paik YK, Park CS (2006) Complement C3a and C4a increased in plasma of patients with aspirin-induced asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173:370–378
Lin CH, Yeakley JM, McDaniel TK, Shen R (2009) Medium- to high-throughput SNP genotyping using VeraCode microbeads. Methods Mol Biol 496:129–142
Macy E, Bernstein JA, Castells MC, Gawchik SM, Lee TH, Settipane RA, Simon RA, Wald J, Woessner KM (2007) Aspirin challenge and desensitization for aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease: a practice paper. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 98:172–174
Moffatt MF, Kabesch M, Liang L, Dixon AL, Strachan D, Heath S, Depner M, von Berg A, Bufe A, Rietschel E, Heinzmann A, Simma B, Frischer T, Willis-Owen SA, Wong KC, Illig T, Vogelberg C, Weiland SK, von Mutius E, Abecasis GR, Farrall M, Gut IG, Lathrop GM, Cookson WO (2007) Genetic variants regulating ORMDL3 expression contribute to the risk of childhood asthma. Nature 448:470–473
Nizankowska-Mogilnicka E, Bochenek G, Mastalerz L, Swierczynska M, Picado C, Scadding G, Kowalski ML, Setkowicz M, Ring J, Brockow K, Bachert C, Wohrl S, Dahlen B, Szczeklik A (2007) EAACI/GA2LEN guideline: aspirin provocation tests for diagnosis of aspirin hypersensitivity. Allergy 62:1111–1118
Oh SH, Park SM, Park JS, Jang AS, Lee YM, Uh ST, Kim YH, Choi IS, Kim MK, Park BL, Shin HD, Park CS (2009) Association analysis of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors gamma gene polymorphisms with aspirin hypersensitivity in asthmatics. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 1:30–35
Park HS, Kim SH, Sampson AP, Lee KW, Park CS (2004) The HLA-DPB1*0301 marker might predict the requirement for leukotriene receptor antagonist in patients with aspirin-intolerant asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114:688–689
Park JS, Chang HS, Park CS, Lee JH, Lee YM, Choi JH, Park HS, Kim LH, Park BL, Choi YH, Shin HD (2005) Association analysis of cysteinyl-leukotriene receptor 2 (CYSLTR2) polymorphisms with aspirin intolerance in asthmatics. Pharmacogenet Genomics 15:483–492
Sanak M, Szczeklik A (2001) Leukotriene C4 synthase polymorphism and aspirin-induced asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 107:561–562
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P (2001) A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 68:978–989
Sturtevant J (1999) NSAID-induced bronchospasm—a common and serious problem. A report from MEDSAFE, the New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority. NZ Dent J 95:84
Van der Zwan RE, Tilanus MG (2000) Sequence-based typing for HLA-DPB1 strategy for ABI sequencing equipment. In: Tilanus MGJ, Hansen JA, Heuley CK (eds) IHWG technical manual. International Histocompatibility Working Group, Seattle, TM14A, pp 1–4
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A090548 & 010249), and by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea Government (MEST) (No. 2009-0080157). The DNA samples were generously provided by Soonchunhyang University, Bucheon Hospital Biobank, a member of the National Biobank of Korea, supported by the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
439_2012_1247_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. The eQTL result of rs1042151 of HLA-DPB1. Red box indicates eQTL rs1042151 of HLA-DPB1 derived from the eQTL browser (http://eqtl.uchicago.edu/cgi-bin/gbrowse/eqtl/) (TIFF 2722 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, B.L., Kim, TH., Kim, JH. et al. Genome-wide association study of aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease in a Korean population. Hum Genet 132, 313–321 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-012-1247-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-012-1247-2