Abstract
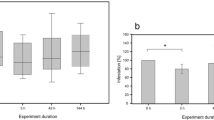
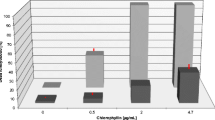
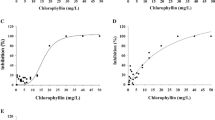
Tests were conducted to determine the efficiency of the photodynamic substance chlorophyllin to kill different life stages of the protozoan parasite Ichthyophthirius mulftifiliis (Fouquet) which causes the white spot disease in many freshwater fish species. This study has developed a new treatment for the control of ichthyophthiriosis, and demonstrated that non-toxic water-soluble chlorophyll (chlorophyllin) is a potential remedial agent at low concentrations for this serious parasitic disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Callinan RB, Rowland SJ (1995) Diseases of silver perch. Silver Perch Culture, Austasia Aquaculture 67–75
He Y-Y, Häder D-P (2002) Involvement of reactive oxygen species in the UV-B damage to the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 66:73–80
Klisch M, Sinha RP, Richter PR, Häder D-P (2001) Mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) protect against UV-B-induced damage in Gyrodinium dorsum Kofoid. J Plant Physiol 158:1449–1454
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592
Paperna I (1991) Diseases caused by parasites in the aquaculture of warm water fish. Annu Rev Fish Dis 1:155–194
Selosse PM, Rowland SJ (1990) Use of common salt to treat ichthyophthiriasis in Australian warmwater fishes. Prog Fish Cult 52:124–127
Tiemann DM, Goodwin AE (2001) Treatment for ich infestation in channel catfish evaluated under static and flow-through water conditions. N Am J Aquacult 63:293–299
Tominaga H, Kodama S, Matsuda N, Suzuki K, Watanabe M (2004) Involvement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the induction of genetic instability by radiation. J Radiat Res 45:181–188
Wahli T, Schmitt M, Meier W (1993) Evaluation of alternatives to malachite green oxalate as a therapeutant for ichthyophthiriosis in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J Appl Ichthyol 9:237–249
Wohllebe S, Richter R, Richter P, Häder D-P (2009) Photodynamic control of human pathogenic parasites in aquatic ecosystems using chlorophyllin and pheophorbid as photodynamic substances. Parasitol Res 104:593–600
Wohllebe S, Ulbrich C, Grimm D, Pietsch J, Erzinger G, Richter R, Lebert M, Richter PR, Häder D-P (2011) Photodynamic treatment of Chaoborus crystallinus larvae with chlorophyllin induces necrosis and apoptosis. Photochem Photobiol 87:1113–1122
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the funding of the Federal Office for Agriculture and Food (BLE) and the Bavarian Institute of Fishery, especially Dr. Wedekind and Dr. Oberle. We thank Dr. Sven Bergmann and Lars Dettmann for the advice and input to our research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wohllebe, S., Richter, P. & Häder, DP. Chlorophyllin for the control of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (Fouquet). Parasitol Res 111, 729–733 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-2893-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-2893-y