Abstract
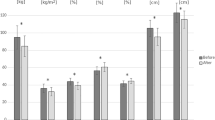
The present study aimed to investigate whether obese children improve their balance and postural performance following a 6-month-weight management program. Twenty-nine obese children aged 6–14 years were examined posturographically before and after participation in weight management program. The interactive balance system evaluated the stability index, Fourier spectral analysis, weight distribution index, and falling index. The performance was evaluated for eight positions requiring closure of eyes, standing on pillows, as well as head turns. Anthropometric measurements (e.g., weight, height, BMI, and BMI percentiles) were also determined before and after the intervention. We found significant increase in height and significant decreased in BMI percentile following the intervention program (p < .05). Pre-intervention BMI percentile was found to be correlated with stability index in most of the positions measured (e.g., normal open position = .464; p = .011). Following the intervention program, an interaction was found between BMI percentile differences (pre- versus post-interventional) and balance (stability index and F2–F4 frequencies of most standing positions). Furthermore, a correlation was found between general stability and the falling index (.446; p = .015). Regression analysis showed that only initial weight distribution index and post-intervention BMI entered the equation as predictors of post-intervention weight distribution index. Conclusion: Weight management program for childhood obesity improved stability, reduced potential vestibular stress/disturbances, and decreased falling probability of the participants. Further longitudinal studies are needed to verify the relationship between physical activity, weight loss, and reduction of subsequent injuries in obese children.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- F1 :
-
Frequencies between 0.01 and 0.10 Hz appear to express “higher level” visual–labyrinthine central nervous system control
- F2–F4 :
-
Deviations of 0.10 to 0.50 Hz reflect vestibular stress and vestibular disturbances
- F5–F6 :
-
Frequencies between 0.50 and 1.00 Hz reflect somatosensory feedback
- F7–F8 :
-
Frequencies between 1.00 and 3.00 Hz are signs of postural tremor or other possible neuropathology
References
Avni N, Avni I, Barenboim E, Azaria B, Zadok D, Kohen-Raz R, Morad Y (2006) Brief posturographic test as an indicator of fatigue. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 60:340–346
Casselbrant ML, Mandel EM, Sparto PJ et al (2010) Longitudinal posturography and rotational testing in children three to nine years of age: normative data. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 142:708–714
Colné P, Frelut ML, Pérès G, Thoumie P (2008) Postural control in obese adolescents assessed by limits of stability and gait initiation. Gait Posture 28:164–169
Daniels SR (2006) The consequences of childhood overweight and obesity. Future Child 16:47–67
De Wit G (1972) Optic versus vestibular and proprioceptive impulses, measured by posturometry. Agressologie 13(Suppl B):75–79
Deforche BI, Hills AP, Worringham CJ, Davies PS, Murphy AJ, Bouckaert JJ, De Bourdeaudhuij IM (2009) Balance and postural skills in normal-weight and overweight prepubertal boys. Int J Pediatr Obes 4:175–182
D’Hondt E, Deforche B, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Lenoir M (2008) Childhood obesity affects fine motor skill performance under different postural constraints. Neurosci Lett 25(440):72–75
Ferber-Viart C, Ionescu E, Morlet T, Froehlich P, Dubreuil C (2007) Balance in healthy individuals assessed with Equitest: maturation and normative data for children and young adults 71:1041–1046
Friedrich M, Grein HJ, Wicher C, Schuetze J, Mueller A, Lauenroth A, Hottenrott K, Schwesig R (2008) Influence of pathologic and simulated visual dysfunctions on the postural system. Exp Brain Res 86:305–314
Goulding A, Jones IE, Taylor RW, Piggot JM, Taylor D (2003) Dynamic and static tests of balance and postural sway in boys: effects of previous wrist bone fractures and high adiposity. Gait Posture 17:136–141
Goulding A, Jones IE, Taylor RW, Williams SM, Manning PJ (2001) Bone mineral density and body composition in boys with distal forearm fractures: a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry study 139:509–515
Goulding A, Taylor RW, Jones IE, McAuley KA, Manning PJ, Williams SM (2000) Overweight and obese children have low bone mass and area for their weight. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24:627–632
Kirk S, Zeller M, Claytor R, Santangelo M, Khoury PR, Daniels SR (2005) The relationship of health outcomes to improvement in BMI in children and adolescents. Obes Res 13:876–882
Kohen-Raz A (1986) Learning disabilities and postural control. Freund, London, pp 27–48
Kohen-Raz R (1991) Application of tetra-ataxiametricposturography in clinical and developmental diagnosis. Percept Mot Skills 73:635–656
Kohen-Raz R, Kohen-Raz A, Erel J, Davidson B, Caine Y, Froom P (1994) Postural control in pilots and candidates for flight training. Aviat Space Environ Med 65:323–326
Kohen-Raz R, Volkmar FR, Cohen DJ (1992) Postural control in children with autism. J Autism Dev Disord 22:419–432
Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS, Grummer-Strawn LM, Flegal KM, Mei Z, Wei R, Curtin LR, Roche AF, Johnson CL (2002) 2000 CDC Growth Charts for the United States: methods and development. Vital Health Stat 11(246):1–190
McGraw B, McClenaghan BA, Williams HG, Dickerson J, Ward DS (2000) Gait and postural stability in obese and non-obese pre pubertal boys. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 81:484–489
Mickle KJ, Munro BJ, Steele JR (2011) Gender and age affect balance performance in primary school-aged children. J Sci Med Sport 14:243–248
Monzavi R, Dreimane D, Geffner ME, Braun S, Conrad B, Klier M, Kaufman FR (2006) Improvement in risk factors for metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in overweight youth who are treated with lifestyle intervention. Pediatrics 117:1111–1118
Morad Y, Azaria B, Avni I, Barkana Y, Zadok D, Kohen-Raz R, Barenboim E (2007) Posturography as an indicator of fatigue due to sleep deprivation. Aviat Space Environ Med 78:859–863
Nemet D, Barkan S, Epstein Y, Friedland O, Kowen G, Eliakim A (2005) Short- and long-term beneficial effects of a combined dietary-behavioral-physical activity intervention for the treatment of childhood obesity. Pediatrics 115:e443–e449
Niederer I, Kriemler S, Zahner L, Bürgi F, Ebenegger V, Hartmann T, Meyer U, Schindler C, Nydegger A, Marques-Vidal P, Puder JJ (2009) Influence of a lifestyle intervention in preschool children on physiological and psychological parameters (Ballabeina): study design of a cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Publ Health 9:94
Oppenheim U, Kohen-Raz R, Alex D, Kohen-Raz A, Azarya M (1999) Postural characteristics of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 22:328–332
Pau M, Kim S, Nussbaum MA (2012) Does load carriage differentially alter postural sway in overweight vs. normal-weight schoolchildren? Gait Posture 35:378–382
Poeta LS, Duarte Mde F, Caramelli B, Jorge M, Giuliano Ide C (2013) Effects of physical exercises and nutritional guidance on the cardiovascular risk profile of obesechildren. Rev Assoc Med Bras 59:56–63
Puder JJ, Marques-Vidal P, Schindler C, Zahner L, Niederer I, Bürgi F, Ebenegger V, Nydegger A, Kriemler S (2011) Effect of multidimensional lifestyle intervention on fitness and adiposity in predominantly migrant preschool children (Ballabeina): cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 13(343):d6195
Sartorio A, Lafortuna CL, Conte G, Faglia G, Narici MV (2001) Changes in motor control and muscle performance after a short-term body mass reduction program in obese subjects. J Endocrinol Invest 24:393–398
Schwartz S, Segal O, Barkana Y, Schwesig R, Avni I, Morad Y (2005) The effect of cataract surgery on postural control. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:920–924
Schwesig R, Goldich Y, Hahn A, Müller A, Kohen-Raz R, Kluttig A, Morad Y (2011) Postural control in subjects with visual impairment. Eur J Ophthalmol 21:303–309
Schwesig R, Lauenroth A, Becker S, Hottenrott K (2006) Das postural system in Abhangigkeit von alters und geschlecht. Man Med 44:385–390
Shultz SP, Anner J, Hills AP (2009) Paediatric obesity, physical activity and the musculoskeletal system. Obes Rev 10:576–582
Sola K, Brekke N, Brekke M (2010) An activity-based intervention for obese and physically inactive children organized in primary care: feasibility and impact on fitness and BMI A one-year follow-up study. Scand J Prim Health Care 28:199–204
Steinberg N, Nemet D, Kohen-Raz R, Pantanowitz M, Eliakim A (2013) Posturography characteristics of obese children with and without associated disorders. Percept Mot Skills. In Press
Taylor ED, Theim KR, Mirch MC, Ghorbani S, Tanofsky-Kraff M, Adler-Wailes DC, Brady S, Reynolds JC, Calis KA, Yanovski JA (2006) Orthopedic complications of overweight in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 117:2167–2174
Teasdale N, Hue O, Marcotte J, Berrigan F, Simoneau M, Doré J, Marceau P, Marceau S, Tremblay A (2007) Reducing weight increases postural stability in obese and morbid obese men. Int J Obes 31:153–160
Wearing SC, Hennig EM, Byrne NM, Steele JR, Hills AP (2006) Musculoskeletal disorders associated with obesity: a biomechanical perspective. Obes Rev 7:239–250
Wills M (2004) Orthopedic complications of childhood obesity. Pediatr Phys Ther 16:230–235
Zahner L, Puder JJ, Roth R, Schmid M, Guldimann R, Pühse U, Knöpfli M, Braun-Fahrländer C, Marti B, Kriemler S (2006) A school-based physical activity program to improve health and fitness in children aged 6–13 years ("Kinder-Sportstudie KISS"): study design of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health 6(6):147
Zlatohlavek L, Vrablik M, Motykova E, Ceska R, Vasickova L, Dlouha D, Hubacek JA (2013) FTO and MC4R gene variants determine BMI changes in children after intensive lifestyle intervention. Clin Biochem 46:313–316
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinberg, N., Eliakim, A., Pantanowitz, M. et al. The effect of a weight management program on postural balance in obese children. Eur J Pediatr 172, 1619–1626 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-2090-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-2090-8