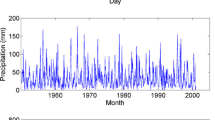
Abstract
Probabilistic regression approaches for downscaling daily precipitation are very useful. They provide the whole conditional distribution at each forecast step to better represent the temporal variability. The question addressed in this paper is: how to simulate spatiotemporal characteristics of multisite daily precipitation from probabilistic regression models? Recent publications point out the complexity of multisite properties of daily precipitation and highlight the need for using a non-Gaussian flexible tool. This work proposes a reasonable compromise between simplicity and flexibility avoiding model misspecification. A suitable nonparametric bootstrapping (NB) technique is adopted. A downscaling model which merges a vector generalized linear model (VGLM as a probabilistic regression tool) and the proposed bootstrapping technique is introduced to simulate realistic multisite precipitation series. The model is applied to data sets from the southern part of the province of Quebec, Canada. It is shown that the model is capable of reproducing both at-site properties and the spatial structure of daily precipitations. Results indicate the superiority of the proposed NB technique, over a multivariate autoregressive Gaussian framework (i.e. Gaussian copula).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
AghaKouchak A (2014) Entropy–copula in hydrology and climatology. J Hydrometeorol 15(6):2176–2189.
AghaKouchak A, Bárdossy A, Habib E (2010) Conditional simulation of remotely sensed rainfall data using a non-Gaussian v-transformed copula. Adv Water Resour 33(6):624–634
Ashkar F, Ouarda TB (1996) On some methods of fitting the generalized Pareto distribution. J Hydrol 177(1):117–141
Bárdossy A (2006) Copula-based geostatistical models for groundwater quality parameters. Water Resour Res 42(11):W11416
Bárdossy A, Li J (2008) Geostatistical interpolation using copulas. Water Resour Res 44(7):W07412
Bárdossy A, Pegram GGS (2009) Copula based multisite model for daily precipitation simulation. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 13(12):2299–2314
Bargaoui ZK, Bárdossy A (2015) Modeling short duration extreme precipitation patterns using copula and generalized maximum pseudo-likelihood estimation with censoring. Adv Water Resour 84:1–13
Ben Alaya MA, Chebana F, Ouarda T (2014) Probabilistic Gaussian copula regression model for multisite and multivariable downscaling. J Clim 27(9):3331–3347
Ben Alaya MA, Chebana F, Ouarda TB (2015) Probabilistic multisite statistical downscaling for daily precipitation using a Bernoulli-generalized Pareto multivariate autoregressive model. J Clim 28(6):2349–2364
Benestad RE, Hanssen-Bauer I, Chen D (2008) Empirical-statistical downscaling. World Scientific, Singapore
Bremnes JB (2004) Probabilistic forecasts of precipitation in terms of quantiles using NWP model output. Mon Weather Rev 132(1):338–347
Buishand TA, Brandsma T (2001) Multisite simulation of daily precipitation and temperature in the Rhine basin by nearest-neighbor resampling. Water Resour Res 37(11):2761–2776
Buishand TA, Brandsma T (1999) Dependence of precipitation on temperature at Florence and Livorno (Italy). Clim Res 12(1): 53–63
Cannon AJ (2008) Probabilistic multisite precipitation downscaling by an expanded Bernoulli-gamma density network. J Hydrometeorol 9(6):1284–1300
Cannon AJ (2011) Quantile regression neural networks: Implementation in R and application to precipitation downscaling. Comput Geosci 37(9):1277–1284
Cawley GC, Janacek GJ, Haylock MR, Dorling SR (2007) Predictive uncertainty in environmental modelling. Neural Netw 20(4):537–549
Chandler RE, Wheater HS (2002) Analysis of rainfall variability using generalized linear models: a case study from the west of Ireland. Water Resour Res 38(10):10–11
Chebana F, Ouarda TB (2011) Multivariate quantiles in hydrological frequency analysis. Environmetrics 22(1):63–78
Coe R, Stern R (1982) Fitting models to daily rainfall data. J Appl Meteorol 21(7):1024–1031
Conway D, Wilby R, Jones P (1996) Precipitation and air flow indices over the British Isles. Clim Res 7:169–183
Czado C, Brechmann EC, Gruber L (2013) Selection of vine copulas. Copulae in Mathematical and Quantitative Finance, Springer, Berlin 17–37
El Adlouni S, Bobée B, Ouarda T (2008) On the tails of extreme event distributions in hydrology. J Hydrol 355(1):16–33
Eum H-I, Gachon P, Laprise R, Ouarda T (2012) Evaluation of regional climate model simulations versus gridded observed and regional reanalysis products using a combined weighting scheme. Clim Dyn 38(7–8):1433–1457
Fang H-B, Fang K-T, Kotz S (2002) The meta-elliptical distributions with given marginals. J Multivariate Anal 82(1):1–16
Fasbender D, Ouarda TBMJ (2010) Spatial Bayesian model for statistical downscaling of AOGCM to minimum and maximum daily temperatures. J Clim 23(19):5222–5242
Friederichs P, Hense A (2007) Statistical downscaling of extreme precipitation events using censored quantile regression. Mon Weather Rev 135(6):2365–2378
Genest C, Chebana F (2015) Copula modeling in hydrologic frequency analysis. In: Singh VP (ed) Handbook of applied hydrology. McGraw-Hill, New York (in press)
Genest C, Plante JF (2003) On Blest’s measure of rank correlation. Can J Stat 31(1):35–52
Giorgi F, Christensen J, Hulme M, Von Storch H, Whetton P, Jones R, Mearns L, Fu C, Arritt R, Bates B (2001) Regional climate information-evaluation and projections. In: Houghton JT et al (eds) Climate change 2001: the scientific basis. Contribution of Working Group to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gräler B (2014) Modelling skewed spatial random fields through the spatial vine copula. Spatial Stat 10:87–102
Guerfi N, Assani AA, Mesfioui M, Kinnard C (2015) Comparison of the temporal variability of winter daily extreme temperatures and precipitations in southern Quebec (Canada) using the Lombard and copula methods. Int J Climatol 35:4237–4246
Harpham C, Wilby RL (2005) Multi-site downscaling of heavy daily precipitation occurrence and amounts. J Hydrol 312(1):235–255
Haylock MR, Cawley GC, Harpham C, Wilby RL, Goodess CM (2006) Downscaling heavy precipitation over the United Kingdom: a comparison of dynamical and statistical methods and their future scenarios. Int J Climatol 26(10):1397–1415
Hessami M, Gachon P, Ouarda TBMJ, St-Hilaire A (2008) Automated regression-based statistical downscaling tool. Environ Model Softw 23(6):813–834
Hobæk Haff I, Frigessi A, Maraun D (2015) How well do regional climate models simulate the spatial dependence of precipitation? An application of pair-copula constructions. J Geophys Res Atmos 120(7):2624–2646
Hofer M, Marzeion B, Mölg T (2012) Comparing the skill of different reanalyses and their ensembles as predictors for daily air temperature on a glaciated mountain (Peru). Clim Dyn 39(7–8):1969–1980
Jeong D, St-Hilaire A, Ouarda T, Gachon P (2012a) Comparison of transfer functions in statistical downscaling models for daily temperature and precipitation over Canada. Stoch Environ Res Risk A 26(5):633–653
Jeong DI, St-Hilaire A, Ouarda TBMJ, Gachon P (2012b) Multisite statistical downscaling model for daily precipitation combined by multivariate multiple linear regression and stochastic weather generator. Clim Change 114(3–4):567–591
Jeong D, St-Hilaire A, Ouarda T, Gachon P (2013) A multivariate multi-site statistical downscaling model for daily maximum and minimum temperatures. Clim Res 54(2):129–148
Joe H (1997) Multivariate models and multivariate dependence concepts. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Khalili M, Van Nguyen VT, Gachon P (2013) A statistical approach to multi-site multivariate downscaling of daily extreme temperature series. Int J Climatol 33(1):15–32
Kleiber W, Katz RW, Rajagopalan B (2012) Daily spatiotemporal precipitation simulation using latent and transformed Gaussian processes. Water Resour Res 48(1):W01523
Lagarias JC, Reeds JA, Wright MH, Wright PE (1999) Convergence properties of the Nelder–Mead simplex method in low dimensions. SIAM J Optim 9(1):112–147
Lee T, Ouarda TB, Jeong C (2012) Nonparametric multivariate weather generator and an extreme value theory for bandwidth selection. J Hydrol 452:161–171
Lee T, Modarres R, Ouarda T (2013) Data-based analysis of bivariate copula tail dependence for drought duration and severity. Hydrol Process 27(10):1454–1463
Li C, Singh VP, Mishra AK (2013a) A bivariate mixed distribution with a heavy-tailed component and its application to single-site daily rainfall simulation. Water Resour Res 49(2):767–789
Li C, Singh VP, Mishra AK (2013b) Monthly river flow simulation with a joint conditional density estimation network. Water Resour Res 49(6):3229–3242
Lindström G, Johansson B, Persson M, Gardelin M, Bergström S (1997) Development and test of the distributed HBV-96 hydrological model. J Hydrol 201(1–4):272–288
Mao G, Vogl S, Laux P, Wagner S, Kunstmann H (2015) Stochastic bias correction of dynamically downscaled precipitation fields for Germany through Copula-based integration of gridded observation data. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 19(4):1787–1806
Mehrotra R, Sharma A (2009) Evaluating spatio-temporal representations in daily rainfall sequences from three stochastic multi-site weather generation approaches. Adv Water Resour 32(6):948–962
Mehrotra R, Sharma A (2006) A nonparametric stochastic downscaling framework for daily rainfall at multiple locations. J Geophys Res Atmos (1984–2012) 111:D15
Mehrotra R, Sharma A, Cordery I (2004) Comparison of two approaches for downscaling synoptic atmospheric patterns to multisite precipitation occurrence. J Geophys Res Atmos (1984–2012) 109:D14
Nelsen RB (2013) An introduction to copulas. Springer Science & Business Media, New York
Oakes D (1982) A model for association in bivariate survival data. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 44:414–422
Ouarda, T. B. M. J., Labadie JW, Fontaine DG (1997) Indexed sequential hydrologic modeling for hydropower capacity estimation. J Am Water Resour Assoc 33(6):1337–1349
Requena AI, Flores I, Mediero L, Garrote L (2015) Extension of observed flood series by combining a distributed hydro-meteorological model and a copula-based model. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 30(5):1–16
Salvadori G, De Michele C (2007) On the use of copulas in hydrology: theory and practice. J Hydrol Eng 12(4):369–380
Serinaldi F (2009a) A multisite daily rainfall generator driven by bivariate copula-based mixed distributions. J Geophys Res Atmos (1984–2012) 114:D10
Serinaldi F (2009b) A multisite daily rainfall generator driven by bivariate copula-based mixed distributions. J Geophys Res Atmos 114:D10
Serinaldi F, Kilsby CG (2014) Simulating daily rainfall fields over large areas for collective risk estimation. J Hydrol 512:285–302
Serinaldi F, Bárdossy A, Kilsby CG (2014) Upper tail dependence in rainfall extremes: would we know it if we saw it? Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 29(4):1211–1233
Shannon C (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27(3):379–423
Smith MS (2014) Copula modelling of dependence in multivariate time series. Int J Forecast 31(3):815–833
Song S, Singh VP (2010) Meta-elliptical copulas for drought frequency analysis of periodic hydrologic data. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 24(3):425–444
Srivastav RK, Simonovic SP (2014) Multi-site, multivariate weather generator using maximum entropy bootstrap. Clim Dyn 44(11–12):3431–3448
Stephenson DB, Rupa Kumar K, Doblas-Reyes FJ, Royer JF, Chauvin F, Pezzulli S (1999) Extreme daily rainfall events and their impact on ensemble forecasts of the Indian monsoon. Mon Weather Rev 127(9):1954–1966
Stern R, Coe R (1984) A model fitting analysis of daily rainfall data. J R Stat Soc Ser A Gen 147:1–34
Vaz de Melo Mendes B, Leal RPC (2010) Portfolio management with semi-parametric bootstrapping. J Risk Manag Financ Inst 3(2):174–183
Vernieuwe H, Vandenberghe S, De Baets B, Verhoest NE (2015) A continuous rainfall model based on vine copulas. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 12(1):489–524
Vinod HD, López-de-Lacalle J (2009) Maximum entropy bootstrap for time series: the meboot R package. J Stat Softw 29(5):1–19
Wilks DS (2010) Use of stochastic weathergenerators for precipitation downscaling. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. Clim Change 1(6):898–907
Wilks DS, Wilby RL (1999) The weather generation game: a review of stochastic weather models. Prog Phys Geogr 23(3):329–357
Williams PM (1998) Modelling seasonality and trends in daily rainfall data. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 10:985–991
Yang C, Chandler RE, Isham VS, Wheater HS (2005) Spatial–temporal rainfall simulation using generalized linear models. Water Resour Res 41(11):1–13
Yee TW, Stephenson AG (2007) Vector generalized linear and additive extreme value models. Extremes 10(1–2):1–19
Yee TW, Wild C (1996) Vector generalized additive models. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 58:481–493
Zhang Q, Xiao M, Singh VP (2015) Uncertainty evaluation of copula analysis of hydrological droughts in the East River basin, China. Global Planet Change 129:1–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Alaya, M.A., Ouarda, T.B.M.J. & Chebana, F. Non-Gaussian spatiotemporal simulation of multisite daily precipitation: downscaling framework. Clim Dyn 50, 1–15 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3578-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3578-0