Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the altered findings of hepatic arteriography after radiofrequency (RF) ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma which can potentially influence subsequent transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
Materials and methods
Hepatic arteriograms of 26 index hepatocellular carcinomas in 24 patients treated only by RF ablation (M:F = 22:2, mean age 55 years), in which hepatic arteriography was performed before and after RF ablation, were retrospectively compared for the altered findings.
Results
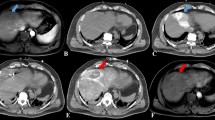
The altered findings of hepatic arteriography after RF ablation of the hepatocellular carcinoma were arterio-portal shunt (n = 3), periablational enhancement (n = 5), varied caliber of the feeding artery to the index tumor (n = 12) among which eight decreased, and occlusion of an adjacent arterial branch (n = 8). Residual unablated or locally progressed tumor was not detected in post-RF ablation arteriography (n = 5) due to the arterio-portal shunt (n = 2) or the periablational enhancement (n = 3). The possibility of not detecting the residual unablated or locally progressed tumor was higher within 24 weeks after RF ablation (Mann–Whitney test, P = 0.041).
Conclusion
The findings of hepatic arteriography are altered after RF ablation, and the altered findings may increase the difficulty in performing super-selective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization due to undetected tumor staining, decreased caliber, or occlusion of the feeding artery.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steele G Jr, Ravikumar TS (1989) Resection of hepatic metastasis from colorectal cancer: biological perspective. Ann Surg 210:127–138
Gayowski TJ, Iwatsuki S, Madariaga JR, et al. (1994) Experience in hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: analysis of clinical and pathologic risk factors. Surgery 116:703–711
Arii S, Okamoto E, Imamura M (1996) Registries in Japan: current status of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan. Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan. Semin Surg Oncol 12:204–211
Cady B, Jenkins RL, Steele GD Jr, et al. (1998) Surgical margin in hepatic resection for colorectal metastasis: a critical and improvable determinant of outcome. Ann Surg 227:566–571
Nakamura H, Hashimoto T, Oi H, et al. (1989) Transcatheter oily chemoembolization of the hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 170:783–786
Uchida H, Ohishi H, Matsuo N, et al. (1990) Transcatheter hepatic segmental arterial embolization using lipiodol mixed with an anticancer drug and gelfoam particles for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 13:140–145
Libraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, et al. (1999) Small hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment with radiofrequency ablation versus ethanol injection. Radiology 210:661–665
Wood TF, Rose DM, Chung M, et al. (2000) Radiofrequency ablation of 231 unresectable hepatic tumors: indications, limitations, and complications. Ann Surg Oncol 7:593–600
Curley SA, Izzo F, Ellis LM, et al. (2000) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular cancer in 110 patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg 232:381–391
Dodd GD III, Soulen MC, Kane RA, et al. (2000) Minimally invasive treatment of malignant hepatic tumors: at the threshold of a major breakthrough. Radiographics 20:9–27
Rossi S, Garbagnati F, Lencioni R, et al. (2000) Percutaneous radio-frequency thermal ablation of nonresectable hepatocellular carcinoma after occlusion of tumor blood supply. Radiology 217:119–126
Lencioni R, Cioni D, Donati F, et al. (2001) Combination of interventional therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 48:8–14
Raman SS, Lu DS, Vodopich DJ, et al. (2000) Creation of radiofrequency lesions in a porcine model: correlation with sonography, CT and histopathology. Am J Roentgenol 175:1253–1258
Chopra S, Dodd GD III, Chintapalli KN, et al. (2001) Tumor recurrence after radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors: spectrum of findings on dual-phase contrast enhanced CT. Am J Roentgenol 177:381–387
Catalano O, Lobianco R, Esposito M, et al. (2001) Hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after percutaneous ablation therapy: helical CT patterns. Abdom Imaging 26:375–383
Cioni D, Lencioni R, Rossi S, et al. (2001) Radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: using contrast-enhanced harmonic power Doppler sonography to assess treatment outcome. Am J Roentgenol 177:783–788
Tsuda M, Majima K, Yamada T, et al. (2001) Hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation therapy: dynamic CT evaluation of treatment. Clin Imaging 25:409–415
Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni MF, et al. (2003) Treatment of focal liver tumors with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: complications encountered in a multicenter study. Radiology 226:441–451
Iannitti DA, Dupuy DE, Mayo-Smith WW, et al. (2002) Hepatic radiofrequency ablation. Arch Surg 137:422–426
Hellekant CH (1976) Vascular complications following needle puncture of the liver. Acta Radiol [Diagn] (Stockh) 17:209–222
Park HS, Lee SH, Kim YI, et al. (2006) Postbiopsy arterioportal fistula in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical significance in transarterial chemoembolization. Am J Roentgenol 186:556–561
Patterson EJ, Scudamore CH, Owen DA, et al. (1998) Radiofrequency ablation of porcine liver in vivo: effect of blood flow and treatment time on lesion size. Ann Surg 227:559–565
Lu DS, Raman SS, Vodopich DJ, et al. (2002) Effect of vessel size on creation of hepatic radiofrequency lesions in pigs: assessment on the “heat sink” effect. Am J Roentgenol 178:47–51
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B.M., Cho, JH., Won, J.H. et al. Altered findings of hepatic arteriography after radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of pre-ablation and post-ablation angiograms. Abdom Imaging 32, 332–338 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-006-9059-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-006-9059-2