Abstract
Rationale
Drugs can function as punishers. However, work on the study of drugs as punishers is limited, as is the range of compounds known to function as punishers. Kappa opioid agonists, which have received much experimental attention as potential therapeutics for drug abuse, reportedly produce aversive effects. However, kappa agonists have yet to be tested as punishers of behavior.
Objective
The goal of the current study was to determine if a kappa agonist could function as a punisher of drug self-administration.
Method
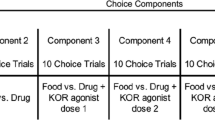
In separate experiments, monkeys were allowed to choose in a two-lever choice design between intravenous injections of equal doses of either cocaine (0.1 mg/kg/injection on each lever) or remifentanil (0.1 μg/kg/injection on each lever) when one of the two options was mixed with various doses of the kappa agonist, salvinorin A.
Results
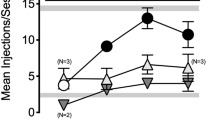
Choice for the cocaine and remifentanil options that were combined with salvinorin A decreased as a function of salvinorin A dose in all monkeys. However, operant response rates were not systematically affected by salvinorin A administration.
Conclusion
The present findings demonstrate that the kappa agonist, salvinorin A, can punish self-administration of a psychotimulant, cocaine, and a mu opioid, remifentanil. In consideration of these findings, it may be possible to curtail the abuse of some drugs by contingently delivering kappa agonists (e.g., as combination formularies for prescription medications).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azrin NH, Holz WC (1966) Punishment. In: Honig WK (ed) Operant behavior: areas of research and application. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, pp 380–447
Banks ML, Negus SS (2012) Preclinical determinants of drug choice under concurrent schedules of drug self-administration. Adv Pharmacol Sci 2012:1–7
Butelman ER, Mandau M, Tidgewell K, Prisinzano TE, Yuferov V, Kreek MJ (2007) Effects of salvinorin A, a kappa opioid hallucinogen, on a neuroendocrine biomarker assay in nonhuman primates with high kappa receptor homology in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:300–306
Carlezon WA Jr, Be Guin C, DiNieri JA, Baumann MH, Richards MR, Todtenkopf MS, Rothman RB, Ma Z, Lee DY, Cohen BM (2006) Depressive-like effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A on behavior and neurochemistry in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:440–447
Chefer VI, Backman CM, Gigante ED, Shippenberg TS (2013) Kappa opioid receptors on dopaminergic neurons are necessary for kappa-mediated place aversion. Neuropsychopharmacology 38(13):2623-2631
Cosgrove KP, Carroll ME (2004) Differential effects of bremazocine on oral phencyclidine (PCP) self-administration in male and female rhesus monkeys. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 12:111–117
Cunningham CW, Rothman RB, Prisinzano TE (2011) Neuropharmacology of the naturally occurring k-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A. Pharmacol Rev 63:316–347
Czoty PW, Nader MA (2012) Individual differences in the effects of environmental stimuli on cocaine choice in socially housed male cynomogus monkeys. Psychopharm 224:69–79
Deroche-Gamonet V, Belin D, Piazza PV (2004) Evidence for addiction-like behavior in the rat. Science 305:1014–1017
Ebner SR, Roitman MF, Potter DN, Rachlin AB, Chartoff EH (2010) Depressive-like effects of the kappa opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A are associated with decreased phasic dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharm 210:241–252
Freeman KB, McMaster BM, Roma PG, Woolverton WL (2014) Punishment with histamine reduces the reinforcing effectiveness of cocaine in monkeys. Psychopharm, in Press
Glick SD, Maisonneuve IM, Raucci J, Archer S (1995) Kappa opioid inhibition of morphine and cocaine self-administration in rats. Brain Res 681:147–152
Goldberg SR (1980) Histamine as a punisher in squirrel monkeys: effects of pentobarbital, chlordiazepoxide, and H1- and H2-receptor antagonists on behavior and cardiovascular responses. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 214:726–736
Grove RN, Schuster CR (1974) Suppression of cocaine self-administration by extinction and punishment. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2:199–208
Holtz NA, Anker JJ, Reiger PS, Claxton A, Carroll ME (2013) Cocaine self-administration punished by i.v. histamine in rat models of high and low drug abuse vulnerability: effects of saccharin preference, impulsivity, and sex. Physiol Behav 122:32–38
Iglauer C, Woods JH (1974) Concurrent performances: reinforcement by different doses of intravenous cocaine in rhesus monkeys. J Exp Anal Behav 22:179–196
Johanson CE (1977) The effects of electric shock on responding maintained by cocaine in a choice procedure in the rhesus monkey. Psychopharm 53:277–282
Johanson CE, Schuster CR (1975) A choice procedure for drug reinforcers: cocaine and methylphenidate in the rhesus monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 193:676–688
Katz JL, Goldberg SR (1986) Effects of H1-receptor antagonists on responding punished by histamine injection or electric shock presentation in squirrel monkeys. Psychopharm 90:461–467
Maisonneuve IM, Archer S, Glick SD (1994) U50488, a k-opioid receptor agonist, attenuates cocaine-induced increases in extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens of rats. Neurosci Lett 181:57–60
Mello NK, Negus SS (1998) Effects of kappa opioid agonists on cocaine- and food-maintained responding by rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:812–824
Mello NK, Negus SS (2000) Interactions between kappa opioid agonists and cocaine. Preclinical studies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 909:104–132
Morani AS, Kivell B, Prisinzano TE, Schenk S (2009) Effect of kappa-opioid receptor agonists U69,593, U50488H, spiradoline and salvinorin A on cocaine-induced drug-seeking in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94:244–249
Negus SS (2005) Effects of punishment on choice between cocaine and food in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharm 181:244–252
Negus SS (2006) Choice between heroin and food in nondependent and heroin-dependent rhesus monkeys: effects of naloxone, buprenorphine, and methadone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:711–723
Negus SS, Mello NK, Portoghese PS, Lin CE (1997) Effects of kappa opioids on cocaine self-administration by rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:1282–1289
Negus SS, Schrode K, Stevenson GW (2007) Mu/Kappa opioid interactions in rhesus monkeys: implications for analgesia and abuse liability. Exp Clin Psychopharm 16:386–399
Pfeiffer A, Brantl V, Herz A, Emrich HM (1986) Psychotomimesis mediated by kappa opiate receptors. Science 233:774–776
Podlesnik CA, Jimez-Gomez C, Woods JH (2010) A choice procedure to assess the aversive effects of drugs in rodents. J Exp Anal Behav 93:203–223
Prisinzano TE, Tidgewell K, Harding WW (2005) k Opioids as potential treatments for stimulant dependence. AAPS J 7:E592–E599
Ruedi-Bettschen D, Rowlett JK, Spealman RD, Platt DM (2010) Attenuation of cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug seeking in squirrel monkeys: kappa opioid and serotonergic mechanisms. Psychopharm 210:169–177
Schenk S, Partridge B, Shippenberg TS (1999) U69593, a kappa-opioid agonist, decreases cocaine self-administration and decreases cocaine-produced drug-seeking. Psychopharm 144:339–346
Woolverton WL (2003) A novel method for studying drugs as punishers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 76:125–131
Woolverton WL, Freeman KB, Myerson J, Green L (2012) Suppression of cocaine self-administration in monkeys: effects of delayed punishment. Psychopharm 220:509–517
Zhang Y, Butelman ER, Schlussman SD, Ho A, Kreek MJ (2004) Effect of the kappa opioid agonist R-84760 on cocaine-induced increases in striatal dopamine levels and cocaine-induced place preference in C57BL/6 J mice. Psychopharm 173:146–152
Zhang Y, Butelman ER, Schlussman SD, Ho A, Kreek MJ (2005) Effects of the plant-derived hallcuinogen salvinorin A on basal dopamine levels in the caudate putamen and in a conditioned place aversion assay in mice: agonist actions at kappa opioid receptors. Psychopharm 179:551–558
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse grants DA019471 and DA026832 to WLW and DA018151 to TEP. The authors thank Steven Ross, Jacob Smith, and Sarah Smith for their expert technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freeman, K.B., Naylor, J.E., Prisinzano, T.E. et al. Assessment of the kappa opioid agonist, salvinorin A, as a punisher of drug self-administration in monkeys. Psychopharmacology 231, 2751–2758 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3436-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3436-2