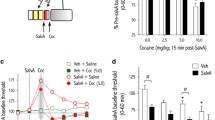
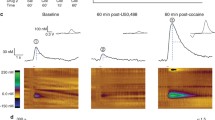
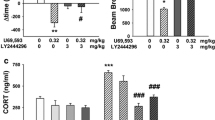
Abstract
Rationale
Kappa opioid receptors (KORs) have been implicated in depressive-like states associated with chronic administration of drugs of abuse and stress. Although KOR agonists decrease dopamine in the nucleus accumbens (NAc), KOR modulation of phasic dopamine release in the core and shell subregions of the NAc—which have distinct roles in reward processing—remains poorly understood.
Objectives
Studies were designed to examine whether the time course of effects of KOR activation on phasic dopamine release in the NAc core or shell are similar to effects on motivated behavior.
Methods
The effect of systemic administration of the KOR agonist salvinorin A (salvA)—at a dose (2.0 mg/kg) previously determined to have depressive-like effects—was measured on electrically evoked phasic dopamine release in the NAc core or shell of awake and behaving rats using fast scan cyclic voltammetry. In parallel, the effects of salvA on intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) and sucrose-reinforced responding were assessed. For comparison, a threshold dose of salvA (0.25 mg/kg) was also tested.
Results
The active, but not threshold, dose of salvA significantly decreased phasic dopamine release without affecting dopamine reuptake in the NAc core and shell. SalvA increased ICSS thresholds and significantly lowered breakpoint on the progressive ratio schedule, indicating a decrease in motivation. The time course of the KOR-mediated decrease in dopamine in the core was qualitatively similar to the effects on motivated behavior.
Conclusions
These data suggest that the effects of KOR activation on motivation are due, in part, to inhibition of phasic dopamine signaling in the NAc core.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberman JE, Salamone JD (1999) Nucleus accumbens dopamine depletions make rats more sensitive to high ratio requirements but do not impair primary food reinforcement. Neuroscience 92:545–552
Aberman JE, Ward SJ, Salamone JD (1998) Effects of dopamine antagonists and accumbens dopamine depletions on time-constrained progressive-ratio performance. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:341–348
Anstrom KK, Miczek KA, Budygin EA (2009) Increased phasic dopamine signaling in the mesolimbic pathway during social defeat in rats. Neuroscience 161:3–12
Aragona BJ, Day JJ, Roitman MF, Cleaveland NA, Wightman RM, Carelli RM (2009) Regional specificity in the real-time development of phasic dopamine transmission patterns during acquisition of a cue-cocaine association in rats. Eur J Neurosci 30:1889–1899
Bals-Kubik R, Ableitner A, Herz A, Shippenberg TS (1993) Neuroanatomical sites mediating the motivational effects of opioids as mapped by the conditioned place preference paradigm in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:489–495
Bari AA, Pierce RC (2005) D1-like and D2 dopamine receptor antagonists administered into the shell subregion of the rat nucleus accumbens decrease cocaine, but not food, reinforcement. Neuroscience 135:959–968
Bassareo V, Di Chiara G (1999) Differential responsiveness of dopamine transmission to food-stimuli in nucleus accumbens shell/core compartments. Neuroscience 89:637–641
Beguin C, Potter DN, Dinieri JA, Munro TA, Richards MR, Paine TA, Berry L, Zhao Z, Roth BL, Xu W, Liu-Chen LY, Carlezon WA Jr, Cohen BM (2008) N-methylacetamide analog of salvinorin A: a highly potent and selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist with oral efficacy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 324:188–195
Britt JP, McGehee DS (2008) Presynaptic opioid and nicotinic receptor modulation of dopamine overflow in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 28:1672–1681
Carey AN, Borozny K, Aldrich JV, McLaughlin JP (2007) Reinstatement of cocaine place-conditioning prevented by the peptide kappa-opioid receptor antagonist arodyn. Eur J Pharmacol 569:84–89
Carlezon WA Jr, Chartoff EH (2007) Intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) in rodents to study the neurobiology of motivation. Nat Protoc 2:2987–2995
Carlezon WA Jr, Thome J, Olson VG, Lane-Ladd SB, Brodkin ES, Hiroi N, Duman RS, Neve RL, Nestler EJ (1998) Regulation of cocaine reward by CREB. Science 282:2272–2275
Carlezon WA Jr, Beguin C, DiNieri JA, Baumann MH, Richards MR, Todtenkopf MS, Rothman RB, Ma Z, Lee DY, Cohen BM (2006) Depressive-like effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A on behavior and neurochemistry in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:440–447
Chartoff EH, Papadopoulou M, MacDonald ML, Parsegian A, Potter D, Konradi C, Carlezon WA Jr (2009) Desipramine reduces stress-activated dynorphin expression and CREB phosphorylation in NAc tissue. Mol Pharmacol 75:704–712
Chavkin C, James IF, Goldstein A (1982) Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science 215:413–415
Chavkin C, Sud S, Jin W, Stewart J, Zjawiony JK, Siebert DJ, Toth BA, Hufeisen SJ, Roth BL (2004) Salvinorin A, an active component of the hallucinogenic sage salvia divinorum is a highly efficacious kappa-opioid receptor agonist: structural and functional considerations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:1197–1203
Cheer JF, Wassum KM, Heien ML, Phillips PE, Wightman RM (2004) Cannabinoids enhance subsecond dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of awake rats. J Neurosci 24:4393–4400
Cheer JF, Heien ML, Aragona BJ, Kim M, Carelli RM, Wightman RM (2005) Simultaneous measurements of fast dopamine release and coincident accumbal firing patterns at the same electrode during goal-directed behavior. Society for Neuroscience Abstract, Washington
Cheer JF, Wassum KM, Sombers LA, Heien ML, Ariansen JL, Aragona BJ, Phillips PE, Wightman RM (2007) Phasic dopamine release evoked by abused substances requires cannabinoid receptor activation. J Neurosci 27:791–795
Cole RL, Konradi C, Douglass J, Hyman SE (1995) Neuronal adaptation to amphetamine and dopamine: molecular mechanisms of prodynorphin gene regulation in rat striatum. Neuron 14:813–823
Cousins MS, Salamone JD (1994) Nucleus accumbens dopamine depletions in rats affect relative response allocation in a novel cost/benefit procedure. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 49:85–91
Day JJ, Roitman MF, Wightman RM, Carelli RM (2007) Associative learning mediates dynamic shifts in dopamine signaling in the nucleus accumbens. Nat Neurosci 10:1020–1028
Gehrke BJ, Chefer VI, Shippenberg TS (2008) Effects of acute and repeated administration of salvinorin A on dopamine function in the rat dorsal striatum. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 197:509–517
Giros B, Jaber M, Jones SR, Wightman RM, Caron MG (1996) Hyperlocomotion and indifference to cocaine and amphetamine in mice lacking the dopamine transporter. Nature 379:606–612
Goussakov I, Chartoff EH, Tsvetkov E, Gerety LP, Meloni EG, Carlezon WA Jr, Bolshakov VY (2006) LTP in the lateral amygdala during cocaine withdrawal. Eur J Neurosci 23:239–250
Hamill S, Trevitt JT, Nowend KL, Carlson BB, Salamone JD (1999) Nucleus accumbens dopamine depletions and time-constrained progressive ratio performance: effects of different ratio requirements. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 64:21–27
Heien ML, Johnson MA, Wightman RM (2004) Resolving neurotransmitters detected by fast-scan cyclic voltammetry. Anal Chem 76:5697–5704
Heien ML, Khan AS, Ariansen JL, Cheer JF, Phillips PE, Wassum KM, Wightman RM (2005) Real-time measurement of dopamine fluctuations after cocaine in the brain of behaving rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Hjelmstad GO, Fields HL (2003) Kappa opioid receptor activation in the nucleus accumbens inhibits glutamate and GABA release through different mechanisms. J Neurophysiol 89:2389–2395
Hodos W (1961) Progressive ratio as a measure of reward strength. Science 134:943–944
Hurd YL, Herkenham M (1993) Molecular alterations in the neostriatum of human cocaine addicts. Synapse 13:357–369
Hyland BI, Reynolds JN, Hay J, Perk CG, Miller R (2002) Firing modes of midbrain dopamine cells in the freely moving rat. Neuroscience 114:475–492
Ikemoto S (2007) Dopamine reward circuitry: two projection systems from the ventral midbrain to the nucleus accumbens-olfactory tubercle complex. Brain Res Rev 56:27–78
Imperato A, Puglisi-Allegra S, Casolini P, Zocchi A, Angelucci L (1989) Stress-induced enhancement of dopamine and acetylcholine release in limbic structures: role of corticosterone. Eur J Pharmacol 165:337–338
Ito R, Dalley JW, Howes SR, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2000) Dissociation in conditioned dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens core and shell in response to cocaine cues and during cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. J Neurosci 20:7489–7495
Ito R, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2004) Differential control over cocaine-seeking behavior by nucleus accumbens core and shell. Nat Neurosci 7:389–397
Jones JL, Day JJ, Aragona BJ, Wheeler RA, Wightman RM, Carelli RM (2009) Basolateral amygdala modulates terminal dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and conditioned responding. Biol Psychiatry
Kelley AE (1999) Functional specificity of ventral striatal compartments in appetitive behaviors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:71–90
Kessler RC (1997) The effects of stressful life events on depression. Annu Rev Psychol 48:191–214
Knoll AT, Carlezon WA Jr (2009) Dynorphin, stress, and depression. Brain Res
Koob GF, Stinus L, Le Moal M, Bloom FE (1989) Opponent process theory of motivation: neurobiological evidence from studies of opiate dependence. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 13:135–140
Lee DY, Karnati VV, He M, Liu-Chen LY, Kondaveti L, Ma Z, Wang Y, Chen Y, Beguin C, Carlezon WA Jr, Cohen B (2005) Synthesis and in vitro pharmacological studies of new C(2) modified salvinorin A analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:3744–3747
Mague SD, Pliakas AM, Todtenkopf MS, Tomasiewicz HC, Zhang Y, Stevens WC Jr, Jones RM, Portoghese PS, Carlezon WA Jr (2003) Antidepressant-like effects of kappa-opioid receptor antagonists in the forced swim test in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:323–330
Mansour A, Watson SJ, Akil H (1995) Opioid-receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: Anatomical and functional implications. Trends Neurosci 18:22–29
Markou A, Koob GF (1991) Postcocaine anhedonia. An animal model of cocaine withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacology 4:17–26
Markou A, Kosten TR, Koob GF (1998) Neurobiological similarities in depression and drug dependence: a self-medication hypothesis. Neuropsychopharmacology 18:135–174
McLaughlin JP, Marton-Popovici M, Chavkin C (2003) Kappa opioid receptor antagonism and prodynorphin gene disruption block stress-induced behavioral responses. J Neurosci 23:5674–5683
Meredith GE, Baldo BA, Andrezjewski ME, Kelley AE (2008) The structural basis for mapping behavior onto the ventral striatum and its subdivisions. Brain Struct Funct 213:17–27
Miliaressis E, Rompre PP, Durivage A (1982) Psychophysical method for mapping behavioral substrates using a moveable electrode. Brain Res Bull 8:693–701
Nestler EJ, Carlezon WA Jr (2006) The mesolimbic dopamine reward circuit in depression. Biol Psychiatry 59:1151–1159
Pfeiffer A, Brantl V, Herz A, Emrich HM (1986) Psychotomimesis mediated by kappa opiate receptors. Science 233:774–776
Phillips PE, Stuber GD, Heien ML, Wightman RM, Carelli RM (2003) Subsecond dopamine release promotes cocaine seeking. Nature 422:614–618
Piazza PV, Le Moal ML (1996) Pathophysiological basis of vulnerability to drug abuse: role of an interaction between stress, glucocorticoids, and dopaminergic neurons. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 36:359–378
Pittenger C, Duman RS (2008) Stress, depression, and neuroplasticity: a convergence of mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:88–109
Pontieri FE, Tanda G, Di Chiara G (1995) Intravenous cocaine, morphine, and amphetamine preferentially increase extracellular dopamine in the “shell” as compared with the “core” of the rat nucleus accumbens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:12304–12308
Roitman MF, Stuber GD, Phillips PE, Wightman RM, Carelli RM (2004) Dopamine operates as a subsecond modulator of food seeking. J Neurosci 24:1265–1271
Roitman MF, Wheeler RA, Carelli RM (2005) Nucleus accumbens neurons are innately tuned for rewarding and aversive taste stimuli, encode their predictors, and are linked to motor output. Neuron 45:587–597
Roitman MF, Wheeler RA, Wightman RM, Carelli RM (2008) Real-time chemical responses in the nucleus accumbens differentiate rewarding and aversive stimuli. Nat Neurosci 11:1376–1377
Roth BL, Baner K, Westkaemper R, Siebert D, Rice KC, Steinberg S, Ernsberger P, Rothman RB (2002) Salvinorin A: a potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous kappa opioid selective agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:11934–11939
Salamone JD, Wisniecki A, Carlson BB, Correa M (2001) Nucleus accumbens dopamine depletions make animals highly sensitive to high fixed ratio requirements but do not impair primary food reinforcement. Neuroscience 105:863–870
Schultz W (1998) Predictive reward signal of dopamine neurons. J Neurophysiol 80:1–27
Senior SL, Ninkina N, Deacon R, Bannerman D, Buchman VL, Cragg SJ, Wade-Martins R (2008) Increased striatal dopamine release and hyperdopaminergic-like behaviour in mice lacking both alpha-synuclein and gamma-synuclein. Eur J Neurosci 27:947–957
Shippenberg TS, Herz A (1987) Place preference conditioning reveals the involvement of D1-dopamine receptors in the motivational properties of mu- and kappa-opioid agonists. Brain Res 436:169–172
Shippenberg TS, Zapata A, Chefer VI (2007) Dynorphin and the pathophysiology of drug addiction. Pharmacol Ther 116:306–321
Sorg BA, Kalivas PW (1991) Effects of cocaine and footshock stress on extracellular dopamine levels in the ventral striatum. Brain Res 559:29–36
Stamford JA, Kruk ZL, Millar J (1989) Dissociation of the actions of uptake blockers upon dopamine overflow and uptake in the rat nucleus accumbens: in vivo voltammetric data. Neuropharmacology 28:1383–1388
Stellar JR, Corbett D (1989) Regional neuroleptic microinjections indicate a role for nucleus accumbens in lateral hypothalamic self-stimulation reward. Brain Res 477:126–143
Svingos AL, Chavkin C, Colago EE, Pickel VM (2001) Major coexpression of kappa-opioid receptors and the dopamine transporter in nucleus accumbens axonal profiles. Synapse 42:185–192
Thompson AC, Zapata A, Justice JB Jr, Vaughan RA, Sharpe LG, Shippenberg TS (2000) Kappa-opioid receptor activation modifies dopamine uptake in the nucleus accumbens and opposes the effects of cocaine. J Neurosci 20:9333–9340
Todtenkopf MS, Marcus JF, Portoghese PS, Carlezon WA Jr (2004) Effects of kappa-opioid receptor ligands on intracranial self-stimulation in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 172:463–470
Tomasiewicz HC, Todtenkopf MS, Chartoff EH, Cohen BM, Carlezon WA Jr (2008) The kappa-opioid agonist U69, 593 blocks cocaine-induced enhancement of brain stimulation reward. Biol Psychiatry 64:982–988
Tsai HC, Zhang F, Adamantidis A, Stuber GD, Bonci A, de Lecea L, Deisseroth K (2009) Phasic firing in dopaminergic neurons is sufficient for behavioral conditioning. Science 324:1080–1084
Wheeler RA, Twining RC, Jones JL, Slater JM, Grigson PS, Carelli RM (2008) Behavioral and electrophysiological indices of negative affect predict cocaine self-administration. Neuron 57:774–785
Wise RA, Spindler J, deWit H, Gerberg GJ (1978) Neuroleptic-induced “anhedonia” in rats: pimozide blocks reward quality of food. Science 201:262–264
Yap JJ, Miczek KA (2008) Stress and rodent models of drug addiction: Role of VTA-accumbens-PFC-amygdala circuit. Drug Discov Today Dis Models 5:259–270
Zahm DS (2000) An integrative neuroanatomical perspective on some subcortical substrates of adaptive responding with emphasis on the nucleus accumbens. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:85–105
Zhang Y, Butelman ER, Schlussman SD, Ho A, Kreek MJ (2005) Effects of the plant-derived hallucinogen salvinorin A on basal dopamine levels in the caudate putamen and in a conditioned place aversion assay in mice: agonist actions at kappa opioid receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 179:551–558
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Morris D. Braun Foundation (EHC) and by National Institutes of Health grants DA023094 (to EHC) and DA025634 (to MFR) and NARSAD (to MFR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM
(DOC 6803 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebner, S.R., Roitman, M.F., Potter, D.N. et al. Depressive-like effects of the kappa opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A are associated with decreased phasic dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology 210, 241–252 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1836-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1836-5