Abstract
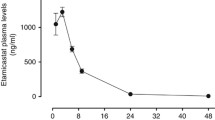
Cardiovascular effects and pharmacokinetics of nebivolol were assessed in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and Wistar Kyoto (WKY) animals. Male SH and WKY rats were treated with vehicle or nebivolol 0.3, 3, or 10 mg kg−1 (i.v.) and effects on blood pressure (BP), heart rate, and blood pressure variability (BPV) were recorded. Plasma pharmacokinetics of d- and l-nebivolol was studied by traditional blood sampling. Short-term and beat-to-beat BPV was assessed by standard deviation and spectral analysis of BP recording, respectively. Nebivolol showed enantioselective pharmacokinetics in both experimental groups; clearance of l-nebivolol was significantly greater than d-enantiomer. Clearance of nebivolol was significantly reduced in SHR with regards to WKY animals. Hypotensive response to nebivolol 3 and 10 mg kg−1 was significantly enhanced in SHR compared with normotensive animals. Spectral analysis of beat-to-beat BPV showed a greater reduction in low frequency BPV in SHR than in WKY rats. Nebivolol 3 and 10 mg kg−1 significantly reduced ratio low frequency/high frequency BPV only in SHR. Short-term BPV was markedly reduced by nebivolol 0.3, 3, and 10 mg kg−1 in WKY and SHR. In conclusion, the hypertensive stage in SHR modifies nebivolol pharmacokinetic properties and enhances its hypotensive response due to a greater attenuation in vascular sympathetic activity and enhancement of endothelial-derived NO activity. Nebivolol markedly attenuates short-term BPV in both experimental groups providing beneficial cardiovascular effects by both controlling high blood pressure and its short-term variability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aimone LD (2005) Overview of pharmacokinetics. Curr Protoc Pharmacol 7(1):1–26
Bertera F, Di Verniero CA, Mayer MA, Chiappetta D, Buontempo F, Polizio AH, Taira CA, Höcht C (2012a) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of carvedilol in fructose hypertensive rats. Xenobiotica 42:206–219
Bertera FM, Del Mauro JS, Chiappetta D, Polizio AH, Buontempo F, Taira CA, Höcht C (2012b) Enantioselective pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of carvedilol in spontaneously hypertensive rats: focus on blood pressure variability. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 385:325–335
Chiladakis JA, Georgiopoulou E, Alexopoulos D (2004) Autonomic effects of nebivolol versus atenolol in healthy subjects. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 18:469–473
Cockcroft JR, Pedersen ME (2012) β-Blockade: benefits beyond blood pressure reduction? J Clin Hypertens 14:112–120
Fazan R Jr, Huber DA, Silva CA, Dias da Silva VJ, Salgado MC, Salgado HC (2008) Sildenafil acts on the central nervous system increasing sympathetic activity. J Appl Physiol 104:1683–1689
Friberg P, Karlsson B, Nordlander M (1998) Sympathetic and parasympathetic influence on blood pressure and heart rate variability in Wistar-Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens Suppl 6:S58–S60
Gao Y, Vanhoutte PM (2012) Nebivolol: an endothelium-friendly selective β1-adrenoceptor blocker. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 59:16–21
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharmacokinetics, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York
Guerrero E, Voces F, Ardanaz N, Montero MJ, Arévalo M, Sevilla MA (2003) Long-term treatment with nebivolol improves arterial reactivity and reduces ventricular hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 42:48–55
Guerrero EI, Ardanaz N, Sevilla MA, Arévalo MA, Montero MJ (2006) Cardiovascular effects of nebivolol in spontaneously hypertensive rats persist after treatment withdrawal. J Hypertens 24:151–158
Höcht C, Di Verniero C, Opezzo JA, Bramuglia GF, Taira CA (2006) Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) modeling of cardiovascular effects of metoprolol in spontaneously hypertensive rats: a microdialysis study. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 373:310–318
Höcht C, Bertera FM, Mayer MA, Taira CA (2010a) Issues in drug metabolism of major antihypertensive drugs: beta-blockers, calcium channel antagonists and angiotensin receptor blockers. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 6:199–211
Höcht C, Bertera FM, Taira CA (2010b) Importance of blood pressure variability in the assessment of cardiovascular risk and benefits of antihypertensive therapy. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 3:617–621
Isanta JR, Lasheras B, Fos D, Cenarruzabeitia E (1987) Comparative diltiazem plasma clearance in normotensive and hypertensive rats. J Pharm Sci 76:862–865
Janssen BJ, Tyssen CM, Struyker-Boudier HA (1991) Modification of circadian blood pressure and heart rate variability by five different antihypertensive agents in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 17:494–503
Janssen BJ, Oosting J, Slaaf DW, Persson PB, Struijker-Boudier HA (1995) Hemodynamic basis of oscillations in systemic arterial pressure in conscious rats. Am J Physiol 269:H62–H71
Kuroedov A, Cosentino F, Lüscher TF (2004) Pharmacological mechanisms of clinically favorable properties of a selective beta1-adrenoceptor antagonist, nebivolol. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 22:155–168
Langager AM, Hammerberg BE, Rotella DL, Stauss HM (2007) Very low-frequency blood pressure variability depends on voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ channels in conscious rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H1321–H1327
Lefebvre J, Poirier L, Poirier P, Turgeon J, Lacourciere Y (2007) The influence of CYP2D6 phenotype on the clinical response of nebivolol in patients with essential hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol 63:575–582
Mancia G, Grassi G (2000) Mechanisms and clinical implications of blood pressure variability. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 35(Suppl 4):S15–S19
Mason RP, Kubant R, Jacob RF, Walter MF, Boychuk B, Malinski T (2006) Effect of nebivolol on endothelial nitric oxide and peroxynitrite release in hypertensive animals: role of antioxidant activity. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 48:862–869
Mason RP, Giles TD, Sowers JR (2009) Evolving mechanisms of action of beta blockers: focus on nebivolol. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 54:123–128
Meier K, Gorbey S, Lemmer B (2004) Effects of nebivolol and metoprolol on nitric oxide urinary excretion, on expression of eNOS and on blood pressure in SH-rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 369(Suppl 1):R42
Miao CY, Xie HH, Zhan LS, Su DF (2006) Blood pressure variability is more important than blood pressure level in determination of end-organ damage in rats. J Hypertens 24:1125–1135
Parati G (2005) Blood pressure variability: its measurement and significance in hypertension. J Hypertens 23(Suppl 1):S19–S25
Pintérová M, Kuneš J, Zicha J (2011) Altered neural and vascular mechanisms in hypertension. Physiol Res 60:381–402
Pladys P, Lahaie I, Cambonie G, Thibault G, Lê NL, Abran D, Nuyt AM (2004) Role of brain and peripheral angiotensin II in hypertension and altered arterial baroreflex programmed during fetal life in rat. Pediatr Res 55:1042–1049
Rothwell PM (2011) Does blood pressure variability modulate cardiovascular risk? Curr Hypertens Rep 13:177–186
Rothwell PM, Howard SC, Dolan E, O’Brien E, Dobson JE, Dahlöf B, Poulter NR, Sever PS, ASCOT-BPLA and MRC Trial Investigators (2010) Effects of beta blockers and calcium-channel blockers on within-individual variability in blood pressure and risk of stroke. Lancet Neurol 9:469–480
Sacco G, Evangelista S, Criscuoli M, Goso C, Bigioni M, Binaschi M, Manzini S, Maggi CA (2005) Involvement of nitric oxide in both central and peripheral haemodynamic effect of D/L-nebivolol and its enantiomers in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 511:167–174
Schillaci G, Pucci G, Parati G (2011) Blood pressure variability: an additional target for antihypertensive treatment? Hypertension 58:133–135
Schutte AE, Schutte R, Huisman HW, van Rooyen JM, Fourie CM, Malan NT, Malan L (2011) Blood pressure variability is significantly associated with ECG left ventricular mass in normotensive Africans: the SABPA Study. Hypertens Res 34:1127–1134
Souza HC, Martins-Pinge MC, Dias da Silva VJ, Borghi-Silva A, Gastaldi AC, Blanco JH, Tezini GC (2008) Heart rate and arterial pressure variability in the experimental renovascular hypertension model in rats. Auton Neurosci 139:38–45
Stauss HM (2007) Identification of blood pressure control mechanisms by power spectral analysis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 34:362–388
Su DF, Miao CY (2001) Blood pressure variability and organ damage. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 28:709–715
Terao N, Shen DD (1983) Alterations in serum protein binding and pharmacokinetics of l-propranolol in the rat elicited by the presence of an indwelling venous catheter. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:369–375
Tomlinson B, Dalal JJ, Huang J, Low LP, Park CG, Rahman AR, Reyes EB, Soenarta AA, Heagerty A, Follath F (2011) The role of β-blockers in the management of hypertension: an Asian perspective. Curr Med Res Opin 27:1021–1033
Van de Water A, Janssens W, Van Neuten J, Xhonneux R, De Cree J, Verhaegen H, Reneman RS, Janssen PA (1988) Pharmacological and hemodynamic profile of nebivolol, a chemically novel, potent, and selective beta 1-adrenergic antagonist. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 11:552–563
Webb AJ, Fischer U, Rothwell PM (2011) Effects of β-blocker selectivity on blood pressure variability and stroke: a systematic review. Neurology 77:731–737
Xie HH, Shen FM, Cao YB, Li HL, Su DF (2005) Effects of low-dose ketanserin on blood pressure variability, baroreflex sensitivity and end-organ damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Sci (Lond) 108:547–552
Xie HH, Shen FM, Zhang XF, Jiang YY, Su DF (2006) Blood pressure variability, baroreflex sensitivity and organ damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats treated with various antihypertensive drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 543:77–82
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Secretaría de Ciencia y Técnica, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Argentina and from the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica (Préstamo BID PICT 00994). Diego Chiappetta, Ariel H. Polizio, and Carlos A. Taira are Career Investigators from CONICET, Argentina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. M. Bertera and J. S. Del Mauro equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertera, F.M., Del Mauro, J.S., Polizio, A.H. et al. Effect of nebivolol on beat-to-beat and short-term blood pressure variability in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 385, 833–843 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0756-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0756-9