Abstract
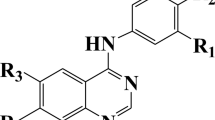
A Bayesian regularized artificial neural network (BR-ANN) model was developed for modeling and accurate prediction of necroptosis inhibitory activities of [1,2,3] thiadiazole and thiophene derivatives as potent tumor necrosis factor-α-induced necroptosis inhibitors. The chemical structure of each compound was converted to 1,481 molecular descriptors by Dragon software. Among these, only seven descriptors relating the activity data to the molecular structures were selected as the significant ones. The best BR-ANN model was a three layer feed forward network with the 7-4-1 architecture. Prediction ability of the proposed model was evaluated by prediction of pEC50 of some compounds in the external (test) data set. The mean square error, mean absolute error, correlation coefficient (R), and mean relative error for the test set were 0.0214, 0.126, 0.978, and 2.475, respectively. The results obtained show the superior prediction ability of the proposed model in the prediction of necroptosis inhibitory activities.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afantitis A, Melagraki G, Sarimveis H, Koutentis PA, Markopoulos J (2006) A novel simple QSAR model for the prediction of anti-HIV activity using multiple linear regression analysis. Mol Divers 10:405–414
Aggarwal KK, Singh Y, Chandra P, Puri M (2005) Bayesian regularization in a neural network model to estimate lines of code using function points. J Comput Sci 1(4):505–509
Arab Chamjangali M (2009) Modeling of cytotoxicity data (CC50) of anti-HIV 1-[5-chlorophenyl) sulfonyl]-1H-pyrrole derivatives using calculated molecular descriptors and Levenberg-Marquardt artificial neural network. J Chem Biol Drug Des 73:456–465
Basak SC, Balaban AT, Grunwald GD, Gute BD (2000) Topological indices: their nature and mutual relatedness. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 4:891–898
Buren FR (1999) Robust QSAR models using Bayesian-regularized neural networks. J Med Chem 42:3183–3187
Caballero J, Fernandez M (2006) Linear and nonlinear modeling of antifungal activity of some heterocyclic ring derivatives using multiple linear regression and Bayesian-regularized neural networks. J Mol Model 12:168–181
Cherqaoui D, Villemin D (1994) Use of a neural network to determine boiling point of alkanes. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 90:97–102
Fernandez M, Caballero J (2006a) Bayesian-regularized genetic neural networks applied to the modeling of non-peptide antagonists for the human luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone receptor. J Mol Graph Model 25:409–421
Fernandez M, Caballero J (2006b) Modelling of activity of cyclic urea HIV-1 protease inhibitors using regularized-artificial neural network. J Bioorg Med Chem 14:280–294
Gevrey M, Dimopoulos I, Lek S (2003) Review and comparison of methods to study the contribution of variables in artificial neural network models. Ecol Model 160:249–264
Goodarzi M, Deshpande S, Murugesan V, Katti SB, Prabhakar YS (2009) Is feature selection essential for ANN modelling. QSAR Comb Sci 28:1487–1499
Gosav S, Praisler M, Dorohoi DO, Popa G (2006) Structure–activity correlation for illicit amphetamines using ANN and constitutional descriptors. J Talanta 70:922–928
Guha R (2005) Methods to improve the reliability, validity and interpretability of QSAR models. PhD Thesis, Pennsylvania State University
Hajan MT, Menhaj MB (1994) Training feed forward networks with the Marquardt algorithm. IEE Trans Neural Netw 5:989–993
Hemmer MC, Steinhauer V, Gasteiger J (1999) The prediction of the 3D structure of organic molecules from their infrared spectra. J Vib Spectrosc 19:151–164
Jagtap PG, Degterev A, Choi S, Keys H, Yuang J, Cuny GD (2007) Structure–activity relationship study of tricyclic necroptosis inhibitors. J Med Chem 50(8):1886–1895
Jalali-Heravi M, Asadollahi-Baboli M (2008) QSAR analysis of platelet-derived growth inhibitors using GA-ANN and shuffling cross validation. J QSAR Comb Sci 6:750–757
Jalali-Heravi M, Mani-Varnosfaderani A (2009) QSAR modelling of 1-(3,3-diphenylpropyl)-piperidinyl amides as CCR5 modulators using multivariate adaptive regression spline and Bayesian regularization genetic neural networks. QSAR Comb Sci 9:946–958
Jalali-Heravi M, Parastar F (2000) Use of artificial neural network in a QSAR study of anti-HIV activity for a large group of HEPT derivatives. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 40:147–154
Jalali-Heravi M, Asadollahi-Baboli M, Shahbazikhah P (2008) QSAR study of herparanase inhibitors activity using artificial neural networks and Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm. Eur Med Chem 43:548–556
Kanduc D, Mittelman A, Serpico R, Sinigaglia E, Sinha AA, Natale C, Santacroce R, Di Corcia MG, Lucchese A, Dini L, Pani P, Santacroce S, Simone S, Bucci R, Farber E (2002) Cell death: apoptosis versus necrosis (review). Int J Oncol 21(1):165–170
Kermani BG, White MW, Nagle HT (1994) A new method in acquiring a better generalization in neural networks. In: Proceeding of the 16th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicinal and biology society, Baltimore, MD, USA
Kermani BG, Schiffman SS, Troy Nagle H (2005) Performance of the Levenberg-Marquardt neural network training method in electronic nose applications. Sens Actuators B 110:13–22
MacKay DJC (1992) Bayesian interpolation. Neural Comput 4:415–447
Roy K, Leonardo JT (2005) QSAR analysis of 3-(4-benzylpiperidin-1-yl)-N-phenylpropylamine derivatives as potent CCR5 antagonists. J Chem Inf Model 45:1352–1368
Schuur JH, Selzer P, Gasteiger J (1996) The coding of the three dimensional structure of molecules by molecular transform and its application to structure–spectra correlation and studies of biological activity. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 36:334–344
Stefan P, Niculescu P (2003) Artificial neural networks and genetic algorithm in QSAR. Mol Struct 622:71–83
Teng X, Degterev A, Jagtap P, Xing X, Choi S, Denu R, Yuang J, Cuny GD (2005) Structure–activity relationship study of novel necroptosis inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:5039–5044
Teng X, Keys H, Jeevanandam A, Porco JA, Degterev A, Yuang J, Cuny GD (2007) Structure–activity relationship study of [1,2,3] thiadiazole necroptosis inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:6836–6840
Wang XG, Tang Z, Tamura H, Ishii M (2004a) A modified error function for the back propagation algorithm. Neurocomputing 57:477–484
Wang XG, Tang Z, Tamura H, Ishii M, Sun W (2004b) An improved back propagation algorithm to avoid the local minima problem. Neurocomputing 56:455–460
Wang K, Li J, Degterev A, Hsu E, Yuang J, Yuang C (2007) Structure–activity relationship study of novel necroptosis inhibitors, Necrostatin-5. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:1455–1465
Weekes D, Fogel GB (2003) Evolutionary optimization, back propagation and data preparation issues in QSAR modeling of HIV inhibition by HEPT derivatives. Biosystems 72:149–158
Yao X, Liu H, Zhang R, Liu M, Hu Z, Panaye A, Doucet JP, Fan B (2005) QSAR and classification study of 1,4 dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists based on least square support vector machines. Mol Pharm 2:348–358
Yasri A, Hartsough D (2001) Toward an optimal procedure for variable selection and QSAR model building. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 41:1218–1227
Zarei K, Atabati M (2009) QSAR study of anti-HIV activities against HIV-1 and some of their mutant strain for a group of HEPT derivatives. J Chin Chem Sci 56:206–213
Zheng W, Degterev A, Hsu E, Yuang J, Yuang C (2008) Structure–activity relationship study of novel necroptosis inhibitors, Necrostatin-7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:4932–4935
Zupan JJ, Gasteiger J (1993) Neural networks for chemists an introduction. VCH Publishers, Weinheim
Zweiri YH, Whidborne JF, Senviratne LD (2003) A three-term back propagation algorithm. Neurocomputing 50:305–318
Acknowledgment
The authors are thankful to the Shahrood University of Technology Research Council for the support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chamjangali, M.A., Ashrafi, M. QSAR study of necroptosis inhibitory activities (EC50) of [1,2,3] thiadiazole and thiophene derivatives using Bayesian regularized artificial neural network and calculated descriptors. Med Chem Res 22, 392–400 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0027-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0027-9