Abstract
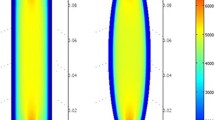
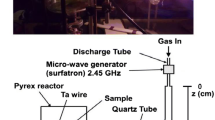
HID lamps (High-Intensity Discharge) are gaining ground in the lighting industry because of their very high energy efficiency (up to 40%). In these lamps, which are operated in the arc regime and which are contained in a ceramic balloon, filled with argon or xenon, mercury, and salts of various rare earth metals and iodine), de-mixing occurs. This de-mixing is driven by differences in diffusion velocities of molecules and atoms. Furthermore, helical instabilities might occur in the lamp. Both phenomena are severely modified under 1 G conditions: convection will bend a horizontally burning arc channel upwards, and a vertically burning arc channel will exhibit convective cells. This makes it impossible to study these phenomena on the ground. If a proper understanding of these phenomena is to be gained, experiments under microgravity are necessary. The main objectives of the experiment are: (1) determination of the critical factors for the onset of helical instabilities in HID lamps and (2) characterisation of the radial de-mixing processes by radially resolved high-resolution emission spectroscopy. To this end, special hardware has been designed and built which houses a very compact high-resolution spectrometer, a video camera and a caroussel with 20 lamps in it. The lamps are measured consecutively. The experiments have been performed successfully by the Dutch astronaut André Kuipers on board the International Space Station during the Dutch Soyuz Mission “DELTA” on 24 and 25 April 2004. Especially the helical instabilities part yielded immediate and surprising results: the arc channel does bend, but does not rotate under microgravity. This fact is very important in improving the performance of the lamps, especially since the instabilities occur mainly in the most efficient lamps.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fischer, E., Axial segregation of additives in mercury-metal-halide arcs, J. Appl. Phys. 47 2954–2960 (1976)
Thorne, A.P., Spectrophysics, Chapman and Hall & Science Paperbacks, London, 1970.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kroesen, G., Haverlag, M., Dekkers, E. et al. ARGES: Radial segregation and helical instabilities in metal halide lamps studied under microgravity conditions in the International Space Station. Microgravity sci. Technol. 16, 191–195 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02945974
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02945974