Abstract
Objective
To assess the treatment and outcome of children with acute myeloid leukemia. The Primary objectives were to assess remission rates, treatment related toxicity and disease free survival. Secondary objective was to assess prognostic factors associated with poor outcome.
Methods
A retrospective analysis of all treated patients with acute myeloid leukemia, less than 18 year of age from Sept 2005 to Aug 2009 was done. Clinical laboratory, treatment and follow up records retrieved to calculate remission rate, treatment related toxicity, disease free survival and poor prognostic factors.
Results
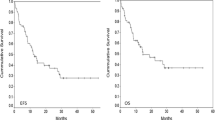
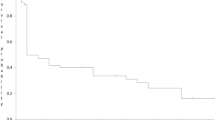
This analysis included thirty five patients (male : female; 23:12), twenty seven (77.1%) achieved remission after one 3 + 7 induction and seven required two inductions. High dose cytosine arabinoside consolidation was given in thirty one patients while one underwent allogenic stem cell transplantation. Two patients died during chemotherapy (TRM- 5.7%), two did not complete the therapy, seventeen relapsed (48.5%) with 80% of relapses occurring within first year of remission and no relapse occurred after 2 years. Fourteen patients are in remission (40%, follow up 5–54 months) and cumulative median disease free survival is of 13 months.
Conclusions
The present data suggests that 3 + 7 induction, followed by high dose cytarabine consolidation has low treatment related toxicity and resource utilization; however, relapse free survival is inferior to more intensive regimens, highlighting the need to intensify chemotherapy regimen once the treatment related mortality has been minimized.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rubnitz JE, Gibson B, Smith FO. Acute myeloid leukemia. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2008;55:21–51.
Kaspers GJ, Creutzig U. Pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: international progress and future directions. Leukemia. 2005;19:2025.
Gibson BE, Wheatley K, Hann IM, et al. Treatment strategy and long-term results in paediatric patients treated in consecutive UK AML trials. Leukemia. 2005;19:2130–8.
Smith FO, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB, et al. Long-term results of children with acute myeloid leukemia: a report of three consecutive phase III trials by the Children’s Cancer Group: CCG 251, CCG 213 and CCG 2891. Leukemia. 2005;19:2054–62.
Creutzig U, Zimmermann M, Ritter J, et al. Treatment strategies and long-term results in paediatric patients treated in four consecutive AML-BFM trials. Leukemia. 2005;19:2030–42.
Webb DK, Harrison G, Stevens RF, et al. Relationships between age at diagnosis, clinical features, and outcome of therapy in children treated in the Medical Research Council AML 10 and 12 trials for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2001;98:1714.
Woods WG, Kobrinsky N, Buckley JD, et al. Timed-sequential induction therapy improves post remission outcome in acute myeloid leukemia: a report from the Children’s Cancer Group. Blood. 1996;87:4979–89.
Riley LC, Hann IM, Wheatley K, et al. Treatment-related deaths during induction and first remission of acute myeloid leukaemia in children treated on the Tenth Medical Research Council Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Trial (MRC AML10). The MCR Childhood Leukaemia Working Party. Br J Haematol. 1999;106:436–44.
Herzig RH, Lazarus HM, Wolff SN, et al. High-dose cytosine arabinoside therapy with and without anthracycline antibiotics for remission re induction of acute non lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1985;3:992.
Amadori S, Testi AM, Arico M, et al. Prospective comparative study of bone marrow transplantation and post remission chemotherapy for childhood acute myelogenous leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1993;11:1046.
Aladjidi N, Auvrignon A, Leblanc T, et al. Outcome in children with relapsed acute myeloid leukemia after initial treatment with the French Leucemie Aique Myeloide Enfant (LAME) 89/91 protocol of the French Society of Pediatric Hematology and Immunology. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:4377.
Ferrara F, Palmieri S, Mele G. Prognostic factors and therapeutic options for relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2004;89:998.
Zwaan CM, Reinhardt D, Corbacioglu S, et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin: first clinical experiences in children with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia treated on compassionate-use basis. Blood. 2003;101:3868.
Oliansky DM, Rizzo JD, Aplan PD, et al. The role of cytotoxic therapy with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the therapy of acute myeloid leukemia in children: an evidence-based review. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007;13:1.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Role of Funding Source
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, N., Seth, T., Mishra, P. et al. Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Children: Experience from a Tertiary Care Hematology Centre in India. Indian J Pediatr 78, 1211–1215 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-010-0300-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-010-0300-1