Abstract
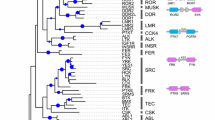
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are key components of cell–cell signalling required for growth and development of multicellular organisms. It is therefore likely that the divergence of RTKs and associated components played a significant role in the evolution of multicellular organisms. We have carried out the present study in hydra, a diploblast, to investigate the divergence of RTKs after parazoa and before emergence of triploblast phyla. The domain-based screening using Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) for RTKs in Genomescan predicted gene models of the Hydra magnipapillata genome resulted in identification of 15 RTKs. These RTKs have been classified into eight families based on domain architecture and homology. Only 5 of these RTKs have been previously reported and a few of these have been partially characterized. A phylogeny-based analysis of these predicted RTKs revealed that seven subtype duplications occurred between ‘parazoan–eumetazoan split’ and ‘diploblast–triploblast split’ in animal phyla. These results suggest that most of the RTKs evolved before the radiata–bilateria divergence during animal evolution.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Celera Assembler
- ECD:
-
extracellular domain
- DDR:
-
discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase
- FGFR:
-
fibroblast growth factor receptor
- HMMs:
-
Hidden Markov Models
- JTT:
-
Jones–Taylor–Thornton
- ME:
-
minimum evolution
- MuSK:
-
muscle-specific kinase
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- Ror:
-
receptor tyrosine kinase–like orphan receptor
- RP:
-
Ringer-Phrap
- RTKs:
-
receptor tyrosine kinases
- RyK:
-
Wnt inhibitory receptor tyrosine kinase
- TK:
-
tyrosine kinase
- TM:
-
transmembrane
References
Aguinaldo AM, Turbeville JM, Linford LS, Rivera MC, Garey JR, Raff RA and Lake JA 1997 Evidence for a clade of nematodes, arthropods and other moulting animals. Nature 387 489–493
Barolo S and Posakony JW 2002 Three habits of highly effective signaling pathways: principles of transcriptional control by developmental cell signalling. Genes Dev. 16 1167–1181
Bode HR 1992 Continuous conversion of neuron phenotype in hydra. Trends Genet. 8 279–284
Bridge DM, Stover NA and Steele RE 2000 Expression of a novel receptor tyrosine kinase gene and a paired-like homeobox gene provides evidence of differences in patterning at the oral and aboral ends of hydra. Dev. Biol. 220 253–262
Castresana J 2000 Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 17 540–552
Chapman JA, Kirkness EF, Simakov O, Hampson SE, Mitros T, Weinmaier T, Rattei T, Balasubramanian PG, et al. 2010 The dynamic genome of Hydra. Nature (London) 464 592–596
Eddy SR 1998 Profile Hidden Markov Models. Bioinformatics 14 755–763
Edgar RC 2004 MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 32 1792–1797
Gerhart J 1999 1998 Warkany lecture: Signaling pathways in development. Teratology 60 226–239
Grassot J, Mouchiroud G and Perrière G 2003 RTKdb: database of receptor tyrosine kinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 31 353–358
Grassot J, Gouy M, Perrière G and Mouchiroud G 2006 Origin and Molecular Evolution of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases with Immunoglobulin-Like Domains. Mol. Biol. Evol. 23 1232–1241
Gu J and Gu X 2003 Natural history and functional divergence of protein tyrosine kinases. Gene 317 49–57
Guder C, Pinho S, Nacak TG, Schmidt HA, Hobmayer B, Niehrs C and Holstein TW 2006 An ancient Wnt-Dickkopf antagonism in Hydra. Development 13 901–911
Guindon S and Gascuel O 2003 A simple, fast and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 52 696–704
Heino TI, Karpanen T, Wahlstorm G, Pulkkinen M, Eriksson K, Alitalo and Roos C 2001 The Drosophila VEGF receptor homolog is expressed in hemocytes. Mech. Dev. 109 69–77
Hobmayer B, Rentzsch F, Kuhn K, Happel CM, von Laue CC, Snyder P, Rothbacher U and Holstein TW 2000 WNT Signalling molecules act in axis formation in the diploblastic metazoan Hydra. Nature (London) 407 186–189
Horibata Y, Sakaguchi K, Okino N, Iida H, Inagaki M, Fujisawa T, Hama Y and Ito M 2004 Unique catabolic pathway of glycosphingolipids in a hydrozoan, Hydra magnipapillata, involving endoglycoceramidase. J. Biol. Chem. 279 33379–33389
Jones DT, Taylor WR and Thornton JM 1992 The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comp. Appl. Biosci. 8 275–282
Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G and Sonnhammer ELL 2001 Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 305 567–580
Kullander K and Klein R 2002 Mechanisms and functions of Eph and ephrin signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3 475–486
Matus DQ, Thomsen GH and Martindale MQ 2007 FGF signaling in gastrulation and neural development in Nematostella vectensis, an anthozoan cnidarians. Dev. Genes Evol. 217137–148
Murai KK and Pasquale EB 2003 ‘Eph’ective signaling: forward, reverse and crosstalk. J. Cell Sci. 116 282–2832
Reidling JC, Miller MA and Steele RE 2000 Sweet Tooth, a Novel Receptor Proteintyrosine Kinase with C-type Lectin-like Extracellular Domains. J. Biol. Chem. 275 10323–10330
Rentzsch F, Fritzenwanker JH, Scholz CB and Technau U 2008 FGF signalling controls formation of the apical sensory organ in the cnidarian Nematostella vectensis. Development 135 1761–1769
Robinson DR, Wu YM and Lin SF 2000 The protein tyrosine kinase family of the human genome. Oncogene 19 5548–5557
Rousset D, Agnes F, Lachaume P, Andre C and Galibert F 1995 Molecular evolution of the genes encoding receptor tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulinlike domains. J. Mol. Evol. 41 421–429
Srivastava M, Simakov O, Chapman J, Fahey B, Gauthier ME A, Mitros T, Richards GS, Conaco C, et al. 2010 The Amphimedon queenslandica genome and the evolution of animal complexity. Nature (London) 466 720–727
Steele RE, Lieu P, Mai NH, Shenk MA and Sarras Jr MP 1996 Response to insulin and the expression pattern of a gene encoding an insulin receptor homologue suggest a role for an insulin-like molecule in regulating growth and patterning in Hydra. Dev. Genes Evol. 206 247–259
Sudhop S, Coulier F, Bieller A, Vogt A, Hotz T and Hassel M 2004 Signalling by the FGFR like tyrosine kinase, Kringelchen, is essential for bud detachment in Hydra vulgaris. Development 131 4001–4011
Suga H, Koyanagi M, Hoshiyama D, Ono K, Iwabe N, Kuma K and Miyata T 1999 Extensive gene duplication in the early evolution of animals before the parazoaneumetazoan split demonstrated by G proteins and protein tyrosine kinases from sponge and hydra. J. Mol. Evol. 48 646–653.
Suga H, Katoh K and Miyata T 2001 Sponge homologs of vertebrate protein tyrosine kinases and frequent domain shufflings in the early evolution of animals before the parazoan eumetazoan split. Gene 280 195–201
Suga H, Sasaki G, Kuma K, Nishiyori H, Hirose N, Zhi-Hui Su, Iwabe N and Takashi M 2008 Ancient divergence of animal protein tyrosine kinase genes demonstrated by a gene family tree including choanoflagellate genes. FEBS. Lett. 582 815–818
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M and Kumar S 2007 MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24 1596–1599
van der Geer P, Hinter T and Lindberg RA 1994 Receptor protein tyrosine kinases and their signal transduction pathways. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 10 251–337
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Prof Thomas Bosch and Dr Georg Hemmrich from Zoological Institute, Christian-Albrechts-University Kiel, Kiel, Germany, for discussions and comments on an earlier draft of the manuscript. PCR acknowledges financial support (Senior Research Fellowship, National Eligibility Test) from University Grants Commission, New Delhi. This work was funded by Department of Biotechnology, India, through Centre of Excellence in Epigenetics and by Agharkar Research Institute, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Tristram Wyatt
[Reddy PC, Bidaye SS and Ghaskadbi S 2011 Genome-wide screening reveals the emergence and divergence of RTK homologues in basal Metazoan Hydra magnipapillata. J. Biosci. 36 289–296] DOI 10.1007/s12038-011-9065-6
Supplementary materials pertaining to this article are available on the Journal of Biosciences Website at http://www.ias.ac.in/jbrosci/Jun2011/pp289-296/suppl.pdf
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1.03 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, P., Bidaye, S.S. & Ghaskadbi, S. Genome-wide screening reveals the emergence and divergence of RTK homologues in basal Metazoan Hydra magnipapillata . J Biosci 36, 289–296 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-011-9065-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-011-9065-6