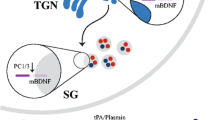
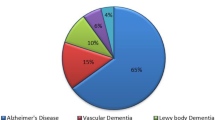
Abstract
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is the most widely distributed neurotrophin in the central nervous system where it plays several pivotal roles in synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival. As a consequence, BDNF became a key target in the physiopathology of several neurological and psychiatric diseases. Recent studies have reported altered levels of BDNF in the circulation, i.e. serum or plasma, of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and low BDNF levels in the CSF as predictor of future cognitive decline in healthy older subjects. Altered BDNF circulating levels have also been reported in other neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders, hampering its use as a specific biomarker for AD. Therefore, BDNF seems to be an unspecific biomarker of neuropsychiatric disorders marked by neurodegenerative changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akatsu, H., Yamagata, H. D., Kawamata, J., Kamino, K., Takeda, M., Yamamoto, T., et al. (2006). Variations in the BDNF gene in autopsy-confirmed Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies in Japan. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 22(3), 216–222.
Albert, M. S., Dekosky, S. T., Dickson, D., Dubois, B., Feldman, H. H., Fox, N. C., et al. (2011). The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers and Dementia, 7(3), 270–279.
Aliaga, E., Silhol, M., Bonneau, N., Maurice, T., Arancibia, S., & Tapia-Arancibia, L. (2010). Dual response of BDNF to sublethal concentrations of beta-amyloid peptides in cultured cortical neurons”. Neurobiology of Disease, 37, 208–217.
Angelucci, F., Spalletta, G., di Lulio, F., Ciaramella, A., Salani, F., Colantoni, L., et al. (2010). Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients are characterized by increased BDNF serum levels. Current Alzheimer Research, 7(1), 15–20.
Arancibia, S., Silhol, M., Moulivre, F., Meffre, J., Höllinger, I., Maurice, T., et al. (2008). Protective effect of BDNF against beta-amyloid induced neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo in rats. Neurobiology of Disease, 31, 316–326.
Bodner, S. M., Berrettini, W., van Deerlin, V., Bennett, D. A., Wilson, R. S., Trojanowski, J. Q., et al. (2005). Genetic variation in the brain derived neurotrophic factor gene in Alzheimer’s disease. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 134B(1), 1–5.
Bramham, C. R., Worley, P. F., Moore, M. J., & Guzowski, J. F. (2008). The immediate early gene arc/arg3.1: Regulation, mechanisms, and function. Journal of Neuroscience, 28, 11760–11767.
Burbach, G. J., Hellweg, R., Haas, C. A., Del Turco, D., Deicke, U., Abramowski, D., et al. (2004). Induction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in plaque-associated glial cells of aged APP23 transgenic mice. Journal of Neuroscience, 24, 2421–2430.
Chao, M. V. (2003). Neurotrophins and their receptors: A converge point for many signaling pathways. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 4(4), 199–209.
Chen, Q., Nakajima, A., Choi, S. H., Xiong, X., Sisodia, S. S., & Tang, Y. P. (2008). Adult neurogenesis is functionally associated with AD-like neurodegeneration. Neurobiology of Disease, 29(2), 316–326.
Chen, T. J., Wang, D. C., & Chen, S. S. (2009). Amyloid-beta interrupts the PI3 K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway that could be involved in brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced Arc expression in rat cortical neurons. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 87, 2297–2307.
Cunha, A. B., Frey, B. N., Andreazza, A. C., et al. (2006). Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor is decreased in bipolar disorder during depressive and manic episodes. Neuroscience Letters, 398(3), 215–219.
Diniz, B. S., Pinto, J. A., Gonzaga, M. L., Guimarães, F. M., Gattaz, W. F., & Forlenza, O. V. (2009). To treat or not to treat? A meta-analysis of the use of cholinesterase inhibitors in mild cognitive impairment for delaying progression to Alzheimer’s disease. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 259(4), 248–256.
Diniz, B. S., Pinto Junior, J. A., & Forlenza, O. V. (2008). Do CSF total tau, phosphorylated tau, and beta-amyloid 42 help to predict progression of mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease? A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. World Journal of Biological Psychiatry, 9(3), 172–182.
Diniz, B. S., Teixeira, A. L., Ojopi, E. B., Talib, L. L., Mendonça, V. A., Gattaz, W. F., et al. (2010a). Higher serum stnfr1 level predicts conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease. Journal Alzheimers Disease, 22(4), 1305–1311.
Diniz, B. S., Teixeira, A. L., Talib, L. L., Mendonça, V. A., Gattaz, W. F., & Forlenza, O. V. (2010b). Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor level is reduced in antidepressant-free patients with late-life depression. World Journal of Biological Psychiatry, 11(3), 550–555.
Dubois, B., Feldman, H. H., Jacova, C., Dekosky, S. T., Barberger-Gateau, P., Cummings, J., et al. (2007). Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurology, 6, 734–746.
Echeverria, V., Berman, D. E., & Arancio, O. (2007). Oligomers of beta-amyloid peptide inhibit BDNF-induced arc expression in cultured cortical Neurons. Current Alzheimer Research, 4(5), 518–521.
Forlenza, O. V., Diniz, B. S., & Gattaz, W. F. (2010a). Diagnosis and biomarkers of predementia in Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Medicine, 8, 89. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-8-89.
Forlenza, O. V., Diniz, B. S., Radanovic, M., Santos, F. S., Talib, L. L., & Gattaz, W. F. (2011a). Disease-modifying properties of long-term lithium treatment for amnestic mild cognitive impairment: Randomised controlled trial. British Journal of Psychiatry, 198(5), 351–356.
Forlenza, O. V., Diniz, B. S., Talib, L. L., Mendonça, V. A., Ojopi, E. B., Gattaz, W. F., et al. (2009). Increased serum IL-1beta level in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorder, 28(6), 507–512.
Forlenza, O. V., Diniz, B. S., Talib, L. L., Radanovic, M., Yassuda, M. S., Ojopi, E. B., et al. (2010b). Clinical and biological predictors of Alzheimer’s disease in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria, 32(3), 216–222.
Forlenza, O. V., Diniz, B. S., Teixeira, A. L., Ojopi, E. B., Talib, L. L., Mendonça, V. A., et al. (2010c). Effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism and serum levels on the progression of mild cognitive impairment. World Journal of Biological Psychiatry, 11(6), 774–780.
Forlenza, O. V., Torres, C. A., Talib, L. L., de Paula, V. J., Joaquim, H. P., Diniz, B. S., et al. (2011b). Increased platelet GSK3B activity in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 45(2), 220–224.
Fu, W., Lu, C., & Mattson, M. P. (2002). Telomerase mediates the cell survival-promoting actions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and secreted amyloid precursor protein in developing hippocampal neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 22(24), 10710–10719.
Fujimura, H., Altar, C. A., Chen, R., Nakamura, T., Nakahashi, T., Kambayashi, J., et al. (2002). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is stored in human platelets and released by agonist stimulation. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 87(4), 728–734.
Fukumoto, N., Fujii, T., Combarros, O., Kamboh, M. I., Tsai, S. J., Matsushita, S., et al. (2010). Sexually dimorphic effect of the Val66Met polymorphism of BDNF on susceptibility to Alzheimer’s disease: New data and meta-analysis. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 153B(1), 224–235.
Gunstad, J., Benitez, A., Smith, J., Glickman, E., Spitznagel, M. B., Alexander, T., et al. (2008). Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor is associated with cognitive function in healthy older adults. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology, 21(3), 166–170.
Hooper, C., Killick, R., & Lovestone, S. (2008). The GSK3 hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neurochemistry, 104, 1433–1439.
Hu, Y., & Russek, S. J. (2008). BDNF and the diseased nervous system: A delicate balance between adaptive and pathological processes of gene regulation. Journal of Neurochemistry, 105, 1–17.
Hwang, J. P., Tsai, S. J., Hong, C. J., Yang, C. H., Lirng, J. F., & Yang, Y. M. (2006). The Val66Met polymorphism of the brain-derived neurotrophic-factor gene is associated with geriatric depression. Neurobiology of Aging, 27(12), 1834–1837.
Jack, C. R., Knopman, D. S., Jagust, W. J., Shaw, L. M., Aisen, P. S., Weiner, M. W., et al. (2009). Hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers of the Alzheimer’s pathological cascade. Lancet Neurology, 9(1), 119–128.
Karege, F., Bondolfi, G., Gervasoni, N., Schwald, M., Aubry, J. M., & Bertschy, G. (2005). Low brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in serum of depressed patients probably results from lowered platelet BDNF release unrelated to platelet reactivity. Biological Psychiatry, 57(9), 1068–1072.
Kimura, N., Takahashi, M., Tashiro, T., & Terao, K. (2006). Amyloid-beta up-regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor production from astrocytes: Rescue from amyloid beta-related neuritic degeneration. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 84, 782–789.
Kunugi, H., Ueki, A., Otsuka, M., Isse, K., Hirasawa, H., Kato, N., et al. (2001). A novel polymorphism of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular Psychiatry, 6(1), 83–86.
Laske, C., Stransky, E., Leyhe, T., Eschweiler, G. W., Maetzler, W., Wittorf, A., et al. (2007). BDNF serum and CSF concentrations in Alzheimer’s disease, normal pressure hydrocephalus and healthy controls. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 41(5), 387–394.
Laske, C., Stransky, E., Leyhe, T., Eschweiler, G. W., Wittorf, A., Richartz, E., et al. (2006). Stage-dependent BDNF serum concentrations in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neural Transmission, 113, 1217–1224.
Lee, J. G., Shin, B. S., You, Y. S., Kim, J. E., Yoon, S. W., Jeon, D. W., et al. (2009). Decreased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in elderly Korean with dementia. Psychiatry Investigation, 6(4), 299–305.
Leyhe, T., Eschweiler, G. W., Stransky, E., Gasser, T., Annas, P., Basun, H., et al. (2009). Increase of BDNF serum concentration in lithium treated patients with early Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimers Disease, 16, 649–656.
Leyhe, T., Stransky, E., Eschweiler, G. W., Buchkremer, G., & Laske, C. (2008). Increase of BDNF serum concentration during donepezil treatment of patients with early Alzheimer’s disease. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 258(2), 124–128.
Li, G., Peskind, E. R., Millard, S. P., Chi, P., Sokal, I., Yu, C. E., et al. (2009). Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and cognitive function in non-demented subjects. PloS One, 4(5), e5424. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005424.
Longo, F. M., Yang, T., Knowles, J. K., Xie, Y., Moore, L. A., & Massa, S. M. (2007). Small molecule neurotrophin receptor ligands: Novel strategies for targeting Alzheimer’s disease mechanisms. Current Alzheimer Research, 4(5), 503–506.
Machado-Vieira, R., Dietrich, M. O., Leke, R., Cereser, V. H., Zanatto, V., Kapczinski, F., et al. (2007). Decreased plasma brain derived neurotrophic factor levels in unmedicated bipolar patients during manic episode. Biological Psychiatry, 61(2), 142–144.
Massa, S. M., Yang, T., Xie, Y., Shi, J., Bilgen, M., Joyce, J. N., et al. (2010). Small molecule BDNF mimetics activate TrkB signaling and prevent neuronal degeneration in rodents. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 120(5), 1774–1785. doi:10.1172/JCI41356.
Mattson, M. P. (2004). Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer’s disease. Nature, 430(7000), 631–639.
Mrak, R. E. (2009). Neuropathology and the neuroinflammation idea”. Journal Alzheimers Disease, 18(3), 473–481.
Nagahara, A. H., Merrill, D. A., Coppola, G., Tsukada, S., Schroeder, B. E., Shaked, G. M., et al. (2009). Neuroprotective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rodent and primate models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Medicine, 15, 331–337.
Nakahashi, T., Fujimura, H., Altar, C. A., Li, J., Kambayashi, J., Tandon, N. N., et al. (2000). Vascular endothelial cells synthesize and secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor. FEBS Letters, 470(2), 113–117.
Nishimura, A. L., Oliveira, J. R., Mitne-Neto, M., Guindalini, C., Nitrini, R., Bahia, V. S., et al. (2004). Lack of association between the brain-derived neurotrophin factor (C-270T) polymorphism and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (LOAD) in Brazilian patients. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 22(3), 257–260.
Nishitomi, K., Sakaguchi, G., Horikoshi, Y., Gray, A. J., Maeda, M., Hirata-Fukae, C., et al. (2006). BACE1 inhibition reduces endogenous Abeta and alters APP processing in wild-type mice. Journal of Neurochemistry, 99(6), 1555–1563.
Olin, D., MacMurray, J., & Comings, D. E. (2005). Risk of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease associated with BDNF C270T polymorphism. Neuroscience Letters, 381(3), 275–278.
Peng, S., Garzon, D. J., Marchese, M., Klein, W., Ginsberg, S. D., Francis, B. M., et al. (2009). Decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor depends on amyloid aggregation state in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuroscience, 29, 9321–9329.
Poon, W. W., Blurton-Jones, M., Tu, C. H., Feinberg, L. M., Chabrier, M. A., Harris, J. W., et al. (2011). beta-Amyloid impairs axonal BDNF retrograde trafficking. Neurobiology of Aging, 32(5), 821–833.
Price, R. D., Milne, S. A., Sharkey, J., & Matsuoka, N. (2007). Advances in small molecules promoting neurotrophic function. Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 115(2), 292–306.
Reichardt, L. F. (2006). Neurotrophin-regulated signaling pathways. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society London, Part B, Biological Science, 361(1473), 1545–1564.
Ribeiro, L., Busnello, J. V., Cantor, R. M., Whelan, F., Whittaker, P., Deloukas, P., et al. (2007). The brain-derived neurotrophic factor rs6265 (Val66Met) polymorphism and depression in Mexican-Americans. Neuroreport, 18(12), 1291–1293.
Rohe, M., Synowitz, M., Glass, R., Paul, S. M., Nykjaer, A., & Willnow, T. E. (2009). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces amyloidogenic processing through control of SORLA gene expression. Journal of Neuroscience, 29(49), 15472–154782009.
Scheuner, D., Eckman, C., Jensen, M., Song, X., Citron, M., Suzuki, N., et al. (1996). Secreted amyloid beta-protein similar to that in senile plaques of Alzheimer’s disease is increased in vivo by the presenilin 1 and 2 APP mutations linked to familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Medicine, 2, 864–870.
Shruster, A., Melamed, E., & Offen, D. (2010). Neurogenesis in the aged and neurodegenerative brain. Apoptosis, 15(11), 1415–1421.
Sousa, R. T., van de Bilt, M. T., Diniz, B. S., Ladeira, R. B., Portela, L. V., Souza, D. O., et al. (2011). Lithium increases plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor in acute bipolar mania: A preliminary 4-week study. Neuroscience Letters, 494(1), 54–56.
Swerdlow, R. H. (2007). Is aging part of Alzheimer’s disease, or is Alzheimer’s disease part of aging? Neurobiology of Aging, 28(10), 1465–1480.
Swerdlow, R. H., Burns, J. M., & Khan, S. M. (2010). The Alzheimer’s disease mitochondrial cascade hypothesis. Journal Alzheimers Disease, 20(Suppl 2), S265–S279.
Tapia-Arancibia, L., Aliaga, E., Silhol, M., & Arancibia, S. (2008). New insights into brain BDNF function in normal aging and Alzheimer disease. Brain Research Reviews, 59(1), 201–220.
Taylor, W. D., Zuchner, S., McQuoid, D. R., Steffens, D. C., Speer, M. C., & Krishnan, K. R. (2007). Allelic differences in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism in late-life depression. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 15(10), 850–857.
Teixeira, A. L., Barbosa, I. G., Diniz, B. S., & Kummer, A. (2010). Circulating levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor: Correlation with mood, cognition and motor function. Biomarkers in Medicine, 4(6), 871–887.
Thornton, E., Vink, R., Blumbergs, P. C., & Van Den Heuvel, C. (2006). Soluble amyloid precursor protein alpha reduces neuronal injury and improves functional outcome following diffuse traumatic brain injury in rats. Brain Research, 1094(1), 38–46.
Tsai, S. J., Hong, C. J., Liu, H. C., Liu, T. Y., Hsu, L. E., & Lin, C. H. (2004). Association analysis of brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphisms with Alzheimer’s disease and age of onset. Neuropsychobiology, 49(1), 10–12.
Tsai, S. J., Hong, C. J., Liu, H. C., Liu, T. Y., & Liou, Y. J. (2006). The brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene as a possible susceptibility candidate for Alzheimer’s disease in a Chinese population. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 21(3), 139–143.
Vepsäläinen, S., Castren, E., Helisalmi, S., Iivonen, S., Mannermaa, A., Lehtovirta, M., et al. (2005). Genetic analysis of BDNF and TrkB gene polymorphisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neurology, 252(4), 423–428.
Wang, D. C., Chen, S. S., Lee, Y. C., & Chen, T. J. (2006). Amyloid-beta at sublethal level impairs BDNF-induced arc expression in cortical neurons. Neuroscience Letters, 398, 78–82.
Winblad, B., Palmer, K., Kivipelto, M., Jelic, V., Fratiglioni, L., Wahlund, L., et al. (2004). Mild cognitive impairment–beyond controversies, towards a consensus: Report of the international working group on mild cognitive impairment. Journal of Internal Medicine, 256, 240–246.
Yasutake, C., Kuroda, K., Yanagawa, T., Okamura, T., & Yoneda, H. (2006). Serum BDNF, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta levels in dementia patients: Comparison between Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 256(7), 402–406.
Yu, H., Zhang, Z., Shi, Y., Bai, F., Xie, C., Qian, Y., et al. (2008). Association study of the decreased serum BDNF concentrations in amnestic mild cognitive impairment and the Val66Met polymorphism in Chinese Han. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 69, 1104–1111.
Zhang, J., Sokal, I., Peskind, E. R., Quinn, J. F., Jankovic, J., Kenney, C., et al. (2008). CSF multianalyte profile distinguishes Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. American Journal of Clinical Pathololgy, 129(4), 526–529.
Acknowledgments
This work was partly funded by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento Pessoal do Ensino Superior (CAPES, Brazil), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, Brazil), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa de Minas Gerais (Fapemig, Brazil), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa de São Paulo (FAPESP, Brazil), and Associação Beneficente Alzira Denise Hertzog da Silva (ABADHS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diniz, B.S., Teixeira, A.L. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Alzheimer’s Disease: Physiopathology and Beyond. Neuromol Med 13, 217–222 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-011-8154-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-011-8154-x