Abstract
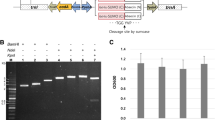
Brevinin-2R, a member of a new family of antimicrobial peptides isolated from the skin of Rana ridibunda, displays antimicrobial activity against bacteria and fungi. In this study, we have used an assembly PCR method for the fast and extremely accurate synthesis of the brevinin-2R gene. A total of six primers were assembled in a single step PCR, and the assembly was then amplified by PCR to produce the final gene. The synthetic gene was cloned into the pET32a (+) vector to allow the expression of brevinin-2R as a Trx fusion protein in Escherichia coli. The results indicated that the expression level of the fusion protein could reach up to 25% of the total cell proteins. The expression products could be easily purified by Ni-NTA chromatography and released from the fusion protein by factor Xa protease. The peptide displayed antimicrobial activity similar to that of the purified brevinin that was reported earlier. This method allows the fast synthesis of a gene that optimized the overexpression in the E. coli system and production of sufficiently large amounts of peptide for functional and structural characterizations.






Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Boman, H. G. (1995). Peptide antibiotics and their role in innate immunity. Annual Review of Immunology, 13, 61–92.
Martin, E., Ganz, T., & Lehrer, R. I. (1995). Defensins and other endogenous peptide antibiotics of vertebrates. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 58, 128–136.
Sima, P., Trebichavsky, I., & Sigler, K. (2003). Mammalian antibiotic peptides. Folia Microbiologica, 48, 123–137.
Noga, E. J., & Silphaduang, U. (2003). Piscidins: a novel family of peptide antibiotics from Wsh. Drug News & Perspectives, 16, 87–92.
Ganz, T. (2003). Defensins: antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nature Reviews. Immunology, 3, 710–720.
Devine, D. A., & Hancock, R. E. (2002). Cationic peptides: distribution and mechanisms of resistance. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 8, 703–714.
ZasloV, M. (2002). Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature, 415, 389–395.
Fales-Williams, A. J., Brogden, K. A., Huffman, E., Gallup, J. M., & Ackermann, M. R. (2002). Cellular distribution of anionic antimicrobial peptide in normal lung and during acute pulmonary inflammation. Veterinary Pathology, 39, 706–711.
Fales-Williams, A. J., Gallup, J. M., Ramirez-Romero, R., Brogden, K. A., & Ackermann, M. R. (2002). Increased anionic peptide distribution and intensity during progression and resolution of bacterial pneumonia. Clinical and Diagnostic Laboratory Immunology, 9, 28–32.
Lai, R., Liu, H., Hui, L. W., & Zhang, Y. (2002). an anionic antimicrobial peptide from toad Bombina maxima. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 295, 796–799.
Hancock, R. E., & Rozek, A. (2002). Role of membranes in the activities of antimicrobial cationic peptides. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 206, 143–149.
Nizet, V., Ohtake, T., & Lauth, X. (2001). Innate antimicrobial peptide protects the skin from invasive bacterial infection. Nature, 414, 454–457.
Montecalvo, M. A. (2003). Ramoplanin: a novel antimicrobial agent with the potential to prevent vancomycin-resistant enterococcal infection in high-risk patients. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 51, S31–S35.
Giles, F. J., Redman, R., Yazji, S., & Bellm, L. (2002). Iseganan HCl: a novel antimicrobial agent. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs, 11, 1161–1170.
Valore, E. V., & Ganz, T. (1997). Laboratory production of antimicrobial peptides in native conformation. Methods in Molecular Biology, 78, 115–131.
Asoodeh, A., Naderi-Manesh, H., Mirshahi, M., & Ranjbar, B., (2004). Purification and characterization of an antibacterial , antifungal and non hemolytic peptide from Rana Ridibunda. Journal of Sciences, Islamic Republic of Iran, 15, 303–309.
Guerdoux-Jamet, P., Henaut, A., Nitschke, P., Risler, J. L., & Danchin, A. (1997). Using codon usage to predict genes origin: is the Escherichia coli outer membrane a patchwork of products from different genomes? DNA Research, 4, 257–265.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., & Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual (2nd ed.). Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Lehrer, R. I., Rosenman, Jackson, M., Eisenhauer, P. (1991). Ultra sensitive assay for endogenous antimicrobial polypeptide. Journal of Immunological Methods, 137, 167–173.
Lazarus, L. H., & Attila, M. (1993). The toad, ugly and venomous, wears yet a precious jewel in his skin. Progress in Neurobiology, 41, 473–507.
Wang, G., Sun, G., Tang, W., Pan, X. (1994). The application of traditional Chinese medicine to the management of hepatic cancerous pain. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 14, 132–138.
Erspamer, V. (1994). Bioactive secretions of the integument. In H. Heatwole & GT Barthalmus (Eds.), Amphibian biology, the integument, vol. 1. Chipping Norton: Surrey Beatty & Sons.
Withers-Martinez, C., Carpenter, E. P., Hackett, F., Ely, B., Sajid, M., Grainger, M., & Blackman, M. J. (1999). PCR-based gene synthesis as an efficient approach for expression of the A+T-rich malaria genome. Protein Engineering, 12, 1113–1120.
Lee, J. H., Kim, J. H., & Hwang, S. W. (2000). High-level expression of antimicrobial peptide mediated by a fusion partner reinforcing formation of inclusion bodies. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 277, 575–580.
Lee, J. H., Minn, H., Park, C. B., & Kim, S. C. (1998). Acid peptide-mediated expression of the antimicrobial peptide Buforin II as tandem repeats in Escherichia coli. Protein Expression and Purification, 12, 53–60.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to show their gratitude toward the research council of Tarbiat Modares University and the Center of High Tech. of the Ministry of Industries and Minings for their financial supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehrnejad, F., Naderi-Manesh, H., Ranjbar, B. et al. PCR-based Gene Synthesis, Molecular Cloning, High Level Expression, Purification, and Characterization of Novel Antimicrobial Peptide, Brevinin-2R, in Escherichia Coli . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 149, 109–118 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-8024-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-8024-z