Abstract
Background
Due to constraints on resources and capacity, as well as advances in surgical technique and care, there has been progressive change toward converting surgical procedures to the outpatient setting when feasible. This study was designed to investigate the safety of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) as an outpatient procedure for morbid obesity in Canada.
Methods
This retrospective analysis included consecutive patients who underwent outpatient LAGB at the Surgical Weight Loss Centre in Ontario, Canada, beginning with our initial experience in February 2005 and continuing to July 2009. Eligible patients were morbidly obese adults whose outpatient clinic surgery had been performed by one of two experienced surgeons.
Results
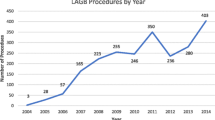
A total of 1,641 patients were included in this analysis. The average presurgical body mass index was 46.7 kg/m2 (range 35.0 to 79 kg/m2). Fifteen patients (0.91%) experienced minor complications during surgery or within 30 days of surgery (dysphagia, n = 5; wound infection, n = 3; port infection, n = 2; all other complications occurred in one patient each). Four patients required transfer to hospital from the clinic on the day of surgery, and three were admitted. None of the complications were serious and all were resolved. The device was explanted in two patients. The average time from sedation to discharge was <4 hours (h).
Conclusions
The ability to treat patients within 4 h and the extremely low complication rates reported here contribute to a growing literature supporting the safe performance of LAGB in an outpatient setting for the treatment of morbid obesity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
O'Brien PE, McPhail T, Chaston TB, et al. Systematic review of medium-term weight loss after bariatric operations. Obes Surg. 2006;16:1032–40.
Cunneen SA. Review of meta-analytic comparisons of bariatric surgery with a focus on laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2008;4:S47–55.
Ledoux S, Msika S, Moussa F, et al. Comparison of nutritional consequences of conventional therapy of obesity, adjustable gastric banding, and gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2006;16:1041–9.
Parikh MS, Laker S, Weiner M, et al. Objective comparison of complications resulting from laparoscopic bariatric procedures. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;202:252–61.
Hinojosa MW, Varela JE, Parikh D, et al. National trends in use and outcome of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2008;5:150–5.
Flum DR, Belle SH, King WC, et al. Perioperative safety in the longitudinal assessment of bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:445–54.
Montgomery KF, Watkins BM, Ahroni JH, et al. Outpatient laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in super-obese patients. Obes Surg. 2007;17:711–6.
McCarty TM. Can bariatric surgery be done as an outpatient procedure? Adv Surg. 2006;40:99–106.
McCarty TM, Arnold DT, Lamont JP, et al. Optimizing outcomes in bariatric surgery: outpatient laparoscopic gastric bypass. Ann Surg. 2005;242:494–8. discussion 8–501.
Sasse KC, Ganser JH, Kozar MD, et al. Outpatient weight loss surgery: initiating a gastric bypass and gastric banding ambulatory weight loss surgery center. JSLS. 2009;13:50–5.
Watkins BM, Ahroni JH, Michaelson R, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in an ambulatory surgery center. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2008;4:S56–62.
Spaw AT, Reddick EJ, Olsen DO. Laparoscopic laser cholecystectomy: analysis of 500 procedures. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1991;1:2–7.
Farha GJ, Green BP, Beamer RL. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy in a freestanding outpatient surgery center. J Laparoendosc Surg. 1994;4:291–4.
Fris RJ. Preoperative low energy diet diminishes liver size. Obes Surg. 2004;14:1165–70.
Colles SL, Dixon JB, Marks P, et al. Preoperative weight loss with a very-low-energy diet: quantitation of changes in liver and abdominal fat by serial imaging. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84:304–11.
Clavien PA, Sanabria JR, Strasberg SM. Proposed classification of complications of surgery with examples of utility in cholecystectomy. Surgery. 1992;111:518–26.
Parikh JA, Yermilov I, Jain S, et al. How much do standardized forms improve the documentation of quality of care? J Surg Res. 2007;143:158–63.
De Waele B, Lauwers M, Van Nieuwenhove Y, et al. Outpatient laparoscopic gastric banding: initial experience. Obes Surg. 2004;14:1108–10.
Watkins BM, Montgomery KF, Ahroni JH, et al. Adjustable gastric banding in an ambulatory surgery center. Obes Surg. 2005;15:1045–9.
Parikh MS, Fielding GA, Ren CJ. U.S. experience with 749 laparoscopic adjustable gastric bands: intermediate outcomes. Surg Endosc. 2005;19:1631–5.
Ahroni JH, Montgomery KF, Watkins BM. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: weight loss, co-morbidities, medication usage and quality of life at one year. Obes Surg. 2005;15:641–7.
Watkins BM, Montgomery KF, Ahroni JH. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: early experience in 400 consecutive patients in the USA. Obes Surg. 2005;15:82–7.
Acknowledgment
The study was reviewed by IRB Services (Aurora, Ontario) for ethics approval.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Cobourn was the recipient of an unrestricted educational grant from Allergan Inc. LAP-BAND is a registered trademark of Allergan, Inc. L. Wells is an employee of and owns stock in Allergan, Inc. M.A. Chapman has received compensation from and owns stock in Allergan, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cobourn, C., Mumford, D., Chapman, M.A. et al. Laparoscopic Gastric Banding Is Safe in Outpatient Surgical Centers. OBES SURG 20, 415–422 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-009-0065-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-009-0065-7