Abstract
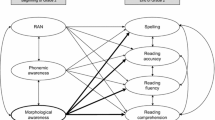
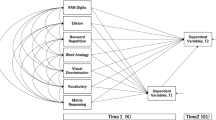
A large battery of reading related skills were orally administered to 111 4-year old and 118 5-year old Korean kindergartners, who were also tested on reading of regular and irregular Korean Hangul words. In regression equations, speeded naming was uniquely associated with reading of both regular and irregular words. In contrast, only the three measures of phonological awareness at the levels of phoneme onset, coda, and syllable uniquely explained Hangul regular word recognition, whereas only morphological awareness consistently explained irregular word recognition. Results suggest somewhat different cognitive demands for reading of regular and irregular words, based on the dual-route model, in Korean Hangul.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, M. J. (1990). Beginning to read: Thinking and learning about print. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Bowers, P. G., & Newby-Clark, E. (2002). The role of naming speed within a model of reading acquisition. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 15, 109–126.
Castles, A., & Coltheart, M. (2004). Is there a causal link from phonological awareness to success in learning to read? Cognition, 91, 77–111.
Chialanti, D., & Caramazza, A. (1995). Where is morphology and how is it processed? The case of written word recognition. In L. B. Feldman (Ed.), Morphological aspects of language processing (pp. 55–76). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Cho, J.-R. (2001). Hangul word-frequency effects in the categorization task. Korean Journal of Experimental and Cognitive Psychology, 13, 113–131.
Cho, J.-R., & Chen, H.-C. (1999). Orthographic and phonological activation in the semantic processing of Korean Hanja and Hangul. Language and Cognitive Processes, 14, 481–502.
Cho, J.-R., & McBride-Chang, C. (2005). Correlates of Korean Hangul acquisition among kindergartners and second graders. Scientific Studies of Reading, 9, 3–16.
Clark, E. V. (1995). The lexicon and syntax. In J. L. Miller, & P. D. Eimas (Eds.), Speech, language, and communication (pp. 303–337). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Coltheart, M., Rastle, K., Perry, C., Langdon, R., & Ziegler, J. C. (2001). DRC: A dual route cascaded model of visual word recognition and reading aloud. Psychological Review, 108, 204–256.
Gardner, M. F. (1996). Test of visual-perceptual skills (non-motor). Burlingame, CA: Psychological and Educational Publications.
Goswami, U. (1986). Use of analogy in learning to read: A developmental study. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 42, 73–83.
Ho, C. S.-H., & Bryant, P. (1997). Phonological skills are important in learning to read Chinese. Developmental Psychology, 33, 119–147.
Ho, C. S.-H., Chan, D. W.-O., Tsang, S.-M., & Lee, S.-H. (2002). The cognitive profile and multiple-deficit hypothesis in Chinese developmental dyslexia. Developmental Psychology, 38, 543–553.
Huang, H.-S., & Hanley, J. R. (1994). Phonological awareness and visual skills in learning to read Chinese and English. Cognition, 54, 73–98.
Kang, H., & Simpson, G. B. (1996). Development of semantic and phonological priming in a shallow orthography. Developmental Psychology, 32, 860–866.
Kim, H.-J., & Cho, J.-R. (2001). Phonological awareness, visual perception, and reading of Hangul in preschool children. Korean Journal of Developmental Psychology, 14, 15–28.
Kim, J., & Davis, C. (2004). Characteristics of poor readers of Korean Hangul: Auditory, visual, and phonological processing. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 17, 153–185.
Kim, S.-O., Gong, S.-J., & Jo, H.-S. (2004). The effects of phonological processing abilities on the reading ability of four- and five-year olds. Korean Journal of Developmental Psychology, 17, 37–56.
Kim-Renaud, Y.K. (Ed.). (1997). The Korean alphabet: Its history and structure. Honolulu, HI: University of Hawaii Press.
Korean Association of Child Studies, & Hansol Education Research Center (2002). Child development report 2001. Seoul, Korea: Hansol Education.
Lee, Y. (1997). Mental lexical pathway and processing resource. In Proceedings of the Korean Experimental and Cognitive Psychology (pp. 11–19). Seoul: Korean Experimental and Cognitive Psychological Association.
Lee, S.-S., Lee, K.-D., Nam, K.-S., Chung, C.-S., Lee, I.-K., & Choi, Y.-C. (1991). Development of a corpus of contemporary Korean for compiling a lexicographical database. Seoul, Korea: Korean Dictionary Compilation Board of Yonsei University.
Lim, J.-R. (2002). The realities of modern Korean vocabulary usage and the properties of its word formation. Korean Language, 30, 41–67.
Manis, F. R., Seidenberg, M. S., & Doi, L. M. (1999). See Dick RAN: Rapid naming and the longitudinal prediction of reading subskills in first and second graders. Scientific Studies of Reading, 3, 129–157.
Mann, V. A., (2000). Introduction to special issues on morphology and the acquisition of alphabetic writing systems. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 12, 143–147.
McBride-Chang, C., Cho, J.-R., Liu, H., Wagner, R. K., Shu, H., Zhou, A., Cheuk, C. S.-M., & Muse, A. (2005a). Changing models across cultures: Associations of phonological and morphological awareness to reading in Beijing, Hong Kong, Korea, and America. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 92, 140–160.
McBride-Chang, C., Chow, B. W.-Y., Zhong, Y., Burgess, S., & Hayward, W. G. (2005b). Chinese character acquisition and visual skills in two Chinese scripts. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 18, 99–128.
McBride-Chang, C., & Ho, C. S.-H. (2000). Developmental issues in Chinese children’s character acquisition. Journal of Educational Psychology, 92, 50–55.
McBride-Chang, C., Shu, H., Zhou, A., Wat, C. P., & Wagner, R. K. (2003). Morphological awareness uniquely predicts young children’s Chinese character recognition. Journal of Educational Psychology, 95, 743–751.
Ministry of Education and Human Resource Development (1988). Korean orthography. Seoul, Korea: National Institute of Korean Language.
Ministry of Education and Human Resource Development (1998). Korean kindergarten curriculum. Seoul, Korea: Special Education Publishing Co.
Morrison, F. J., Smith, L., & Dow-Ehrensberger, M. (1995). Education and cognitive development: A natural experiment. Developmental Psychology, 31, 789–799.
Nunes, T., Bryant, P., & Olsson, J. (2003). Learning morphological and phonological spelling rules: An intervention study. Scientific Studies of Reading, 7, 289–307.
Park, H.-W., Kwak, K.-J., & Park, K.-B. (1995). Korean-Wechsler preschool and primary scale of intelligence. Seoul, Korea: Special Education Publishing Co.
Seidenberg, M. S. (1985). The time course of phonological code activation in two writing systems. Cognition, 19, 1–30.
Simpson, G. B., & Kang, H. (1994). The flexible use of phonological information in word recognition in Korean. Journal of Memory and Language, 33, 319–331.
Siok, W. T., & Fletcher, P. (2001). The role for phonological awareness and visual-orthographic skills in Chinese reading acquisition. Developmental Psychology, 37, 886–899.
Sprenger-Charolles, L., Siegel, L. S., & Bonnet, P. (1998). Reading and spelling acquisition in French: The role of phonological mediation and orthographic factors. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 68, 134–165.
Taylor, I., & Taylor, M. (1995). Writing and literacy in Chinese, Korean, and Japanese. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Co.
Wagner, R. K., & Torgesen, J. (1987). The nature of phonological processing and its causal role in the acquisition of reading skills. Psychological Bulletin, 101, 192–212.
Yoon, H.-K., Bolger, D. J., Kwon, O.-S., & Perfetti, C. A. (2002). Subsyllabic units in reading: A difference between Korean, English. In L. Verhoeven, C. Elbro, & P. Reitsma (Eds.), Precursors of functional literacy (pp.139–163). Amsterdam: J. Benjamins.
Zho, M.-H., Lee, J.-M., Kim, J.-O., Shin, H.-J., Yi, K.-O., Do, K.-S., Lee, Y., Lee, H.-J., Kim Y.-J., Kim S.-Y., Koh, S.-Y., & Chung, H.-S. (2003). Psychology of language. Seoul, Korea: Hagjisa.
Ziegler, J. C., & Goswami, U. (2005). Reading acquisition, developmental dyslexia, and skilled reading across languages: A psycholinguistic grain size theory. Psychological Bulletin, 131, 3–29.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (MOEHRD) (R05-2004-000-11520-0) to Jeung-Ryeul Cho. This research was also partially supported by Research Grants Council grant #4257/03H from the Hong Kong government to Catherine McBride-Chang. We are grateful to In-Sug Whang, Young-Me Paek, Hae-Won Park, and Sue-Eun Cho for their assistance in data collection. We also thank the students, teachers, and headmasters of Hansarang, Yoosung, and Daeja Kindergartens in Korea for the participation in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, JR., McBride-Chang, C. & Park, SG. Phonological awareness and morphological awareness: differential associations to regular and irregular word recognition in early Korean Hangul readers. Read Writ 21, 255–274 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-007-9072-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-007-9072-z