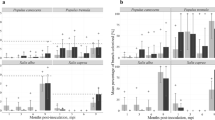
Abstract
This study aims to investigate the colonization of poplar by the endophyte Pseudomonas putida W619 and its capacity to promote plant growth. Poplar cuttings were inoculated with P. putida W619 (wild-type or gfp-labelled). The colonization of both strains was investigated and morphological, physiological and biochemical parameters were analyzed to evaluate plant growth promotion. Inoculation with P. putida W619 (wild-type) resulted in remarkable growth promotion, decreased activities of antioxidative defence related enzymes, and reduced stomatal resistance, all indicative of improved plant health and growth in comparison with the non-inoculated cuttings. In contrast, inoculation with gfp-labelled P. putida W619 did not promote growth; it even had a negative effect on plant health and growth. Furthermore, compared to the wildtype strain, colonization by the gfp-labelled P. putida W619::gfp1 was much lower; it only colonized the rhizosphere and root cortex while the wild-type strain also colonized the root xylem vessels. Despite the strong plant growth promoting capacity of P. putida W619 (wild-type), after gfp labelling its growth promoting characteristics disappeared and its colonization capacity was strongly influenced; for these reasons gfp labelling should be applied with sufficient caution.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkhipova TN, Prinsen E, Veselov SU, Martinenko EV, Melentiev AI, Kudoyarova GR (2007) Cytokinin producing bacteria enhance plant growth in drying soil. Plant Soil 292:305–315
Asghar HN, Zahir ZA, Arshad M (2004) Screening rhizobacteria for improving the growth, yield and soil content of canola (Brassica napus L.). Australian Journal of Agriculture Research 55:187–194
Babalola OO, Osir EO, Sanni AI, Odhiambo GD, Bulimo WD (2003) Amplification of 1-amino-cuclopropane-1-carboxylic (ACC) deaminase from plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in Striga-infected soil. Afr J Biotechnol 2:157–160
Barac T, Taghavi S, Borremans B, Provoost A, Oeyen L, Colpaert JV, Vangronsveld J, van der Lelie D (2004) Engineered endophytic bacteria improve phytoremediation of water-soluble, volatile, organic pollutants. Nat Biotechnol 22:583–588
Barac T, Weyens N, Oeyen L, Taghavi S, van der Lelie D, Dubin D, Split M, Vangronsveld J (2009) Field note: Hydraulic containment of a BTEX plume using poplar trees. Int J Phytoremediat 11:416–424
Belimov AA, Hontzeas N, Safronova VI, Demchinskaya SV, Piluzza G, Bullitta S, Glick BR (2005) Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with the roots of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.). Soil Biol Biochem 37:241–250
Bent E, Tuzun S, Chanway CP, Enebak S (2001) Alterations in plant growth and in root hormone levels of lodgepole pines inoculated with rhizobacteria. Can J Microbiol 47:793–800
Beraha L, Wisniewski V, Garber ED (1983) Avirulence and reduced extracellular enzyme activity in Geotrichum candidum. Bot Gaz 144:461–465
Bergmeyer HU, Gawenn K, Grassl M (1974) Enzymes as biochemical reagents. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods in Enzymatic Analysis. Academic, NewYork, pp 425–522
Bertagnolli BL, Soglio FKD, Sinclair JB (1996) Extracellular enzyme profiles of the fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani isolate 2B-12 and of two antagonists, Bacillus megaterium strain B153-2-2 and Trichoderma harzianum isolate Th008. I. Possible correlations with inhibition of growth and biocontrol. Physiol Mol Plant P 48:145–160
Bloemberg GV, Carvajal MMC (2006) Microbial interactions with plants: a hidden world. In: Schulz BJE, Boyle CJC, Sieber TN (eds) Microbial root endophytes. Springer, Berlin, pp 321–336
Buyer JS, Leong J (1986) Iron transport mediated antagonism between plant growth-promoting and plant-deleterious Pseudomonas strains. J Biol Chem 261:791–794
Cánovas D, Cases I, de Lorenzo V (2003) Heavy metal tolerance and metal homeostasis in Pseudomonas putida as revealed by complete genome analysis. Environ Microbiol 5:1242–1256
Cassman KG, Liska AJ (2007) Food and fuel for all: realistic or foolish? Biofuels Bioprod Bioref 1:18–23
Coombs JT, Franco CMM (2003) Visualization of an endophytic Streptomyces species in wheat seed. Appl Environ Microb 69:4260–4262
Cunningham J, Kuiack C (1992) Production of citric and oxalic acids and solubilization of calcium phosphate by Penicillium bilaii. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(5):1451–1458
Dell’Amico E, Cavalca L, Andreoni V (2005) Analysis of rhizobacterial communities in perennial Graminaceae from polluted water meadow soil, and screening of metal-resistant, potentially plant growth-promoting bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 52:153–162
de Salamone IEG, Hynes RK, Nelson LM (2001) Cytokinin production by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and selected mutants. Can J Microbiol 47:404–411
Doty SL (2008) Enhancing phytoremediation through the use of transgenics and endophytes. New Phytol 179:318–333
Dowling DN, O’Gara F (1994) Metabolites of Pseudomonas involved in the biocontrol of plant disease. Trends Biotechnol 12:133–141
Gao Q, Peng SL, Zhao P, Zeng XP, Cai X, Yu M, Shen WJ, Liu YH (2003) Explanation of vegetation succession in subtropical southern China based on ecophysiological characteristics of plant species. Tree Physiol 23:641–648
Germaine K, Keogh E, Borremans B, van der Lelie D, Barac T, Oeyen L, Vangronsveld J, Porteus Moore F, Moore ERB, Campbel CD, Ryan D, Dowling D (2004) Colonisation of poplar trees by gfp expressing endophytes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:109–118
Haberl H, Beringer T, Bhattacharya SC, Erb K-H, Hoogwijk M (2010) The global technical potential of bio-energy in 2050 considering sustainable constraints. Current opinion in Environmental Sustainability 2:394–403
Haseloff J, Siemering KR, Prasher DC, Hodge S (1997) Removal of a cryptic intron and subcellular localization of green fluorescent protein are required to mark transgenic Arabidopsis plants brightly. P Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2122–2127
Hurek T, Reinhold-Hurek B, Van Montagu M, Kellenberger E (1994) Root colonization and systemic spreading of Azoarcus sp. strain BH72 in grasses. J Bacteriol 176:1913–1923
James EK (2000) Nitrogen fixation in endophytic and associative symbiosis. Field crop res 65:197–209
James EK, Reis VM, Olivares FL, Baldani JI, Döbereiner J (1994) Infection of sugar cane by the nitrogen fixing bacterium Acetobacter diazotrophicus. J Exp Bot 45:757–766
Kloepper JW, Ryu CM, Zhang S (2004) Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp. Phytopathology 94:1259–1266
Krechel A, Faupal A, Hallmann J, Ulrich A, Berg G (2002) Potato-associated bacteria and their antogonistic potential towards plant-pathogenic fungi and the plant-parasitic nematode Meloidogyne incognita (Kofoid and White) Chitwood. Can J Microbiol 48:772–786
Lamb TG, Tonkyn DW, Kluepfel DA (1996) Movement of Pseudomonas aureofaciens from the rhizosphere to aerial plant tissue. Can J Microbiol 42:1112–1120
Mahaffee WF, Kloepper JW, Van Vuurde JWL, Van der Wolf JM, Van den Brink M (1997) Endophytic colonization of Phaseolus vulgaris by Pseudomonas fluorescens strain 89B-27 and Enterobacter asburiae strain JM22. In: Ryder MHR, Stevens PM, Bowen GD (eds) Improving plant productivity in rhizosphere bacteria. CSIRO, Melbourne, p 180
Mastretta C, Barac T, Vangronsveld J, Newman L, Taghavi S, van der Lelie D (2006) Endophytic bacteria and their potential application to improve the phytoremediation of contaminated environments. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 23:175–207
Mayer AM (1958) Determination of Indole Acetic Acid by the Salkowsky Reaction. Nature 182:1670–1671
McCord J, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase: an enzymatic function for erythrocuperein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
Merckx R, van Ginkel JH, Sinnaeve J, Cremers A (1986) Plant induced changes in the rhizosphere of maize and wheat. Plant Soil 96:85–93
Mergeay M, Nies D, Schlegel HG, Gerits J, Charles P, Van Gijsegem F (1985) Alcaligenes eutrophus CH34 is a facultative chemolithotroph with plasmid-bound resistance to heavy metals. J Bacteriol 162:328–334
Newman KL, Almeida RPP, Purcell AH, Lindow SE (2003) Use of a green fluorescent strain for analysis of Xylella fastidiosa colonization of Vitis vinifera. Appl Environ Microb 69:7319–7327
O’Sullivan DJ, O’Gara F (1992) Traits of fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. involved in suppression of plant root pathogens. Microbiology Reviews 56:662–676
Patten C, Glick B (2002) Role of Pseudomonas putida indoleacetic acid in development of the host plant root system. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(8):3795–3801
Petri C, Wang H, Alburquerque N, Faize M, Burgos L (2008) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) leaf explants. Plant Cell Rep 27:1317–1324
Porteous Moore F, Barac T, Borremans B, Oeyen L, Vangronsveld J, van der Lelie D, Campbell CD, Moore ERB (2006) Endophytic bacterial diversity in Poplar trees growing on a BTEX-contaminated site: The characterisation of isolates with potential to enhance phytoremediation. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:539–556
Prinsen E, Van Dongen W, Esmans E, Van Onckelen H (1997) HPLC Linked electrospray tandem mass spectrometry: a rapid and reliable method to analyze indole-3-acetic acid metabolism in bacteria. J Mass Spectrom 32:12–22
Quadt-Hallmann A, Kloepper JW (1996) Immunological detection and localization of the cotton endophyte Enterobacter asburiae JM22 in different plant species. Can J Microbiol 42:1144–1154
Quadt-Hallmann A, Benhamou N, Kloepper JW (1997) Bacterial endophytes in cotton: mechanisms entering the plant. Can J Microbiol 43:577–582
Ramos-Gonzalez MI, Campos MJ, Ramos JL (2005) Analysis of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 gene expression in maize rhizosphere: in vitro expression technology capture and indentification of root-activated promoters. J Bacteriol 187:4033–4041
Redig P, Shaul O, Inzé D, Van Montagu M, Van Onckelen H (1996) Levels of endogenous cytokinins, indole-3-acetic acid and abscisic acid during the cell cycle of synchronized tobacco BY-2 cells. FEBS Lett 391:175–180
Spiertz H (2010) Food production, crops and sustainability: restoring confidence in science and technology. Current opinion in Environmental Sustainability 2:439–443
Sprent JI, de Faria SM (1988) Mechanisms of infection of plants by nitrogen fixing organisms. Plant Soil 110:157–165
Schwyn B, Neilands J (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160(1):47–56
Taghavi S, Barac T, Greenberg B, Borremans B, Vangronsveld J, van der Lelie D (2005) Horizontal gene transfer to endogenous endophytic bacteria from Poplar improves phytoremediation of toluene. Appl Environ Microb 71:8500–8505
Taghavi S, Garafola C, Monchy S, Newman L, Hoffman A, Weyens N, Barac T, Vangronsveld J, van der Lelie D (2009) Genome survey and characterization of endophytic bacteria exhibiting a beneficial effect on growth and development of poplar. Appl Environ Microb 75:748–757
Tanimoto E (2007) Regulation of plant growth by plant hormones – Roles for Auxin and Gibberelin. Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:249–265
van Loon LC, Bakker PAHM, Pieterse CMJ (1998) Systemic resistance induced by rhizosphere bacteria. Annu Rev Phytopathol 36:453–483
Verbeke G, Molenberghs G (2000) Linear mixed models for longitudinal data. Springer Series in Statistics. Springer, New York
Vessey JK (2003) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant Soil 255:571–586
Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H (1994) Toxic effects of metals. In: Farago M (ed) Plants and the chemical elements. VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Germany, pp 149–177
Weyens N, van der Lelie D, Taghavi S, Vangronsveld J (2009a) Phytoremediation: plant–endophyte partnerships take the challenge. Curr Opin Biotech 20:248–254
Weyens N, van der Lelie D, Taghavi S, Newman L, Vangronsveld J (2009b) Exploiting plant–microbe partnerships for improving biomass production and remediation. Trends Biotechnol 27:591–598
Weyens N, Taghavi S, Barac T, van der Lelie D, Boulet J, Artois T, Vangronsveld J (2009c) Bacterial diversity associated with English Oak and Common Ash growing on a TCE-contaminated site: characterization of strains with potential to improve phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut R 16:830–843
Weyens N, van der Lelie D, Artois T, Smeets K, Taghavi S, Newman L, Carleer R, Vangronsveld J (2009d) Bioaugmentation with engineered endophytic bacteria improves contaminant fate in phytoremediation. Environ Sci Technol 43:9413–9418
Weyens N, Truyens S, Dupae J, Newman L, van der Lelie D, Carleer R, Vangronsveld J (2010) Potential of Pseudomonas putida W619-TCE to reduce TCE phytotoxicity and evapotranspiration in poplar cuttings. Environ Pollut 158:2915–2919
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Institute for the Promotion of Innovation through Science and Technology in Flanders (IWT-Vlaanderen) for N.W. and by the Fund for Scientific Research Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen), Ph.D. grant for J.B. The project was further supported by the UHasselt Methusalem project 08 M03 VGRJ. Work by S.T. was funded by Laboratory Directed Research and Development funds (LDRD05-063 and LDRD09-005) at the Brookhaven National Laboratory under contract with the U.S. Department of Energy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Euan K. James.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weyens, N., Boulet, J., Adriaensen, D. et al. Contrasting colonization and plant growth promoting capacity between wild type and a gfp-derative of the endophyte Pseudomonas putida W619 in hybrid poplar. Plant Soil 356, 217–230 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0831-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0831-x