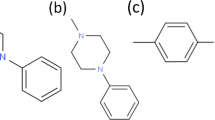
Abstract
Purpose
To examine whether myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) inhibitors can reduce intestinal epithelial permeability increases in vitro.
Materials and Methods
Isolated rat, mouse and human colonic tissue mucosae and Caco-2 monolayers were exposed to cytochalasin D (cD) and sodium caprate (C10), in the absence and presence of the MLCK inhibitors, ML-9 and D PIK. Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) and Papp of [14C]-mannitol or FITC-dextran 4000 (FD-4) were measured. Western blots were used to measure MLC phosphorylation.
Results
Increases in Papp of [14C]-mannitol and decreases in TEER were induced by tight junction openers. These changes were attenuated by ML-9. D-PIK offset the FD-4 Papp increase induced by C10 in Caco-2 only, while ML-9 and PIK inhibited MLC directly. cD induced constriction of peri-junctional actin in Caco-2 monolayers, but this was prevented by ML-9. Although mannitol fluxes across colonic mucosae from dextran-sulphate (DSS)-treated mice were higher than control, they were not ameliorated by either ML-9 or PIK in vitro.
Conclusions
ML-9 inhibits paracellular permeability increases in several intestinal epithelial models. D-PIK reduced stimulated paracellular fluxes in Caco-2 monolayers, but not in tissue. Pre-established increases were not modified by two MLCK inhibitors in a mouse model of IBD.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. M. Cobrin, and M. T. Abreu. Defects in mucosal immunity leading to Crohn’s disease. Immunol. Rev. 206:277–295 (2005).
K. Welcker, A. Martin, P. Kolle, M. Siebeck, and M. Gross. Increased intestinal permeability in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Eur. J. Med. Res. 9:456–460 (2004).
A. A. Lima, Y. M. Lyerly, T. D. Wilkins, D. J. Innes, and R. L. Guerrant. Effects of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B in rabbit small and large intestine in vivo and on cultured cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 56:582–588 (1988).
B. M. Fihn, A. Sjoqvuist, and M. Jodal. Effect of cholera toxin on passive transepithelial transport of 51Cr-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and 14C-mannitol in rat jejunum. Acta Physiol. Scand. 171:153–160 (2001).
D. E. Shifflett, D. R. Clayburgh, A. Koutsouris, J. R. Turner, and G. A. Hecht. Enteropathogenic E. coli disrupts tight junction barrier function and structure in vivo. Lab. Invest 85:1308–1324 (2005).
J. R. Turner, B. K. Rill, S. L. Carlson, D. Carnes, R. Kerner, J. Mrsny, and J. L. Madara. Physiological regulation of epithelial tight junctions is associated with myosin light-chain phosphorylation. Am. J. Physiol. 273:C1378–C1385 (1997).
F. Wang, W. V. Graham, Y. Wang, E. D. Witkowski, B. T. Schwarz, and J. R. Turner. Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha synergize to induce intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by up-regulating myosin light chain kinase expression. Am. J. Pathol. 166:409–419 (2005).
J. R. Turner. Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation. Am. J. Pathol. 169:1901–1909 (2006).
J. J. Berglund, M. Riegler, Y. Zolotaresvsky, E. Wenzl, and J. R. Turner. Regulation of human jejunal transmucosal resistance and MLC phosphorylation by Na(+)-glucose cotransport. Am. J. Physiol. 281:G1487–G1493 (2001).
L. Shen, E. D. Black, E. D. Witkowski, W. I. Lencer, V. Guerriero, E. E. Schneeberger, and J. R. Turner. Myosin light chain phosphorylation regulates barrier function by remodelling tight junction structure. J. Cell Sci. 119:2095–2104 (2006).
J. Bain, H. MacLauchlan, M. Elliott, and P. Cohen. The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update. Biochem. J. 371:199–204 (2003).
Y. Zolotarevsky, G. Hecht, A. Koutsouris, D. E. Gonzalez, C. Quan, J. Tom, R. J. Mrsny, and J. R. Turner. A membrane-permeant peptide that inhibits MLC kinase restores barrier function in in vitro models of intestinal disease. Gastroenterology 123:163–172 (2002).
S.-E. Owens, W. V. Graham, D. Siccardi, J. R. Turner, and R. J. Mrsny. A strategy to identify stable membrane permeant peptide inhibitors of myosin light chain kinase. Pharm. Res. 22:703–709 (2005).
T. J. Lucas, S. Mirzoeva, U. Slomczynska, and D. M. Watterson. Identification of novel classes of protein kinase inhibitors using combinatorial peptide chemistry based on functional genomics knowledge. J. Med. Chem. 42:910–919.
D. R. Clayburgh, T. A. Barrett, Y. Tang, J. B. Meddings, J. J. Van Eldik, D. M. Watterson, L. L. Clarke, R. J. Mrsny, and J. R. Turner. Epithelial myosin light chain kinase-dependent barrier dysfunction mediates T cell activation-induced diarrhea in vivo. J. Clin. Invest 115:2702–2715 (2005).
D. J. Brayden, E. Creed, E. Meehan, and K. E. O’Malley. Passive transepithelial diltiazem absorption across intestinal tissue leading to tight junction openings. J. Control. Rel. 38:193–203 (1996).
A. C. Chao, J. V. Nguyen, M. Broughall, A. Griffin, J. Fix, and P. E. Daddona. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of effects of sodium caprate on enteral peptide absorption and on mucosal morphology. Int. J. Pharm. 191:15–24 (1999).
T. Y. Ma, N. T. Hoa, D. D. Tran, V. Bui, A. Pedram, S. Mills, and M. Merryfield. Cytochalasin B modulation of Caco-2 tight junction barrier: role of myosin light chain kinase. Am. J. Physiol. 279:G875–G885 (2000).
T. W. Leonard, J. Lynch, M. J. McKenna, and D. J. Brayden. Promoting absorption of drugs in humans using medium-chain fatty acid-based solid dosage forms: GIPET. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 3:685–692 (2006).
M. Tomita, M. Hayashi, and S. Awazu. Absorption-enhancing mechanism of sodium caprate and decanoyl carnitine in Caco-2 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 272:739–743 (1995).
F. R. Byrne, and J. L. Viney. Mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease. Curr. Opin. Drug Disc. Develop 9:207–217 (2006).
A. Venkatraman, B. S. Ramakrishna, A. B. Pulimood, S. Patra, and S. Murthy. Increased permeability in dextran sulphate colitis in rats: time course of development and effect of butyrate. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 35(no. 10); 1053–1059 (2000).
A. W. Cuthbert, and H. S. Margolius. Kinins stimulate net chloride secretion by the rat colon. Br. J. Pharmacol. 75:587–598 (1982).
N. P. Hyland, and H. M. Cox. The regulation of veratridine-stimulated electrogenic ion transport in mouse colon by neuropeptide Y (NPY), Y1 and Y2 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 146:712–722 (2005).
D. Moriarty, J. Goldhill, N. Selve, D. P. O’Donoghue, and A. W. Baird. Human colonic anti-secretory activity of the potent NK(1) antagonist, SR140333: assessment of potential anti-diarrhoeal activity in food allergy and inflammatory bowel disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 133:1346–5134 (2001).
J. Soni, A. W. Baird, L. M. O’Brien, M. McElroy, J. J. Callanan, H. F. Bassett, D. Campion, and D. J. Brayden. Rat, ovine and bovine Peyer’s patches mounted in horizontal diffusion chambers display sampling function. J. Control. Release 115:68–77 (2006).
P. Artursson. Epithelial transport of drugs in cell culture. I: A model for studying the passive diffusion of drugs over intestinal absorptive (Caco-2) cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 79:476–482 (1990).
T. Lindmark, T. Nikkila, and P. Artursson. Mechanisms of absorption enhancement by medium chain fatty acids in intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 275:958–964 (1995).
T. Lindmark, Y. Kimura, and P. Artursson. Absorption enhancement through intracellular regulation of tight junction permeability by medium chain fatty acids in Caco-2 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 284:362–369 (1998).
E. K. Anderberg, T. Lindmark, and P. Artursson. Sodium caprate elicits dilatations in human intestinal tight junctions and enhances drug absorption by the paracellular route. Pharm. Res. 10:857–864 (1993).
M. Ikebe. Mode of inhibition of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase by synthetic peptide analogs of the regulatory site. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 168:714–720 (1990).
H. L. Cameron, and M. H. Perdue. Stress impairs murine intestinal barrier function: improvement by glucagon-like peptide-2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 314:214–220 (2005).
B. Hameed, D. M. Smith, J. J. Verrechio, J. D. Schmidt, L. E. Gillooley, M. C. Valenzano, S. A. Lewis, and J. M. Mullin. Indocyanine green alters transepithelial electrical parameters of the distal colon. Dig Dis. Sci. 49:1381–1386 (2004).
R. Schicho, D. Krueger, F. Zeller, C. W. Von Weyhern, T. Frieling, H. Kimura, I. Ishii, R. De Giorgio, B. Campi, and M. Schemann. Hydrogen sulfide is a novel prosecretory neuromodulator in the Guinea-pig and human colon. Gastroenterology 131:1542–1552 (2006).
N. G. Schipper, K. M. Varum, and P. Artursson. Chitosans as absorption enhancers for poorly absorbable drugs. 1: Influence of molecular weight and degree of acetylation on drug transport across human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. Pharm. Res. 13:1686–1692 (1996).
F. Obermeier, G. Kojouharoff, W. Hans, J. Scholmerich, V. Gross, and W. Falk. Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)- and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-induced nitric oxide as toxic effector molecule in chronic dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 116:238–245 (1999).
J. L. Madara, D. Barenberg, and S. Carlson. Effects of cytochalasin D on occluding junctions of intestinal absorptive cells: further evidence that the cytoskeleton may influence paracellular permeability and junctional charge selectivity. J. Cell Biol. 102:2125–2136 (1986).
D. R. Stevenson, and D. A. Begg. Concentration-dependent effects of cytochalasin D on tight junctions and actin filaments in MDCK epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 107:367–375 (1994).
M. Schliwa. Action of cytochalasin D on cytoskeletal networks. J. Cell Biol. 92:79–91 (1982).
C. Wallon, Y. Braaf, M. Wolving, G. Olaison, and J. D. Soderholm. Endoscopic biopsies in Ussing chambers evaluated for studies of macromolecular permeability in the human colon. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 40:586–595 (2005).
J. D. Soderholm, G. Olaison, K. H. Peterson, L. E. Franzen, T. Lindmark, M. Wiren, C. Tagesson, and R. Sjodahl. Augmented increase in tight junction permeability by luminal stimuli in the non-inflamed ileum of Crohn’s disease. Gut 50:307–313 (2002).
T. Lindmark, Y. Kimura, and P. Artursson. Absorption enhancement through intracellular regulation of tight junction permeability by medium chain fatty acids in Caco-2 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 284:362–369 (1998).
S. Wirtz, and M. F. Neurath. Mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 50:1073–1083 (2007).
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Irish Health Research Board Grant RP/86/2002 and Science Foundation Investigator Grant 04/IN3/B575 to David Brayden. Thanks also to Professor Paul Moynagh at National University of Ireland, Maynooth, for assistance with the MLC Western blots.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feighery, L.M., Cochrane, S.W., Quinn, T. et al. Myosin Light Chain Kinase Inhibition: Correction of Increased Intestinal Epithelial Permeability In Vitro . Pharm Res 25, 1377–1386 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9527-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9527-6