Abstract
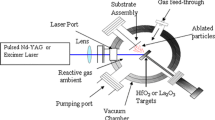
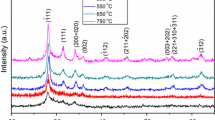
Hafnium oxide (HfO2) has emerged as the most promising highkdielectric for MOS devices. As-deposited sputtered HfO2 thin films have large number of defects resulting in increased oxide charge and leakage current. In this paper the effect of sputtering voltage, bias sputtering and post deposition thermal annealing is investigated. The I–V and C–V characteristics of the dielectric film are studied employing Al–HfO2–Si MOS capacitor structure. It is found that oxide charge increases with increasing sputtering voltage. Thermal annealing in oxygen reduces the interface/oxide charges and leakage current. It is shown that applying substrate bias during film deposition leakage current is further reduced by an order of magnitude. The microstructure of thin film is examined by AFM. The reduction in surface roughness with bias sputtering is shown. The experimental results are presented and discussed for device application.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Technology Road Map for Semiconductors (SanJose, CA, 1999) p. 105
M. Housa, High k gate dielectric, IPO, Bristal (2004) Chapter 1
G.D. Wilk, R. Wallance, G. Anthony, J. Appl. Phys. 87, 5243 (2001)
Y.H. Kim, J.C. Lee, Microelectronics & Relaib. 44, 183 (2004)
H. Kim, P.C. McLntyre, K.C. Saraswat, Appl. Phys. Letts. 82, 106 (2003)
L. Pereira, A. Marques, H. Aguas, N Netev, S. Georgiev, E. Fortunato, R. Martins, Mat. Sci. & Engg. B 109, 89 (2004)
H. Gruger, C.H. Kunath, E. Kurth, S. Sorge, W. Pufe, T. Pechstein, Thin Solid Films 447, 509 (2004)
B. Sen, C.K. Sarkar, H. Wong, M. Chan, C.W. Kok, Solid State Elect. 50, 237 (2006)
R. Puthenkovilakam, M. Sawkar, J.P. Chang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 202902 (2005)
B.H. Lee, L. Kang, J.C. Lee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 1926 (2000)
R. Garg, N.A. Chowdhury, D. Misra, J. Electrochem. Soc. 151, 1 (2004)
B.H. Lee, L. Kang, J.C. Lee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 1926 (2000)
Y. Homma, S. Tsunekawa, J. Electro. Chem. Soc. 132, 1466 (1985)
H. Wong, K.L. Ng, M.C. Poon, C.W. Kok, J. Vac. Sci. & Techno. B22, 1094 (2004)
J. Robertson, Solid State Electron. 49, 283 (2005)
C.T. Kuo, R. Kwor, K.M. Jones, Thin Solid Films 213, 257 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nahar, R.K., Singh, V. & Sharma, A. Study of electrical and microstructure properties of high dielectric hafnium oxide thin film for MOS devices. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 18, 615–619 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-006-9111-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-006-9111-6