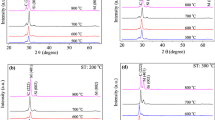
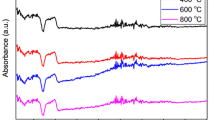
Abstract
The electrical properties of hafnium oxide (HfO2) gate dielectric as a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitor structure deposited using pulse laser deposition (PLD) technique at optimum substrate temperatures in an oxygen ambient gas are investigated. The film thickness and microstructure are examined using ellipsometer and atomic force microscope (AFM), respectively to see the effect of substrate temperatures on the device properties. The electrical J–V, C–V characteristics of the dielectric films are investigated employing Al–HfO2–Si MOS capacitor structure. The important parameters like leakage current density, flat-band voltage (Vfb) and oxide-charge density (Qox) for MOS capacitors are extracted and investigated for optimum substrate temperature. Further, electrical studies of these MOS capacitors have been carried out by incorporating La2O3 into HfO2 to fabricate HfO2/La2O3 dielectric stacks at an optimized substrate temperature of 800 °C using a PLD deposition technique under oxygen ambient. These Al–HfO2–La2O3–Si dielectric stacks MOS capacitor structure are found to possess better electrical properties than that of HfO2 based MOS capacitors using the PLD deposition technique.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Wong, H. Iwai, Microelectron. Eng. 83, 1867 (2006)
H. Wong, H. Iwai, Phys. World 18, 40 (2005)
T. Zimmermann, Y. Cao, D. Jena, H.G. Xing, Int. J. High Speed Electron. Syst. 19, 153 (2009)
G.B. Alers, D.J. Werder, Y. Chabal, H.C. Lu, E.P. Gusev, E. Garfunkel, T. Gustafsson, R.S. Urdahl, Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 1517 (1998)
C.M. Tanner, Y.-C. Perng, C. Frewin, S.E. Saddow, J.P. Chang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 203510 (2007)
S. Chakraborty, M.K. Bera, S. Bhattacharya, C.K. Maiti, Microelectron. Eng. 81, 188 (2005)
D. Zade, S. Sato, K. Kakushima, A. Srivastava, P. Ahmet, K. Tsutsui, A. Nishiyama, N. Sugii, K. Natori, T. Hattori, C.K. Sarkar, H. Iwai, Microelectron. Reliab. 51, 746 (2011)
T. Ngai, W.J. Qi, R. Sharma, J. Fretwell, X. Chen, J.C. Lee, S. Banerjee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 502 (2000)
J. Zhu, Y.R. Li, Z.G. Liu, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 37, 2896 (2004)
A. Srivastava, R. K. Nahar, V. Gupta, C. K. Sarkar, Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference on Nanotechnology (Portland, Oregon, USA, 2011), p. 504
R.K. Nahar, V. Singh, A. Sharma, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 18, 615 (2007)
A. Srivastava, R.K. Nahar, C.K. Sarkar, W.P. Singh, Y. Malhotra, Microelectron. Reliab. 51, 751 (2011)
A. Srivastava, R.K. Nahar, C.K. Sarkar, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 22, 882 (2011)
P.M. Tirmali, A.G. Khairnar, B.N. Joshi, A.M. Mahajan, Solid State Electron. 62, 44 (2011)
K.L. Ng, N. Zhan, C.W. Kok, M.C. Poon, H. Wong, Microelectron. Reliab. 43, 1289 (2003)
J. Zhu, Z.G. Liu, Y.R. Li, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 38, 446 (2005)
J. Zhu, Z.G. Liu, Appl. Phys. A 80, 1769 (2005)
H.Y. Yu, J.F. Kang, C. Ren, J.D. Chen, Y.T. Hou, C. Shen, M.F. Li, D.S.H. Chan, K.L. Bera, C.H. Tung, D.-L. Kwong, IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 25, 70 (2004)
H.F. Wolf, Semiconductors (Wiley, New York, 1971)
H. Wong, K.L. Ng, N. Zhan, M.C. Poon, C.W. Kok, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 22, 1094 (2004)
S.M. Sze, Physics of Semiconductor Devices, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 1981)
F.-C. Chiu, H.-W. Chou, J.Y.-M. Lee, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 103503 (2005)
I. Horcas, R. Fernández, J.M. Gómez-Rodríguez, J. Colchero, J. Gómez-Herrero, A.M. Baro, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78, 013705 (2007)
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (OM) is thankful to the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India for financial assistance in term of award of Senior Research Fellowship (NET). The authors would also like to thank Prof. V. R. Rao, Electrical Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, for useful comments, suggestion and experimental support to do electrical characterization under the INUP project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, A., Mangla, O., Nahar, R.K. et al. Study of electrical and micro-structural properties of high-κ gate dielectric stacks deposited using pulse laser deposition for MOS capacitor applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 3257–3263 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2011-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2011-2