Summary
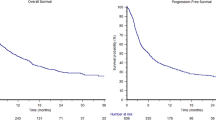
Purpose Activation of EGFR can stimulate proliferative and survival signaling through mTOR. Preclinical data demonstrates synergistic activity of combined EGFR and mTOR inhibition. We undertook a phase I trial of temsirolimus (T, an mTOR inhibitor) and EKB-569 (E, an EGFR inhibitor) to determine the safety and tolerability. Methods The primary aim was to determine the maximally tolerated dose (MTD) of this combination in adults with solid tumors. Following the dose-escalation phase, (Cohort A), two subsequent cohorts were used to assess any pharmacokinetic (PK) interaction between the agents. Results Forty eight patients were enrolled. The MTD of this combination was E, 35 mg daily and T, 30 mg on days 1–3 and 15–17 using a 28-day cycle. The most common toxicities were nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, anorexia, stomatitis, rash, anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and hypertriglyceridemia. Sixteen patients (36%) had at least one grade 3 toxicity. The most frequent grade 3/4 toxicities were diarrhea, dehydration, and nausea and vomiting (19% each). No grade 5 events were seen. Four patients had a partial response and 15 had stable disease. Clinical benefit was seen across a range of tumor types and in all cohorts. PK analysis revealed no significant interaction between E and T. Conclusions This combination of agents is associated with tolerable toxicities at doses that induced responses. PK studies revealed no interaction between the drugs. Further investigations of this targeting strategy may be attractive in renal cell carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer, alveolar sarcoma, and carcinoid tumor.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbet NC, Schneider U, Helliwell SB, Stansfield I, Tuite MF, Hall MN (1996) TOR controls translation initiation and early G1 progression in yeast. Mol Biol Cell 7(1):25–42
Hay N, Sonenberg N (2004) Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev 18(16):1926–1945. doi:10.1101/gad.1212704
Beevers CS, Li F, Liu L, Huang S (2006) Curcumin inhibits the mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated signaling pathways in cancer cells. Int J Cancer 119(4):757–764. doi:10.1002/ijc.21932
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, Lindeman N, Gale CM, Zhao X, Christensen J, Kosaka T, Holmes AJ, Rogers AM, Cappuzzo F, Mok T, Lee C, Johnson BE, Cantley LC, Janne PA (2007) MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 316(5827):1039–1043
Engelman JA, Janne PA (2008) Mechanisms of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(10):2895–2899
Ogino A, Kitao H, Hirano S, Uchida A, Ishiai M, Kozuki T, Takigawa N, Takata M, Kiura K, Tanimoto M (2007) Emergence of epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation during chronic exposure to gefitinib in a non small cell lung cancer cell line. Cancer Res 67(16):7807–7814
Yamasaki F, Johansen MJ, Zhang D, Krishnamurthy S, Felix E, Bartholomeusz C, Aguilar RJ, Kurisu K, Mills GB, Hortobagyi GN, Ueno NT (2007) Acquired resistance to erlotinib in A-431 epidermoid cancer cells requires down-regulation of MMAC1/PTEN and up-regulation of phosphorylated Akt. Cancer Res 67(12):5779–5788
Ansell SM, Inwards DJ, Rowland KM Jr, Flynn PJ, Morton RF, Moore DF Jr, Kaufmann SH, Ghobrial I, Kurtin PJ, Maurer M, Allmer C, Witzig TE (2008) Low-dose, single-agent temsirolimus for relapsed mantle cell lymphoma: a phase 2 trial in the North Central Cancer Treatment Group. Cancer 113(3):508–514
Witzig TE, Geyer SM, Ghobrial I, Inwards DJ, Fonseca R, Kurtin P, Ansell SM, Luyun R, Flynn PJ, Morton RF, Dakhil SR, Gross H, Kaufmann SH (2005) Phase II trial of single-agent temsirolimus (CCI-779) for relapsed mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 23(23):5347–5356
Torrance CJ, Jackson PE, Montgomery E, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Wissner A, Nunes M, Frost P, Discafani CM (2000) Combinatorial chemoprevention of intestinal neoplasia.[see comment]. Nat Med 6(9):1024–1028
Carter TA, Wodicka LM, Shah NP, Velasco AM, Fabian MA, Treiber DK, Milanov ZV, Atteridge CE, Biggs WH 3rd, Edeen PT, Floyd M, Ford JM, Grotzfeld RM, Herrgard S, Insko DE, Mehta SA, Patel HK, Pao W, Sawyers CL, Varmus H, Zarrinkar PP, Lockhart DJ (2005) Inhibition of drug-resistant mutants of ABL, KIT, and EGF receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(31):11011–11016
Erlichman C, Hidalgo M, Boni JP, Martins P, Quinn SE, Zacharchuk C, Amorusi P, Adjei AA, Rowinsky EK (2006) Phase I study of EKB-569, an irreversible inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor, in patients with advanced solid tumors.[see comment]. J Clin Oncol 24(15):2252–2260
Laheru D, Croghan G, Bukowski R, Rudek M, Messersmith W, Erlichman C, Pelley R, Jimeno A, Donehower R, Boni J, Abbas R, Martins P, Zacharchuk C, Hidalgo M (2008) A phase I study of EKB-569 in combination with capecitabine in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(17):5602–5609
Folprecht G, Tabernero J, Kohne CH, Zacharchuk C, Paz-Ares L, Rojo F, Quinn S, Casado E, Salazar R, Abbas R, Lejeune C, Marimon I, Andreu J, Ubbelohde U, Cortes-Funes H, Baselga J (2008) Phase I pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study of EKB-569, an irreversible inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in combination with irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, and leucovorin (FOLFIRI) in first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(1):215–223
Rao RD, Mladek AC, Lamont JD, Goble JM, Erlichman C, James CD, Sarkaria JN (2005) Disruption of parallel and converging signaling pathways contributes to the synergistic antitumor effects of simultaneous mTOR and EGFR inhibition in GBM cells. Neoplasia (New York) 7(10):921–929
Buckner JC, Forouzesh B, Erlichman C, Hidalgo M, Boni JP, Dukart G, Berkenblit A, Rowinsky EK (2010) Phase I, pharmacokinetic study of temsirolimus administered orally to patients with advanced cancer. Invest New Drugs 28(3):334–342. doi:10.1007/s10637-009-9257-1
Raymond E, Alexandre J, Faivre S, Vera K, Materman E, Boni J, Leister C, Korth-Bradley J, Hanauske A, Armand JP (2004) Safety and pharmacokinetics of escalated doses of weekly intravenous infusion of CCI-779, a novel mTOR inhibitor, in patients with cancer.[see comment]. J Clin Oncol 22(12):2336–2347
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada.[see comment]. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(3):205–216
Amorusi P (2001) EKB-569: validation of an LC/MS/MS bioanalytical method for the quantitation of EKB-569 in human plasma. Wyeth-Ayerst Research RPT-40374. Wyeth-Ayerst Research RPT-40374, vol Wyeth-Ayerst Research RPT-40374. Pearl River (NY)
Punt CJ, Boni J, Bruntsch U, Peters M, Thielert C (2003) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of CCI-779, a novel cytostatic cell-cycle inhibitor, in combination with 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin in patients with advanced solid tumors. Ann Oncol 14(6):931–937
Wong KK, Fracasso PM, Bukowski RM, Lynch TJ, Munster PN, Shapiro GI, Janne PA, Eder JP, Naughton MJ, Ellis MJ, Jones SF, Mekhail T, Zacharchuk C, Vermette J, Abbas R, Quinn S, Powell C, Burris HA (2009) A phase I study with neratinib (HKI-272), an irreversible pan ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 15(7):2552–2558. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1978
Tsou HR, Overbeek-Klumpers EG, Hallett WA, Reich MF, Floyd MB, Johnson BD, Michalak RS, Nilakantan R, Discafani C, Golas J, Rabindran SK, Shen R, Shi X, Wang YF, Upeslacis J, Wissner A (2005) Optimization of 6,7-disubstituted-4-(arylamino)quinoline-3-carbonitriles as orally active, irreversible inhibitors of human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 kinase activity. J Med Chem 48(4):1107–1131. doi:10.1021/jm040159c
Burris HA 3rd, Hurwitz HI, Dees EC, Dowlati A, Blackwell KL, O'Neil B, Marcom PK, Ellis MJ, Overmoyer B, Jones SF, Harris JL, Smith DA, Koch KM, Stead A, Mangum S, Spector NL (2005) Phase I safety, pharmacokinetics, and clinical activity study of lapatinib (GW572016), a reversible dual inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic carcinomas. J Clin Oncol 23(23):5305–5313. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.16.584
Wood ER, Truesdale AT, McDonald OB, Yuan D, Hassell A, Dickerson SH, Ellis B, Pennisi C, Horne E, Lackey K, Alligood KJ, Rusnak DW, Gilmer TM, Shewchuk L (2004) A unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells. Cancer Res 64(18):6652–6659. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1168
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors’ Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interests
JB is a paid employee of Pfizer, Inc.
Supported CA69912, 5ULRR024150, and CA090628
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bryce, A.H., Rao, R., Sarkaria, J. et al. Phase I study of temsirolimus in combination with EKB-569 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 30, 1934–1941 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9742-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9742-1