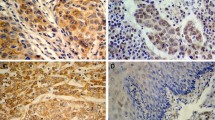
Abstract
To gain insights into metastatic mechanisms in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), we established sublines (MLuB1 and MLuC1) with different capacity of spontaneous lung metastasis by subcutaneous injection of a human ESCC cell line (EC 9706) into nude mices. The incidence of the mice with lung metastasis produced by MLuC1 (87%) was significantly higher than that of MLuB1 (22%). The gene expression profiles of the two sublines were compared with cDNA arrays containing 5,000 known genes, and 47 genes were differentially expressed ≥2.0 fold. Laminin-5γ2 chain (Ln-5γ2) was one of the up-regulated genes in MLuC1 cells. Proteolytically processed forms of γ2 are known to promote migration of a multitude of epithelial cells in vitro. Western-blotting analysis revealed that degraded fragments of Ln-5γ2 and active form of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MT1-MMP) in MLuC1 was significantly higher than those in MLuB1. Expression of MT1-MMP was observed in 60 of 75 Ln-5γ2-positive carcinoma tissues (80%). Co-expression of the two proteins was significantly associated with depth of invasion (P = 0.012). Moreover, proteolytic fragments of Ln-5γ2 and active forms of MT1-MMP were frequently found in tumor tissues, whereas in the corresponding normal esophageal tissues there were only intact forms of γ2 and MT1-MMP. siRNA-mediated silencing of MT1-MMP significantly reduced production of γ2′ and γ2x in MLuC1 cells and inhibited cell migration. The results suggest that MT1-MMP is an enzyme responsible for Ln-5γ2 cleavage in ESCC, and interaction between them may play a critical role in promoting invasion and metastasis of human ESCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ln-5γ2:
-
Laminin-5γ2
- MT1-MMP:
-
Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1
- ESCC:
-
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceralde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- CA12:
-
Carbonic anhydrase XII
- HMGA2:
-
High mobility group AT-hook 2
- CTSS:
-
Cathepsin S
- COL4A6:
-
Collagen type IV alpha 6
- COL7A1:
-
Collage type VII alpha 1
- TSPAN-1:
-
Tetraspan 1
Reference
Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F et al (1999) Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in. Int J Cancer 83:18–29
Pimkhaokham A, Shimada Y, Fukuda Y et al (2000) Nonrandom chromosomal imbalances in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines: possible involvement of the ATF3 and CENPF genes in the 1q32 amplicon. Jpn J Cancer Res 91:1126–1133
Sugimachi K, Ohno S, Matsuda H et al (1988) Lugol-combined endoscopic detection of minute malignant lesions of the thoracic esophagus. Ann Surg 208:179–183
Ohashi K, Nemoto T, Nakamura K et al (2000) Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase 7 and 9 and membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer 88:2201–2209
Peracchia A, Bonavina L, Ruol A et al (2000) Esophageal cancer: a European perspective. Recent Results Cancer Res 155:119–122
Hirai T, Kuwahara M, Yoshida K et al (1998) Clinical results of transhiatal esophagectomy for carcinoma of the lower thoracic esophagus according to biological markers. Dis Esophagus 11:221–225
Inada S, Koto T, Futami K et al (1999) Evaluation of malignancy and the prognosis of esophageal cancer based on an immunohistochemical study (p53, E-cadherin, epidermal growth factor receptor). Surg Today 29:493–503
Iihara K, Shiozaki H, Tahara H et al (1993) Prognostic significance of transforming growth factoralpha in human esophageal carcinoma. Implication for the autocrine proliferation. Cancer 71:2902–2909
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B et al (1991) p53 mutations in human cancers. Science 253:49–53
Nakagawa H, Zukerberg L, Togawa K et al (1995) Human cyclin D1 oncogene and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 76:541–549
Natsugoe S, Xiangming C, Matsumoto M et al (2002) Smad4 and transforming growth factor?-1 expression in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Clin Cancer Res 8:1838–1842
Fukai Y, Fukuchi M, Masuda N et al (2003) Reduced expression of transforming growth factor-receptors is an unfavorable prognostic factor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 104:161–166
Yamamoto H, Itoh F, Iku S et al (2001) Expression of the gamma(2) chain of laminin-5 at the invasive front is associated with recurrence and poor prognosis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 7:896–900
Koshikawa N, Giannelli G., Cirulli V et al (2000) Role of cell surface metalloprotease MT1-MMP in epithelial cell migration over laminin-5. J Cell Biol 148:615–624
Gilles C, Polette M, Coraux C et al (2001) Contribution of MT1-MMP and of human laminin-5 gamma2 chain degradation to mammary epithelial cell migration. J Cell Sci 114(Pt 16):2967–2976
Koshikawa N, Schenk S, Moeckel G et al (2004) Proteolytic processing of laminin-5 by MT1-MMP in tissues and its effects on epithelial cell morphology. FASEB J 18:364–366
Veitch DP, Nokelainen P, McGowan KA et al (2003) Mammalian tolloid metalloproteinase, and not matrix metalloprotease 2 or membrane type 1 metalloprotease, processes laminin-5 in keratinocytes and skin. J Biol Chem 278:15661–15668
Koshikawa N, Minegishi T, Sharabi A et al (2005) Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MT1-MMP) is a processing enzyme for human laminin gamma 2 chain. J Biol Chem 280:88–93
Oku N, Sasabe E, Ueta E et al (2006) Tight junction protein claudin-1 enhances the invasive activity of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by promoting cleavage of laminin-5 gamma2 chain via matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and membrane-type MMP-1. Cancer Res 66:5251–5257
Han Y, Wei F, Xu X et al (2002) Establishment and comparative genomic hybridization analysis of human esophageanl carcinomas cell line EC9706. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 19:455–457
Mariadason JM, Corner GA, Augenlicht LH (2000) Genetic reprogramming in pathways of colonic cell maturation induced by short chain fatty acids: comparison with trichostatin A, sulindac, and curcumin and implications for chemoprevention of colon cancer. Cancer Res 60:4561–4572
Mariadason JM, Arango D, Corner GA et al (2002) A gene expression profile that defines colon cell maturation in vitro. Cancer Res 62:4791–4804
Katoh K, Nakanishi Y, Akimoto S et al (2002) Correlation between Laminin-5 γ2 Chain expression and epidermal growth factor receptor expression and its clinicopathological significance in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Oncology 62:318–326
Moriya Y, Niki T, Yamada T et al (2001) Increased expression of laminin-5 and its prognostic significance in small-sized lung adenocarcinoma: an immunohistochemical analysis of 102 cases. Cancer 91:1129–1141
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Weber K et al (2002) Analysis of gene function in somatic mammalian cells using small interfering RNAs. Method 26:199–213
Hess KR, Zhang W, Baggerly KA et al (2001) Microarrays: handling the deluge of data and extracting reliable information. Trends Biotechnol 19:463–468
Butte A (2002) The use and analysis of microarray data. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:951–960
Murray GI, Duncan ME, O’Neil P et al (1998) Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is associated with poor prognosis in oesophageal cancer. J Pathol 185:256–261
Simon-Assmann P, Kedinger M (1993) Heterotypic cellular cooperation in gut morphogenesis and differentiation. Semin Cell Biol 4:221–230
Mizushima H, Koshikawa N, Moriyama K (1998) Wide distribution of laminin-5 gamma 2 chain in basement membranes of various human tissues. Horm Res 50(Suppl 2):7–14
Katayama M, Sekiguchi K (2004) Laminin-5 in epithelial tumour invasion. J Mol Histol 35:277–286
Koshikawa N, Moriyama K, Takamura H et al (1999) Overexpression of laminin gamma2 chain monomer in invading gastric carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 59:5596–5601
Lenander C, Habermann JK, Ost A et al (2001) Laminin-5 gamma 2 chain expression correlates with unfavorable prognosis in colon carcinomas. Anal Cell Pathol 22:201–209
Aoki S, Nakanishi Y, Akimoto S (2002) Prognostic significance of laminin-5 gamma2 chain expression in colorectal carcinoma: immunohistochemical analysis of 103 cases. Dis Colon Rectum 45:1520–1527
Pyke C, Salo S, Ralfkaer E et al (1995) Laminin-5 is a marker of invading cancer cells in some human carcinomas and is coexpressed with the receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator in budding cancer cells in colon adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 55:4132–4139
Soini Y, Maata M, Salo S et al (1996) Expression of laminin gamma 2 chain in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Pathol 180:290–294
Tani T, Karttunen T, Kiviluoto T (1996) Alpha 6 beta 4 integrin and newly deposited laminin-1 and laminin-5 from the adhesion mechanism of gastric carcinoma. Am J Pathol 149:781–793
Etoh T, Inoue H, Yoshikawa Y et al (2000) Increased expression of collagenase-3 (MMP-13) and MT1-MMP in oesophageal cancer is related to cancer aggressiveness. Gut 47:50–56
Acknowledgments
Supported by National Science Fund (30470969), State Key Basic Research Grant of China (2004CB518705, 2002CB513101), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20050023046) and Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT0416).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, XM., Wu, YP., Feng, YB. et al. Interaction of MT1-MMP and laminin-5γ2 chain correlates with metastasis and invasiveness in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 24, 541–550 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-007-9091-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-007-9091-9