Abstract
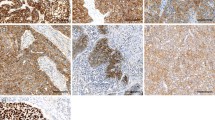
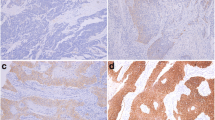
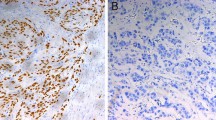
The subjects in this study consisted of 40 preoperative untreated esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. While p53 did not significantly correlate with the clinicopathological factors, E-cadherin significantly correlated with lymphatic invasion, vascular invasion, the depth of invasion, the degree of lymph node metastasis, the histological stage, and the number of lymph node metastases. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) significantly correlated with age, the depth of invasion, and the number of lymph node metastases. The 5-year cumulative survival rate was 45.7% in the p53-positive cases and 61.9% in the p53-negative cases, with no significant difference, and 87.8% in the E-cadherinpositive cases and 19.1% in the-negative cases, and the difference was significnat. The prognosis was significantly poor in EGFR-positive subjects: the 5-year survival rate was 38.6% in EGFR-positive cases and 68% in-negative cases. The 5-year survival rate in E-cadherin-negative, EGFR-positive cases was 0%, while it was 91.7% in the reverse pattern, and this difference was significant. These findings suggest that both E-cadherin and EGFR are important prognostic factors, and a more precise prognosis can thus be obtained by combining them. Such a combined technique may be very useful as an indicator for grading the biological malignancy of esophageal cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muroi M (1995) A clinicopathological study on extensive lymph node dissection for thoracic esophageal cancer (in Japanese with English abstract). Nippon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi (J Jpn Assoc Thorac Surg) 43:287–299
Kakegawa T, Yamana H (1995) Progress in surgical treatment of carcinoma of the intrathoracic esophagus (in Japanese with English abstract). Gan To Kagaku Ryoho (Jpn J Cancer Chemother) 22:855–862
Kotoh T, Arima S, Inada S, Futami K (1995) A study of lymph node metastasis and recurrence in thoracic esophageal cancer. Med Bull Fukuoka Univ 22:53–60
Japanese Society for Esophageal Disease (1992) Guidelines for the clinical and pathological studies on carcinoma of the esophagus, 8th edn. Kinahara, Tokyo
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life tables (with discussion). J R Stat Soc B 34:187–220
Nigro JM, Baker SJ, Preisinger AC, Jessup JM, Hostetter R, Cleary K, Bigner SH, Davidson N, Baylin S, Devilee P, Glover T, Collins FS, Weston A, Modali R, Harris CC, Vogelstein B (1989) Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumor types. Nature 342:705–708
Wagata T, Ishizaki K, Imamura M, Shimada Y, Ikenaga M, Tobe T (1991) Deletion of 17p and amplification of the int-2 gene in esophageal carcinomas. Cancer Res 51:2113–2117
Hollstein MC, Metcalf RA, Welsh JA, Montesano R, Harris CC (1990) Frequent mutation of the p53 gene in human esophageal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9958–9961
Hollstein MC, Peri L, Mandard AM, Welsh JA, Montesano R, Metcalf RA, Bak M, Harris CC (1991) Genetic analysis of human esophageal tumors from two high-incidence geographic areas: frequent p53 base substitutions and absence of ras mutation. Cancer Res 51:4102–4106
Finlay CA, Hinds PW, Tan TH, Eliyahu D, Oren M, Levine AJ (1988) Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc 70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol 8:531–539
Sarbia M, Porschen R, Borchard F, Horstmann O, Willers R, Gabbert HE (1994) p53 protein expression and prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer 74:2218–2223
Goukon Y, Sasano H, Nishihira T, Nagura H, Mori S (1994) p53 overexpression in human esophageal carcinoma: a correlation with tumor DNA ploidy and two parameter flow cytometric study. Anticancer Res 14:1305–1312
Shimaya K, Shinozaki H, Inoue M, Tahara H, Monden T, Shimano T, Mori T (1993) Significance of p53 expression as a prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Virchows Arch (A) 422:271–276
Shiozaki H, Miyata M, Kobayashi K, Tahara H, Tamura S, Yano H, Oka H, Doki Y, Iihara K, Mori T, Hirano S, Takeichi M (1991) Correlation between E-cadherin expression and lymphnode metastasis in esophageal cancer (in Japanese with English abstract). Nippon Syoukakigeka Gakkai Zassi (Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg) 24:1117–1120
Kadowaki T, Shiozaki H, Inoue M, Tamura S, Oka H, Doki Y, Iihara K, Matsui S, Iwazawa T, Nagafuchi A, Tsukita S, Mori T (1994) E-cadherin and α catenin expression in human esophageal cancer. Cancer Res 54:291–296
Cohen S, Ushio H, Stoscheck C, Chinkers M (1982) A native 170 000 epidermal growth factor receptor kinase complex from shed plasma membrane vesicle. J Biol Chem 257:1523–1531
Yamamoto T, Kamata N, Kawano H, Shimizu S, Kuroki T, Toyoshima K, Rikimaru K, Nomura N, Ishizaki R, Pastan I, Gamou S, Shimizu N (1986) High incidence of amplification of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in human squamous carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 46:414–416
Lewis S, Locker A, Todd JH, Bell JA, Nicholson R, Elston CW, Blamey RW, Ellis IO (1990) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in breast carcinoma. J Clin Pathol 43:385–389
Yonemura Y, Sugimati K, Kamata T, Fushida S, Yamaguchi A, Miwa K, Miyazaki I (1988) Correlation of epidermal growth factor receptor status and clinical outcome in gastric carcinoma (in Japanese with English abstract). Nippon Geka Gakkai Zasshi (J Jpn Surg Soc) 89:1611–1615
Arai M, Hirose K, Nakagawara G, Inuzuka M (1994) Expression of human epidermal growth factor and its receptor of the gastric carcinomas with special reference to DNA ploidy patterns and nucleolar organizer regions (in Japanese with English abstract). Nippon Geka Gakkai Zasshi (J Jpn Surg Soc) 95:171–178
Yano H, Shiozaki H, Kobayashi K, Yano T, Tahara H, Tamura S, Mori T (1991) Immunohistologic detection of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 67:91–98
Itakura Y, Sasano H, Shiga C, Shiga K, Nishihira T, Nagura H, Mori S (1993) Immunohistochemical analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) overexpression in esophageal carcinoma (in Japanese with English abstract). Shokakigan No Hassei To Shinten (J Jpn Res Gastroenterol Carcinogen) 5:195–199
Fukuda M, Okamura K, Fujita S, Böhm N, Rohrbach R, Sandritter W (1978) The different stem cell populations in mouse epidermis and lingual epithelium, Pathol Res Pract 163:205–227
Fukuyama R, Shimizu N (1991) Detection of epidermal growth factor receptors and E-cadherin in the basolateral membrane of A431 cells by laser scanning florescence microscopy. Jpn J Cancer Res 82:8–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inada, S., Koto, T., Futami, K. et al. Evaluation of malignancy and the prognosis of esophageal cancer based on an immunohistochemical study (p53, E-cadherin, epidermal growth factor receptor). Surg Today 29, 493–503 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482343
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482343