Abstract
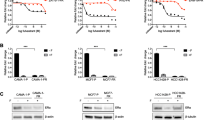
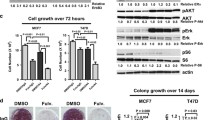
Seven fulvestrant resistant cell lines derived from the estrogen receptor α positive MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line were used to investigate the importance of epidermal growth factor receptor (ErbB1-4) signaling. We found an increase in mRNA expression of EGFR and the ErbB3/ErbB4 ligand heregulin2 (hrg2) and a decrease of ErbB4 in all resistant cell lines. Western analyses confirmed the upregulation of EGFR and hrg2 and the downregulation of ErbB4. Elevated activation of EGFR and ErbB3 was seen in all resistant cell lines and the ErbB3 activation occurred by an autocrine mechanism. ErbB4 activation was observed only in the parental MCF-7 cells. The downstream kinases pAkt and pErk were increased in five of seven and in all seven resistant cell lines, respectively. Treatment with the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib preferentially inhibited growth and reduced the S phase fraction in the resistant cell lines concomitant with inhibition of Erk and unaltered Akt activation. In concert, inhibition of Erk with U0126 preferentially reduced growth of resistant cell lines. Treatment with ErbB3 neutralizing antibodies inhibited ErbB3 activation and resulted in a modest but statistically significant growth inhibition of two resistant cell lines. These data indicate that ligand activated ErbB3 and EGFR, and Erk signaling play important roles in fulvestrant resistant cell growth. Furthermore, the decreased level of ErbB4 in resistant cells may facilitate heterodimerization of ErbB3 with EGFR and ErbB2. Our data support that a concerted action against EGFR, ErbB2 and ErbB3 may be required to obtain complete growth suppression of fulvestrant resistant cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Osborne CK (1999) Tamoxifen in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 339:1609–1618
Brünner N, Frandsen TL, Holst-Hansen C et al (1993) MCF7/LCC2 A 4-hydroxytamoxifen resistant human breast cancer variant that retains sensitivity to the steroidal antiestrogen ICI 182,780. Cancer Res 53:3229–3232
Lykkesfeldt AE, Madsen MW, Briand P (1994) Altered expression of estrogen-regulated genes in a tamoxifen-resistant and ICI 164,384 and ICI 182,780 sensitive human breast cancer cell line, MCF-7/TAMR-1. Cancer Res 54:1587–1595
Howell A, DeFriend D, Robertson J et al (1995) Response to a specific antioestrogen (ICI 182780) in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer. Lancet 345:29–30
Howell A (2006) Pure oestrogen antagonists for the treatment of advanced breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 13:689–706
Lykkesfeldt AE, Larsen SS, Briand P (1995) Human breast cancer cell lines resistant to pure anti-estrogens are sensitive to tamoxifen treatment. Int J Cancer 61:529–534
Fan M, Yan PS, Hartman-Frey C et al (2006) Diverse gene expression and DNA methylation profiles correlate with differential adaptation of breast cancer cells to the antiestrogens tamoxifen and fulvestrant. Cancer Res 66:11954–11966
McClelland RA, Barrow D, Madden TA et al (2000) Enhanced epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in MCF7 breast cancer cells after long-term culture in the presence of the pure antiestrogen ICI 182,780 (Faslodex). Endocrinology 142:2776–2788
Frogne T, Jepsen JS, Larsen SS et al (2005) Antiestrogen-resistant human breast cancer cells require activated protein kinase B/Akt for growth. Endocr Relat Cancer 12:599–614
Gu Z, Lee RY, Skaar TC et al (2002) Association of interferon regulatory factor-1, nucleophosmin, nuclear factor-kappaB, and cyclic AMP response element binding with acquired resistance to Faslodex (ICI 182,780). Cancer Res 62:3428–3437
Citri A, Yarden Y (2006) EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:505–516
Linggi B, Carpenter G (2006) ErbB receptors: new insights on mechanisms and biology. Trends Cell Biol 16:649–656
Witton CJ, Reeves JR, Going JJ et al (2003) Expression of the HER1–4 family of receptor tyrosine kinases in breast cancer. J Pathol 200:290–297
Nicholson RI, McClelland RA, Gee JM et al (1994) Transforming growth factor-alpha and endocrine sensitivity in breast cancer. Cancer Res 54:1684–1689
Atlas E, Cardillo M, Mehmi I et al (2003) Heregulin is sufficient for the promotion of tumorigenicity and metastasis of breast cancer cells in vivo. Mol Cancer Res 1:165–175
Britton DJ, Hutcheson IR, Knowlden JM et al (2006) Bidirectional cross talk between ERalpha and EGFR signalling pathways regulates tamoxifen-resistant growth. Breast Cancer Res Treat 96:131–146
Hynes NE, Lane HA (2005) ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 5:341–354
Normanno N, Bianco C, Strizzi L et al (2005) The ErbB receptors and their ligands in cancer: an overview. Curr Drug Targets 6:243–257
Sergina NV, Rausch M, Wang D et al (2007) Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the kinase-inactive HER3. Nature 445:437–441
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T et al (2007) MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 316:1039–1043
Wilson KJ, Mill CP, Cameron EM et al (2007) Inter-conversion of neuregulin2 full and partial agonists for ErbB4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 364:351–357
Memon AA, Sorensen BS, Melgard P et al (2004) Expression of HER3, HER4 and their ligand heregulin-4 is associated with better survival in bladder cancer patients. Br J Cancer 91:2034–2041
Memon AA, Sorensen BS, Meldgaard P (2006) The relation between survival and expression of HER1 and HER2 depends on the expression of HER3 and HER4: a study in bladder cancer patients. Br J Cancer 94:1703–1709
Sorensen BS, Torring N, Bor MV et al (2000) Quantitation of the mRNA expression of the epidermal growth factor system: selective induction of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor and amphiregulin expression by growth factor stimulation of prostate stromal cells. J Lab Clin Med 136:209–217
de Cremoux P, Tran-Perennou C, Brockdorff BL et al (2003) Validation of real-time RT-PCR for analysis of human breast cancer cell lines resistant or sensitive to treatment with antiestrogens. Endocr Relat Cancer 10:409–418
Horst EH, Murgia M, Treder M et al (2005) Anti-HER-3 MAbs inhibit HER-3-mediated signaling in breast cancer cell lines resistant to anti-HER-2 antibodies. Int J Cancer 115:519–527
Zhou BB, Peyton M, He B et al (2006) Targeting ADAM-mediated ligand cleavage to inhibit HER3 and EGFR pathways in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell 10:39–50
Dunn M, Sinha P, Campbell R et al (2004) Co-expression of neuregulins 1, 2, 3 and 4 in human breast cancer. J Pathol 203:672–680
Breuleux M (2007) Role of heregulin in human cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2358–2377
Nakano N, Higashiyama S, Ohmoto H et al (2004) The N-terminal region of NTAK/neuregulin-2 isoforms has an inhibitory activity on angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 19:11465–11470
Zahnow CA (2006) ErbB receptors and their ligands in the breast. Expert Rev Mol Med 8:1–21
Nicholson RI, Hutcheson IR, Jones HE et al (2007) Growth factor signalling in endocrine and anti-growth factor resistant breast cancer. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 8:241–253
Sommer A, Hoffmann J, Lichtner RB et al (2003) Studies on the development of resistance to the pure antiestrogen Faslodex in three human breast cancer cell lines. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 85:33–47
Jensen BL, Skouv J, Lundholt BK et al (1999) Differential regulation of specific genes in MCF-7 and the ICI 182780-resistant cell line MCF-7/182R-6. Br J Cancer 79:386–392
Arpino G, Wiechmann L, Osborne CK et al (2008) Crosstalk between the Estrogen Receptor and the HER tyrosine kinase receptor family: molecular mechanism and clinical implications for endocrine therapy resistance. Endocr Rev 29(2):217–233
Liu B, Ordonez-Ercan D, Fan Z et al (2007) Downregulation of erbB3 abrogates erbB2-mediated tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 120:1874–1878
Hutcheson IR, Knowlden JM, Hiscox SE et al (2007) Heregulin beta1 drives gefitinib-resistant growth and invasion in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 9:R50
Revillion F, Pawlowski V, Lhotellier V et al (2003) mRNA expression of the type I growth factor receptors in the human breast cancer cells MCF-7: regulation by estradiol and tamoxifen. Anticancer Res 23:1455–1460
Pitfield SE, Bryant I, Penington DJ et al (2006) Phosphorylation of ErbB4 on tyrosine 1056 is critical for ErbB4 coupling to inhibition of colony formation by human mammary cell lines. Oncol Res 16:179–193
Naresh A, Long W, Vidal GA et al (2006) The ERBB4/HER4 intracellular domain 4ICD is a BH3-only protein promoting apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:6412–6420
Zhu Y, Sullivan LL, Nair SS et al (2006) Coregulation of estrogen receptor by ERBB4/HER4 establishes a growth-promoting autocrine signal in breast tumor cells. Cancer Res 66:7991–7998
Määttä JA, Sundvall M, Junttila TT et al (2006) Proteolytic cleavage and phosphorylation of a tumor-associated ErbB4 isoform promote ligand-independent survival and cancer cell growth. Mol Biol Cell 17:67–79
Junttila TT, Sundvall M, Lundin M et al (2005) Cleavable ErbB4 isoform in estrogen receptor-regulated growth of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 65:1384–1393
Suo Z, Risberg B, Kalsson MG et al (2002) EGFR family expression in breast carcinomas. c-erbB-2 and c-erbB-4 receptors have different effects on survival. J Pathol 196:17–25
Abd El-Rehim DM, Pinder SE, Paish CE et al (2004) Expression and co-expression of the members of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family in invasive breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer 91:1532–1542
Larsen SS, Madsen MW, Jensen BL et al (1999) Acquired antiestrogen resistance in MCF-7 human breast cancer sublines is not accomplished by altered expression of receptors in the ErbB-family. Breast Cancer Res Treat 58:41–56
Agus DB, Akita RW, Fox WD (2002) Targeting ligand-activated ErbB2 signaling inhibits breast and prostate tumor growth. Cancer Cell 2:127–137
Wu G, Xing M, Mambo E et al (2005) Somatic mutation and gain of copy number of PIK3CA in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 7:R609–R616
Jordan NJ, Gee JM, Barrow D et al (2004) Increased constitutive activity of PKB/Akt in tamoxifen resistant breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 87:167–180
Hutcheson IR, Knowlden JM, Madden TA et al (2003) Oestrogen receptor-mediated modulation of the EGFR/MAPK pathway in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 81:81–93
Kirkegaard T, Witton CJ, McGlynn LM (2005) AKT activation predicts outcome in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. J Pathol 207:139–146
Gee JM, Robertson JF, Ellis IO et al (2001) Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase is associated with poor response to anti-hormonal therapy and decreased patient survival in clinical breast cancer. Int J Cancer 95:247–254
Acknowledgements
We thank Inger Heiberg, Ole Nielsen, Hanife Dzaferi and Dorrit Lützhøft for excellent technical assistance. Also, thanks to Prof. William Gullick for the antibodies to hrg2α and hrg2β. We appreciate the financial support from; Danish Cancer Society, The Danish Medical Research Council, The Danish Cancer Research Foundation, Købmand Bernhard Rasmussen og hustru Meta Rasmussens Mindelegat, Else og Aage Grønbeck-Olsens Legat, Grosserer A.V. Lykfeldt og hustrus Legat, Fru Astrid Thaysens Legat for Lægevidenskabelig Grundforskning.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frogne, T., Benjaminsen, R.V., Sonne-Hansen, K. et al. Activation of ErbB3, EGFR and Erk is essential for growth of human breast cancer cell lines with acquired resistance to fulvestrant. Breast Cancer Res Treat 114, 263–275 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-0011-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-0011-8