Abstract
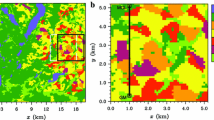
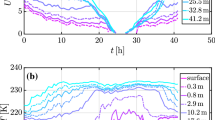
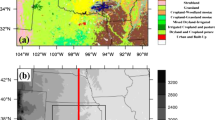
Land-surface heterogeneity effects on the subgrid scale of regional climate and numerical weather prediction models are of vital interest for the energy and mass exchange between the surface and the atmospheric boundary layer. High-resolution numerical model simulations can be used to quantify these effects, and are a tool used to obtain area-averaged surface fluxes over heterogeneous land surfaces. We present high-resolution model simulations for the LITFASS area near Berlin during the LITFASS-2003 experiment, which were carried out using the non-hydrostatic model FOOT3DK of the University of Köln with horizontal resolutions of 1 km and 250 m. The LITFASS-2003 experimental dataset is used for comparison. The screen level quantities show good quality for the simulated pressure, temperature, humidity and wind speed and direction. Averaged over the four week experimental period, simulated surface energy fluxes at land stations show a small bias for the turbulent heat fluxes and an underestimation of the net radiation caused by excessive cloudiness in the simulations. For eight selected days with low cloud amounts, the net radiation bias is close to zero, but the sensible heat flux shows a strong positive bias. Large differences are found for latent heat fluxes over a lake, which are partly due to local effects on the measurements, but an additional problem seems to be the overestimation of the turbulent exchange under stable conditions in the daytime internal boundary layer over the lake. In the area average over the LITFASS area of 20 × 20 km2, again a strong positive bias of 70 W m−2 for the sensible heat is present. For the low soil moisture conditions during June 2003, the simulation of the turbulent heat fluxes is sensitive to variations in the soil type and its hydrological properties. Under these conditions, the supply of ground water to the lowest soil layer should be accounted for. Different area-averaging methods are tested. The experimental set-up of the LITFASS-2003 experiment is found to be well suited for the computation of area-averaged turbulent heat fluxes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ament F, Simmer C (2006) Improved representation of land-surface heterogeneity in a non-hydrostatic numerical weather prediction model. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 121:xx–xx
Bange J, Spieß T, Herold M, Beyrich F, Hennemuth B (2006) Turbulent fluxes from helipod flights above quasi-homogeneous patches within the LITFASS Area. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 121: xx–xx
Beyrich F, Herzog H-J, Neisser J (2002) The LITFASS project of DWD and the LITFASS-98 experiment: the project strategy and the experimental setup. Theor Appl Climatol 73:3–18
Beyrich F, Adam WK, Bange J, Behrens K, Berger FH, Bernhofer C, Bösenberg J, Dier H, Foken T, Gödecke M, Görsdorf U, Güldner J, Hennemuth B, Heret C, Huneke S, Kohsiek W, Lammert A, Lehmann V, Leiterer U, Leps J-P, Liebethal C, Lohse H, Lüdi A, Mauder M, Meijinger WML, Mengelkamp H-T, Queck R, Richter SH, Spieß T, Stiller B, Tittebrand A, Weisensee U, Zittel P (2004) Verdunstung über einer heterogenen Landoberfläche – Das LITFASS-2003 Experiment. Arbeitsergebnisse Nr. 79, Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach, Deutschland, ISSN 1430–0281
Beyrich F, Leps J-P, Mauder M, Bange J, Foken T, Huneke S, Lohse H, Lüdi A, Meijninger WML, Mironov D, Weisensee U, Zittel P (2006) Area-averaged surface fluxes over the LITFASS region from eddy-covariance measurements. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 121:xx–xx
Brücher W, Kerschgens M, Martens R, Thielen H, Maßmeyer K (1998) Tracer experiments in the Freiburg-Schauinsland area – comparison with flow and dispersion models. Meteorol Zeitschrift NF 7:32–35
Charnock H (1955) Wind stress on a water surface. Quart J Roy Meteorol Soc 81:639–640
Clapp RB, Hornberger GM (1978) Empirical equations for some soil hydraulic properties. Water Resour Res 14:601–604
Clark, TL (1991) Lateral and upper boundary conditions. In: ECMWF seminar proceedings, numerical methods in atmospheric models, vol II, Reading, pp 43–71
Davies HC (1976) A lateral boundary formulation for multilevel prediction models. Quart J Roy Meteorol Soc 103:255–268
Deardorff JW (1977) A parameterization of ground-surface moisture content for use in atmosphere prediction models. J Appl Meteorol 16:1182–1185
DWD (Deutscher Wetterdienst) – Meteorologisches Observatorium Lindenberg (2003) Kartierung der Landnutzung im LITFASS-Gebiet während LITFASS-2003. Unpublished, based on the land use data of Luftbild Brandenburg GmbH (1994)
Giorgi F, Avissar R (1997) Representation of heterogeneity effects in earth system modeling: experience from land surface modeling. Rev Geophys 35:413–438
Heinemann G (2003) Forcing and feedback mechanisms between the katabatic wind and sea ice in the coastal areas of polar ice sheets. Global Atmos-Ocean Syst 9:169–201
Heinemann G (2006) On the consideration of mesoscale transports in climate modelling. Theor Appl Climatol 83:35–50. DOI 10.1007/s00704-005-0159-7
Heinemann G, Kerschgens M (2005) Comparison of methods for area-averaging surface energy fluxes over heterogeneous land surfaces using high-resolution non-hydrostatic simulations. Int J Climatol 25:379–403. DOI 10.1002/joc1123
Hense A, Kerschgens M, Raschke E (1982) An economical method for computing the radiative energy transfer in circulation models. Quart J Roy Meteorol Soc 108:231–252
Hübener H, Schmidt M, Sogalla M, Kerschgens M (2005) Simulating evapotranspiration in a semi-arid environment. Theor Appl Climatol 80:153–167. DOI 10.1007/s00704-004-0097-9
Jacobsen I, Heise E (1982) A new economic method for the computation of the surface temperature in numerical models. Contrib Atmos Phys 55:128–141
LGB (Landesvermessungsamt Brandenburg) (1996) Digitales Geländemodell DGM 25. http://www.geobasis-bb.de. Cited 6 June 2006
Louis J-F (1979) A parametric model of vertical eddy fluxes in the atmosphere. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 17:187–202
Luftbild Brandenburg GmbH (1994) Biotoptypen- und Landnutzungskartierung Brandenburg aus CIR-Luftbildern. Karl-Liebknecht-Str. 1, 15711 Königs Wusterhausen, Germany
Mahrt L (1996) The bulk aerodynamical formulation over heterogeneous surfaces. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 78:87–119
Maurer B, Heinemann G (2006) Validation of the ‘Lokalmodell’ over heterogeneous land surfaces using aircraft-based measurements of the REEEFA experiment. Meteorol Atmos Phys 91:107–128. DOI 10.1007/s00703-004-0105-8
Meijninger WML, Beyrich F, Lüdi A, Kohsiek W, de Bruin HAR (2006) Scintillometer fluxes of sensible and latent heat over a heterogeneous land surface – a contribution to LITFASS-2003. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 121:xx–xx
Mellor GL, Yamada T (1982) Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev Geophys Space Phys 20:851–875
Mengelkamp H-T, Beyrich F, Heinemann G, Ament F, Bange J, Berger F, Bösenberg J, Foken T, Hennemuth B, Heret C, Huneke S, Johnsen K-P, Kerschgens M, Kohsiek W, Leps J-P, Liebethal C, Lohse H, Mauder M, Meijninger W, Raasch S, Simmer C, Spieß T, Tittebrand A, Uhlenbrock J, Zittel P (2006) Evaporation over a heterogeneous land surface: The EVA_GRIPS project. Bull Amer Meteorol Soc 87:775–786
Noilhan J, Planton S (1989) A simple parameterisation of land surface processes for meteorological models. Mon Wea Rev 117:536–549
Schlünzen KH, Katzfey JJ (2003) Relevance of sub-grid-scale land-use effects for mesoscale models. Tellus 55A:232–246
Shao Y, Sogalla M, Kerschgens MJ, Brücher W (2001) Treatment of land surface heterogeneity in a meso-scale atmospheric model. Meteorol Atmos Phys 78:157–181
SBA (Statistisches Bundesamt) (1997) Daten zur Bodenbedeckung für die Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Federal Statistical Office, Wiesbaden, Germany, CDROM
Uhlenbrock J, Raasch S, Hennemuth B, Zittel P, Meijinger WML (2004) Effects of land surface heterogeneities on the boundary structure and turbulence during LITFASS-2003: large-eddy simulations in comparison with turbulence measurements. In: Proceedings 16th symposium on boundary layers and turbulence, American Meteorological Society, Portland/Maine, USA, 9–13 August 2004, Paper 9.3. http://ams.confex.com/ams/BLTAIRSE/techprogram/paper_78249.htm. Cited 6 June 2006
USGS (1997) GTOPO30 Digital elevation model. EROS Data Center, US Geological Survey, Sioux Falls, SD. http://edcdaac.usgs.gov/gtopo30/gtopo30.asp. Cited 6 June 2006
Weaver CP, Avissar R (2001) Atmospheric disturbances caused by human modification of the landscape. Bull Amen Meteorol Soc 82:269–281
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinemann, G., Kerschgens, M. Simulation of surface energy fluxes using high-resolution non-hydrostatic simulations and comparisons with measurements for the LITFASS-2003 experiment. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 121, 195–220 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-006-9107-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-006-9107-z