Abstract
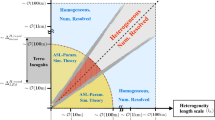
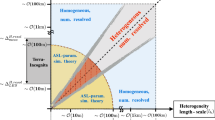
This interpretative literature survey examines problems with application of the bulk aerodynamic method to spatially averaged fluxes over heterogeneous surfaces. This task is approached by tying together concepts from a diverse range of recent studies on subgrid parameterization, the roughness sublayer, the roll of large “inactive” boundary-layer eddies, internal boundary-layer growth, the equilibrium sublayer, footprint theory and the blending height. Although these concepts are not completely compatible, qualitative scaling arguments based on these concepts lead to a tentative unified picture of the qualitative influence of surface heterogeneity for a wide spectrum of spatial scales.
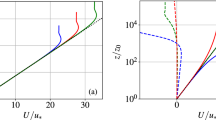
Generalization of the velocity scale is considered to account for nonvanishing heat and moisture fluxes in the limit of vanishing time-averaged wind speed and to account for the influence of subgrid mesoscale motions on the grid-averaged turbulent flux. The bulk aerodynamic relationship for the heat flux usually employs the surface radiation temperature or, equivalently, the temperature from the modelled surface energy budget. The corresponding thermal roughness length is quite variable and its dependence on available parameters is predictable only in special cases.
An effective transfer coefficient to relate the spatially averaged surface fluxes to spatially averaged air-ground differences of temperature and other scalars can be most clearly defined when the blending height occurs below the reference level (observational level or first model level). This condition is satisfied only for surface heterogeneity occurring over horizontal scales up to a few times the boundary-layer depth, depending on the stability and height of the reference level. For surface heterogeneity on larger scales (small mesoscale), an effective transfer coefficient for the spatially averaged flow must be defined, for which predictive schemes are unavailable. For surface variations on large mesoscales, homogeneous subareas may be maintained where traditional similarity theory is locally applicable. Surface variations on these scales may generate thermally-driven mesoscale motions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
André, J. C. and collaborators: 1988, ‘Evaporation over Land-surfaces, First Results from HAPEX-MOBIHLY Special Observing Period’, Ann. Geophys. B 6, 477–492.
Andreas, E. L.: 1987, ‘A Theory for the Scalar Roughness and the Scalar Transfer Coefficients over Snow and Sea Ice’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 38, 159–184.
Avissar, R. and Pielke, R. A.: 1989, ‘A Parameterization of Heterogeneous Land Surfaces for Atmospheric Numerical Models and its Impact on Regional Meteorology’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 117, 2113–2136.
Avissar, R. and Chen, F.: 1993, ‘Development and Analysis of Prognostic Equations for Mesoscale Kinetic Energy and Mesoscale (Subgrid-Scale) Fluxes for Large-Scale Atmospheric Models’, J. Atmos. Sci. 50, 3751–3774.
Bache, D. H. and Unsworth, M. H.: 1977, ‘Some Aerodynamic Features of a Cotton Canopy’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 103, 121–134.
Baldocchi, D. D. and Meyers, T. P.: 1988, ‘A Spectral and Lag-Correlation Analysis of Turbulence in a Deciduous Forest Canopy’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 45, 31–58.
Beljaars, A. C.: 1995, ‘The Parametrization of Surface Fluxes in Large Scale Models Under Free Convection’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 121, 255–270.
Beljaars, A. C. and Holtslag, A. A. M.: 1991, ‘Flux Parameterization Over Land Surfaces for Atmospheric Models’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 30, 327–341.
Beljaars, A. C. M. and Viterbo, P.: 1994, ‘The Sensitivity of Winter Evaporation to the Formulation of Aerodynamic Resistance in the ECMWF Model’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 71, 135–149.
Blyth, E. M.: 1995, ‘Using a simple SVAT scheme to describe the effect of scale on aggregation’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 72, 267–285.
Blyth, E. M., Dolman, A. J., and Wood, N.: 1993, ‘Effective Resistance to Sensible and Latent-Heat Flux in Heterogeneous Terrain’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 119, 423–442.
Brutsaert, W. H.: 1979, ‘Heat and Mass Transfer to and from Surfaces With Dense Vegetation or Similar Permeable Roughness’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 16, 365–388.
Brutsaert, W. H.: 1982, Evaporation into the Atmosphere-Theory, History, and Applications. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht, 299 pp.
Brutsaert, W. H. and Kustas, W.: 1985, ‘Evaporation of Humidity Profiles in Neutral Conditions Over Rugged Hilly Terrain’, J. Climate and Appl. Meteorol. 24, 915–923.
Brutsaert, W. H. and Sugita, M.: 1990, ‘The Extent of the Unstable Monin-Obukhov Layer for Temperature and Humidity Above Complex Grassland’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 51, 383–400.
Businger, J. A.: 1973, ‘A Note on Free Convection’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 4, 322–326.
Businger, J. A., 1982: ‘The Fluxes of Specific Enthalpy, Sensible Heat and Latent Heat Near the Earth's Surface’, J. Atmos. Soc. 39, 1889–1892.
Claussen, M.: 1989, ‘Subgrid-Scale Fluxes and Flux Divergence in a Neutrally Stratified, Horizontally Inhomogeneous Surface-Layer’, Beitr. Phys. Atmosph. 62, 235–246.
Claussen, M.: 1990, ‘Area-Averaging of Surface Fluxes in a Neutrally Stratified, Horizontally Inhomogeneous Atmospheric Boundary Layer’, Atmospheric Environment 24a, 1349–1360.
Claussen, M.: 1991, ‘Estimation of Areally-Averaged Surface Fluxes’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 54, 387–410.
Claussen, M. and Klaassen, K.: 1992, ‘On Regional Surface Fluxes over Partly Forested Areas’, Beitr. Phys. Atmosph. 65, 243–248.
Claussen, M.: 1995, ‘Flux Aggregation at Large Scales: on the Limits of Validity of the Concept of Blending Height’, J. Hydrol. 166, 371–382.
de Bruin, H. A. R., Bink, N. J., and Kroon, L. J. M.: 1991, ‘Fluxes in the Surface Layer under Advective Conditions’, in T. J. Schmugge and J-C André (eds.), Land Surface Evaporation; Measurement and Parameterization. Springer Verlag, New York, pp. 157–170.
Dolman, A. J.: 1992, ‘A Note on Areally-Averaged Evaporation and the Value of the Effective Surface Conductance’, J. Hydrol. 138, 583–589.
Doran, J. C., Shaw, W. J., and Hubbe, J. M.: 1995, ‘Boundary Layer Characteristics Over Areas of Inhomogeneous Surface Fluxes’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 34, 559–571.
Ducoudré, N. I., Laval, K., and Perrier, A.: 1993, ‘SECHIBA, a New Set of Parameterizations of the Hydrologic Exchanges at the Land/Atmosphere Interface within the LMD Atmospheric General Circulation Model’, J. Climate 6, 248–273.
Duynkerke, P.G.: 1991, ‘The Roughness Length for Heat and Other Vegetation Parameters for a Surface of Short Grass’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 31, 579–586.
Dyer, A. J.: 1963, ‘The Adjustment of Profiles and Eddy FLuxes’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 89, 276–280.
Emanuel, K. A.: 1983, ‘On the Dynamical Definition(s) of “Mesoscale”’, in D. K. Lilly and T. Gal-Chen (eds.), Mesoscale Meteorology — Theories, Observations and Models. Reidel, pp. 1–12.
Engman, E. T. and Gurney, R. J.: 1991, Remote Sensing in Hydrology, Chapman and Hall, New York, 225 pp.
Esbensen, S. K. and Reynolds, R. W.: 1981, ‘Estimating Monthly Averaged Air-Sea Transfers of Heat and Momentum Using the Bulk Aerodynamic Method’, J. Phys. Ocean. 11, 457–465.
Etling, D. and Brown, R. A.: 1993, ‘Roll Vortices in the Planetary Boundary- Layer: A Review’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 65, 215–248.
Garratt, J.R. 1978: ‘Transfer Characteristics for a Heterogeneous Surface of Large Aerodynamic Roughness’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 104, 491–502.
Garratt, J. R.: 1980, ‘Surface Influence Upon Vertical Profiles in the Atmospheric Near-Surface Layer’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 106, 803–819.
Garratt, J. R.: 1990, ‘The Internal Boundary Layer — A Review’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 50, 171–203.
Garratt, J. R.: 1992a, The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Cambridge University Press, 316 pp.
Garratt, J. R.: 1992b, ‘Extreme Maximum Land Surface Temperatures’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 31, 1096–1105.
Garratt, J. R. and Hicks, B. B.: 1973, ‘Momentum, Heat and Water Vapour Transfer to and from Natural and Artificial Surfaces’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 99, 680–687.
Garratt, J. R. and Francey, R. J.: 1978, ‘Bulk Characteristics of Heat Transfer in the Unstable, Baroclinic Atmospheric Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 15, 399–421.
Garratt, J. R., Pielke, R. A., Miller, W. F., and Lee, T. J.: 1990, ‘Mesoscale Model Response To Random, Surface-Based Perturbations — A Sea-Breeze Experiment’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 52, 313–334.
Garratt, J.R., Hicks, B. B., and Valigura, R. A.: 1993, ‘Comments on “The Roughness Length for Heat and other Vegetation Parameters for a Surface of Short Grass”’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 32, 1301–1303.
Gash, J. H. C.: 1986, ‘A Note on Estimating the Effect of Limited Fetch on Micrometeorological Evaporation Measurements’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 35, 409–413.
Godfrey, J. S. and A. C. M. Beljaars: 1991, ‘On the Turbulent Fluxes of Buoyancy, Heat and Moisture at the Air-Sea Interface at Low Wind Speeds’, J. Geophy. Res. 96, 22,043–22,048.
Goutorbe, J. P.: 1991, ‘A Critical Assessment of the Samer Network Accuracy’, Land Surface Evaporation; Measurement and Parameterization. T. J. Schmugge and J.C. André, Eds, Springer Verlag, New York, 171–182.
Hadfield, M. G., Cotton, W. R., and Pielke, R. A.: 1992, ‘Large-Eddy Simulations of Thermally Forced Circulations in the Convective Boundary Layer, Part II: The Effect of Changes in Wavelength and Wind Speed’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 58, 307–327.
Hall, F. G., Huemmrich, K. F., Goetz, S. J., Sellers, P. J., and Nickeson, J. E.: 1992, ‘Satellite Remote Sensing of Surface Energy Balance:Success, Failures, and Unresolved Issues in FIFE’, J. Geophys. Res. 97, 19,061–19,089.
Hatfield, J. L., Reginato, R. L., and Idso, S. B.: 1984, ‘Evaluation of Canopy Temperature-Evapotranspiration Models Over Various Crops’, Agric. For. Meteorol. 32, 41–53.
Hauf, T. and Clark, T. L.: 1989, ‘Three-Dimensional Numerical Experiments on Convectively Forced Internal Waves’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 115, 309–333.
Hignett, P.: 1994, ‘Roughness Lengths for Temperature and Momentum over Heterogeneous Terrain’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 68, 225–236.
Højstrup, J.: 1982, ‘Velocity Spectra in the Unstable Planetary Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Soc. 39, 2239–2248.
Högström, U.: 1990, ‘Analysis of Turbulence Structure in the Surface Layer with a Modified Similarity Formulation for Near Neutral Conditions’, J. Atmos. Sci. 47, 1949–1972.
Holtslag, A. A. M. and Ek, M.: 1995, ‘Simulation of Surface Fluxes and Boundary Layer Development over the Pine Forest in HAPEX-MOBILHY’, submitted to J. Appl. Meteorol.
Horst, T. W. and Weil, J. C.: 1992, ‘Footprint Estimation for Scalar Flux Measurements in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 52, 279–296.
Horst, T. W. and Weil, J. C.: 1994, ‘How Far is Far Enough?: The Fetch Requirements for Micrometeorological Measurement of Surface Fluxes’, J. Atmos. Oceanic Tech. 11, 1018–1025.
Huang, X. and Lyons, T. J.: 1995, ‘The Simulation of Surface Heat Fluxes in a Land Surface-Atmosphere Model’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 34, 1099–1111.
Jensen, N. O.: 1978, ‘Change of Surface Roughness and the Planetary Boundary Layer’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 104, 351–356.
Klaassen, W. and Claussen, M.: 1995, ‘Landscape Variability and Surface Flux Parameterization in Climate Models’, Ag. and For. Meteorol. 73, 181–188.
Kohsiek, W, de Bruin, H. A. R., The, H., and van de Hurk, B.: 1993, ‘Estimation of the Sensible Heat Flux of a Semi-Arid Area Using Surface Radiative Temperature Measurements’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 63, 213–230.
Koster, R. D., and Suarez, M. J.: 1992, ‘Modelling the Land Surface Boundary in Climate Models as a Composite of Independent Vegetation Stands’, J. Geophys. Res. 97, 2697–2715.
Kristensen, L., Jensen, N. O., and Peterson, E.L.: 1982, ‘Lateral Dispersion of Pollutants in a Very Stable Atmosphere; The Effect of the Meandering’, Atmos. Environ. 15, 837–844.
Kubota, A. and Sugita, M.: 1994, ‘Radiometrically Determined Skin Temperature and Scalar Roughness to Estimate Surface Heat Flux. Part I: Parameterization of Radiometric Scalar Roughness’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 69, 397–416.
Kustas, W. P., Choudhury, B. J., Moran, M. S., Reginato, R.D. Jackson, R.J.,Gay, L.W., and Weaver, H.L.: 1989, ‘Determination of Sensible Heat FluxOver Sparse Canopy Using Thermal Infrared Data’, Agric. For. Meteorol. 44, 197–216.
Kustas, W. P., Choudhury, B. J., Inoue, Y., Pinter, P. J., Moran, M. S., Jackson, R. D., and Reginato, R. J.: 1990a, ‘Ground and Aircraft Infrared Observations Over a Partially-Vegetated Area’, Int. J. Remote Sensing 11, 409–427.
Kustas, W. P., Choudhury, B. J., Inoue, Y., Pinter, P. J., Moran, M. S., Jackson, R. D., and Reginato, R. J.: 1990b, ‘Instantaneous and Daily Values of the Surface Energy Balance over Agricultural Fields using Remote Sensing and a Reference Field in an Arid Environment’, Remote Sens. Environ. 32, 125–141.
Lange, A. R. G., McNaughton, K. G., Chen, F., Bradley, E. F., and Ohtaki, E.: 1983, ‘Inequality of Eddy Transfer Coefficients for Vertical Transport of Sensible and Latent Heats During Advective Inversions’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 25, 25–41.
Leclerc, M. Y. and Thurtell, G. W.: 1990, ‘Footprint Prediction of Scalar Fluxes Using a Markovian Analysis’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 52, 247–258.
Lee, X. and Black, T. A.: 1993, ‘Atmospheric Turbulence within and Above a Douglas-Fir Stand. Part II: Eddy Fluxes of Sensible Heat and Water Vapour’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 64, 369–390.
LeMone, M. A.: 1973, ‘The Structure and Dynamics of Horizontal Roll Vortices in the Planetary Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Soc. 33, 1308–1320.
Lenschow, D. H.: 1995 ‘Micrometeorological Techniques for Measuring Biosphere-Atmosphere Trace Gas Exchange’, in P. A. Matson and R. C. Harriss (eds.), BiogenicTrace Gases; Measuring Emissions from Soil and Water., Blackwell Science, pp. 126–163.
Lenschow, D. H. and Stephens, P. L.: 1980, ‘The Role of Thermals in the Convective Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 19, 509–532.
Lettau, H. H.: 1979, ‘Wind and Temperature Profile Prediction for Diabatic Surface Layers Including Strong Inversion Cases’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 17, 443–464.
Lhomme, J.-P., Chehbouni, A., and Monteny, B.: 1994, ‘Effective Parameters of Surface Energy Balance in Heterogeneous Landscape’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 71, 297–309.
Lilly, D. K.: 1983a, ‘Stratified Turbulence and the Mesoscale Variability of the Atmosphere’, J. Atmos. Soc. 40, 749–761.
Lilly, D. K.: 1983b, ‘Mesoscale Variability of the Atmosphere’, in D. K. Lilly and T. Gal-Chen (eds.), Mesoscale Meteorology — Theories, Observations and Models, Reidel, Dordrecht, pp. 13–24.
Liu, W. T., Katsaros, K. B., Businger, J. A., and Tillman, J.E.: 1979, ‘Heat Transport and Thermal Structure in the Interfacial Boundary Layer Measured in an Open Tack of Water in Turbulent Free Convection’, J. Atmos. Sci. 36, 1722–1735.
Louis, J.-F.: 1979, ‘A Parametric Model of Vertical Eddy Fluxes in the Atmosphere’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 17, 187–202.
Malhi, Y.: 1995, ‘The Behavior of the Roughness Length for Temperature Over Heterogeneous Surfaces’, To appear Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc.
Mahrt, L.: 1987, ‘Grid-averaged Surface Fluxes’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 115, 1550–1560.
Mahrt, L., Desjardins, R. L., and Macpherson, J. I.: 1994a, ‘Observations of Fluxes over Heterogeneous Surfaces’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 67, 345–367.
Mahrt, L., Sun, J., Vickers, D., MacPherson, J. I., Pederson, J. R., and Desjardins, R. L.: 1994b, ‘Observations of Fluxes and Inland Breezes Over a Heterogeneous Surface’, J. Atmos. Soc. 51, 2484–2499.
Mahrt, L. and Howell, J. F.: 1994, ‘The Influence of Coherent Structures and Microfronts on Scaling Laws Using Global and Local Transforms’, J. Fluid Mech. 260, 247–270.
Mahrt, L. and Sun, J.: 1995a, ‘Multiple Velocity Scales in the Bulk Aerodynamic Relationship for Spatially Averaged Fluxes’, Month. Wea. Rev. 123, 3032–3041.
Mahrt, L. and Sun, J.: 1995b, ‘Dependence of Exchange Coefficients on Averaging Scale or Grid Size’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. in press.
Mann, J. and Lenschow, D. H.: 1994, ‘Errors in Airborne Flux Measurements’, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 14,519–14,526.
Manqian, M. and Jinjun, J.: 1993, ‘A Coupled Model on Land-Atmosphere Interactions — Simulating the Characteristics of the PBL over a Heterogeneous Surface’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 66, 247–264.
Mason, P. J.: 1988, ‘The Formation of Areally Averaged Roughness Lengths’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 114, 399–420.
Matthias, A. D., Yates, S. R., Zhang, R., and Warrick, A. W.: 1987, ‘Radiant Temperatures of Sparse Plant Canopies and the Soil Using IR Thermometry’, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing GE-25, 516–519.
Miller, M. J., Beljaars, A. C. M., and Palmer, T. N.: 1992, ‘The Sensitivity of the ECMWF Model to the Parameterization of Evaporation from the Tropical Oceans’, J. Climate 5, 418–434.
Miyake, M., Stewart, R. W., and Burling, R. W.: 1970, ‘Spectra and Cospectra of Turbulence Over Water’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 75, 138–143.
Monteith, J. L. and Unsworth, M. H.: 1990, Principles of Environmental Physics, Second edition, Edward Arnold, London, 291 pp.
Mourad, P. D. and Brown, R. A.: 1990, ‘Multiscale Large Eddy States in Weakly Stratified Planetary Boundary Layers’, J. Atmos. Soc. 47, 414–438.
Mulhearn, P. J. and Finnigan, J. J.: 1978, ‘Turbulent Flow Over a Very Rough, Random Surface’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 15, 109–132.
Norman, J. M., Kustas, W. P., and Humes, K. S.: 1995, ‘A Two-source Approach for Estimating Soil and Vegetation Energy Fluxes from Observations of Directional Radiometric Surface Temperature’, Agri. For. Meteorol., in press.
Oke, T. R.: 1988, ‘The Urban Energy Balance’, Prog. Phys. Geogr. 12, 471–508.
Otterman, J., Brakke, T. W., and Susskand, J.: 1992, ‘A Model for Inferring Canopy and Underlying Soil Temperatures from Multi-Directional Measurements’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 61, 81–98.
Owen, P. R. and Thomson, W. R.: 1963, ‘Heat Transfer Across Rough Surfaces’, J. Fluid Mech. 15, 321–324.
Parlange, M. and Brutsaert, W.: 1993, ‘Regional Shear Stress of Broken Forest from Radiosonde Wind Profiles in the Unstable Surface Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 64, 355–368.
Pasquill, F.: 1972, ‘Some Aspects of Boundary Layer Description’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 98, 469–494.
Penman, H. L.: 1948, ‘Natural Evaporation from Open Water, Bare Soil, and Grass’, Proc. Roy. Soc. London A193, 120–195.
Qualls, R. J. and Brutsaert, W.: 1995, ‘The Effect of Vegetation Density on the Parameterization of Scalar Roughness to Estimate Spatially Distributed Sensible Heat Fluxes’, Submitted to J. Hydrol. Res.
Raupach, M. R.: 1993, ‘The Averaging of Surface Flux Densities in Heterogeneous Landscapes’, in H.-J. Bolle, R. A. Feddes, and J. D. Kalma (eds.), Exchange Processes at the Land Surface for a Range of Space and Time Scales, IAHS publication no. 212, pp. 343–356.
Raupach, M. R.: 1994, ‘Simplified Expressions for Vegetation Roughness Length and Zero-Plane Displacement as Functions of Canopy Height and Area Index’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 71, 211–216.
Raupach, M. R. and Thom, A. S.: 1981, ‘Turbulence in and Above Plant Canopies’, Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 13, 97–129.
Raupach, M. R., Antonia, R. A., and Rajagopalan, S.: 1991, ‘Rough-Wall Turbulent Boundary Layers’, Appl. Mechs. Revs. 44, 1–25.
Rotach, M. W.: 1993, ‘Turbulence Close to a Rough Urban Surface Part I: Reynolds Stress’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 65, 1–28.
Roth, M.: 1993, ‘Turbulent Transfer Relationships Over an Urban Surface. II: Integral Statistics’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 119, 1105–1120.
Roth, M. and Oke, T. R.: 1993, ‘Turbulent Transfer Relationships Over an Urban Surface. Part I: Spectral Characteristics’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 119, 1071–1104.
Roth, M. and Oke, T. R.: 1995, ‘Relative Efficiencies of Turbulent Transfer of Heat, Mass and Momentum over a Patchy Urban Surface’, J. Atmos. Soc.
Schmid, H. P.: 1994, ‘Source Areas for Scalars and Scalar Fluxes’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 67, 293–318.
Schmid, H. P. and Oke, T. R.: 1990, ‘A Model to Estimate the Ssource Area Contributing to Turbulent Exchange in the Surface Layer over Patchy Terrain’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 116, 965–988.
Schmid, H. P. and Bünzli, D.: 1995a, ‘The Influence of Surface Texture on the Effective Roughness Length’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 121, 1–21.
Schmid, H. P. and Bünzli, D.: 1995b, ‘Reply to Comments by E. M. Blyth on ‘The Influence of Surface Texture on the Effective Roughness Length’’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 121, to appear.
Schmidt, W.: 1921, ‘Wird die Luft durch Konvektion von der Erdoberfläche her erwärmt?’, Meterol. Zeitschr. 38, 262.
Schuepp, P. H., MacPherson, J.I., and Desjardins, R.L.: 1992, ‘Adjustment of Footprint Correction for Airborne Flux Mapping Over the FIFE Site’, J. Geophy. Res. 97, 18,455–18,466
Schumann, U.: 1988, ‘Minimum Friction Velocity and Heat Transfer in the Rough Surface Layer of a Convective Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 44, 311–326.
Segal, M., Schreiber, W.E., Kallos, G., Garrat, J. R., Rodi, A., Weaver, J., and Pielke, R. A.: 1989, ‘The Impact of Crop Areas in Northeast Colorado on Midsummer Mesoscale Thermal Circulations’ Mon. Wea. Rev. 117, 809–825.
Segal, M. and Arritt, R. W.: 1992, ‘Non-Classical Mesoscale Circulations Caused by Surface Sensible Heat Flux Gradients’, Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 73, 1593–1604.
Shuttleworth, W. J.: 1988, ‘Macrohydrology — the New Challenge for Process Hydrology’, J. Hydrol. 100, 31–56.
Smith, E. A., Hsu, A. Y., Crosson, W. L., Field, R. T., Fritschen, L. J., Gurney, R. J., Kanemasu, E. T., Kustas, W. P., Nie, D., Shuttleworth, W. J., Stewart, J. B., Verma, S. B., Weaver, H. L., and Wesely, M. L.: 1992, ‘Area-Averaged Surface Fluxes and their Time-Space Variability Over the FIFE Experimental Domain’, J. Geophys. Res. 97, 18,599–18,622.
Stewart, J. B., Kustas, W. P., Humes, K. S., Nichols, W. D., Moran, M. S., and de Bruin, H. A. R.: 1994, ‘Sensible Heat Flux-Radiometric Surface Temperature Relationship for Eight Semiarid Areas’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 33, 1110–1117.
Stull, R. B.: 1994, ‘A Convective Transport Theory for Surface Fluxes’, J. Atmos. Sci. 51, 3–22.
Sugita, M. and Brutsaert, W.: 1990, ‘Regional Surface Fluxes from Remotely Sensed Skin Temperature and Lower Boundary Layer Measurements’, Water Resources. Res. 26, 2937–2944.
Sun, J. and Mahrt, L., 1994: ‘Spatial Distribution of Surface Fluxes Estimated from Remotely Sensed Variables’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 33, 1341–1353.
Sun, J. and Mahrt, L.: 1995a, ‘Determination of Surface Fluxes from the Surface Radiative Temperature’, J. Atmos. Sci. 52, 1096–1106.
Sun, J. and Mahrt, L.: 1995b, ‘Relationship of the Heat Flux to Microscale Temperature Variations: Application to BOREAS’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol., in press.
Sun, J., Esbensen, S. K., and Mahrt, L.: 1995, ‘Estimation of Surface Heat Flux’, J. Atmos. Sci. 17, 3162–3171.
Taylor, P. A.: 1987, ‘Comments and Further Analysis on Effective Roughness Lengths for use in Numerical Three-Dimensional Models’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 39, 403–418.
Taylor, P. A., Sykes, R. I. and Mason, P. J.: 1989, ‘On the Parameterization of Drag over Smallscale Topography in Neutrally-Stratified Boundary-Layer Flow’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 48, 409–422.
Thom, A.S.: 1971, ‘Momentum Absorption by Vegetation’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 97, 414–428.
Thom, A.S.: 1972, ‘Momentum, Mass and Heat Exchange of Vegetation’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 98, 124–134.
Townsend, A. A.: 1976, The Structure of Turbulent Shear Flow, Cambridge University Press, 429 pp.
van Ulden, A. P.: 1978, ‘Simple Estimates for Vertical Diffusion from Sources Near the Ground’, Atm. Environ. 12, 2125–2129.
Wetzel, P. J. and Chang, J.T.: 1988, ‘Evapotranspiration from Non-Uniform Surfaces: A First Approach for Short-Term Numerical Weather Prediction’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 116, 600–621.
Wieringa, J., 1986: ‘Roughness-Dependent Geographical Interpolation of Surface Wind Speed Averages’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 112, 867–889.
Wieringa, J.: 1993, ‘Representative Roughness Parameters for Homogeneous Terrain’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 63, 323–364.
Wilczak, J. M. and Tillman, J. E.: 1980, ‘The Three-Dimensional Structure of Convection in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 2424–2443.
Williams, A. G.and Hacker, J. M.: 1993, ‘Interactions between Coherent Eddies in the Lower Convective Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 64, 55–74.
Wilson, J. D. and Swaters, G. E.: 1991, ‘The Source Area Influencing a Measurement in the Planetary Boundary Layer: The “Footprint” and the “Distribution of Contact Distance”’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 55, 25–46.
Wood, N. and Mason, P. J.: 1991, ‘The Influence of Stability on the Effective Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Heat Flux’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 117, 1025–1056.
Zilitinkevich, S.: 1995, ‘Heat and Mass Transfer in the Convective Atmosphere with Weak Winds’, submitted to Boundary-Layer Meteorol.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahrt, L. The bulk aerodynamic formulation over heterogeneous surfaces. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 78, 87–119 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00122488
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00122488