Abstract
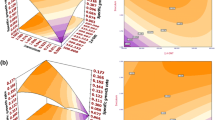
The effect of p-nitrophenol (PNP) concentration with or without glucose and yeast extract on the growth and biodegradative capacity of Ralstonia eutropha was examined. The chemical constituents of the culture medium were modeled using a response surface methodology. The experiments were performed according to the central composite design arrangement considering PNP, glucose and yeast extract as the selected variables whose influences on the degradation was evaluated (shaking in reciprocal mode, temperature of 30°C, pH 7 and test time of about 9 h). Quadratic polynomial regression equations were used to quantitatively explain variations between and within the models (responses: the biodegradation capacity and the biomass formation). The coefficient of determination was high (R 2adjusted = 0.9783), indicating the constructed polynomial model for PNP biodegradative capacity explains the variation between the regressors fairly well. A PNP removal efficiency of 74.5% occurred within 9 h (15 mg/L as the initial concentration of PNP with use of yeast extract at 0.5 g/L).





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PNP:
-
p-nitrophenol
- LC:
-
Liquid culture
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodology
- CCD:
-
Central composite design
- NAs:
-
Nitroaromatics
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
References
Ahmadi M, Vahabzadeh F, Bonakdarpour B, Mehranian M (2006) Empirical modeling of olive oil mill wastewater treatment using loofa-immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Proc Biochem 41:1148–1154
Andreev J, Dibrov PA, Braun S (1994) Motility and chemotaxis in Bacillus sphaericus dependence upon stage of growth. FEBS Lett 349:411–415
Baranyi J, Roberts TA (1995) Mathematics of predictive microbiology. Int J Food Microbiol 26:199–218
Bhushan B, Chauhan A, Samanta SK, Jain RK (2000a) Kinetics of biodegradation of p-nitrophenol by different bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 274:626–630
Bhushan B, Samanta SK, Chauhan A, Chakraborti AK, Jain RK (2000b) Chemotaxis and biodegradation of 3-methyl-4-nitrophenol by Ralstonia sp. SJ98. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 275:129–133
Ecker S, Widmann T, Lenke H, Dickel O, Fischer P, Bruhn C, Knackmuss HJ (1992) Catabolism of 2, 6-dinitrophenol by Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP 134 and JMP 222. Arch Microbiol 158:149–154
Fristedt U, Weinander R, Martinsson HS, Persson BL (1999) Characterization of purified and unidirectionally reconstituted Pho84 phosphate permease of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 458:1–5
Geeraerd AH, Valdramidis VP, Devlieghere F, Bernaert H, DeDebevere J, Van Impe JF (2004) Development of a novel approach for secondary modeling in predictive microbiology: incorporation of microbiological knowledge in black box polynomial modeling. Int J Food Microbiol 91:229–244
Gemini VL, Gallego A, de Oliveira VM, Gomez CE, Manfio GP, Korol SE (2005) Biodegradation and detoxification of p-nitrophenol by Rhodococcus wratislaviensis. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 55:103–108
Heitkamp MA, Camel V, Reuter TJ, Adams WJ (1990) Biodegradation of p-nitrophenol in an aqueous waste stream by immobilized bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2967–2973
Keweloh H, Heipieper HJ (1996) Trans unsaturated fatty acids in bacteria. Lipids 31:129–137
Kulkarni M, Chaudhari A (2006) Biodegradation of p-nitrophenol by P. putida. Bioresour Technol 97:982–988
Lapin LL (1997) Modern engineering statistics. Belmont, CA, USA, Wardsworth Publishing Company, ISBN 0-534-50883-9
Leonard D, Lindley N (1999) Growth of Ralstonia eutropha on inhibitory concentrations of phenol: diminished growth can be attributed to hydrophobic perturbation of phenol hydroxylase activity. Enzyme Microb Technol 25:271–277
Marvin-Sikkema FD, Bont JAM (1994) Degradation of nitroaromatic compounds by microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42:499–507
Mc Meekin TA, Olley J, Ratkowsky DA, Ross T (2002) Predictive microbiology: towards the interface and beyond. Int J Food Microbiol 73:395–407
Muller RH, Babel W (1996) Growth rate-dependent expression of phenol-assimilation pathways in Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP 134–the influence of formate as an auxiliary energy source on phenol conversion characteristics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46:156–162
Muller S, Bley T, Babel W (1999) Adaptive responses of Ralstonia eutropha to feast and famine conditions analysed by flow cytometry. J Biotechnol 75:81–97
Pandey G, Chauhan A, Samanta SK, Jain RK (2002) Chemotaxis of a Ralstonia sp. SJ98 toward co-metabolizable nitroaromatic compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 299:404–409
Raymond DGM, Alexander M (1971) Microbial metabolism and cometabolism of nitrophenols. Pest Biochem Physiol 1:123–130
Samanta SK, Bhushan B, Chauhan A, Jain RK (2000) Chemotaxis of a Ralstonia sp. SJ98 toward different nitroaromatic compounds and their degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 269:117–123
Schenzle A, Lenke H, Fischer P, Williams PA, Knackmuss HJ (1997) Catabolism of 3-nitrophenol by Ralstonia eutropha JMP 134. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1421–1427
Schmidt SK, Scow MK, Alexander M (1987) Kinetics of p-nitrophenol mineralization by a Pseudomonas sp.: effects of second substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:617–623
Sharma P, Singh L, Dilbaghi N (2009) Response surface methodological approach for the decolorization of simulated dye effluent using Aspergillus fumigatus fresenius. J Hazard Mater 161:1081–1086
Shen J, He R, Yu H, Wang L, Zhang J, Sun X, Li J, Han W, Xu L (2009) Biodegradation of 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol (picric acid) in a biological aerated filter (BAF). Bioresour Technol 100:1922–1930
Shinozaki Y, Kimura N, Nakahara T (2002) Difference in degrading p-nitrophenol between indigenous bacteria in a reactor. J Biosci Bioeng 93:512–519
Simkins S, Alexander M (1984) Models for mineralization kinetics with the variables of substrate concentration and population density. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:1299–1306
Stanier RY, Adelberg EA, Ingraham J (1976) The microbial word, 4th edn. ISBN 0-13-581025-6
Vining GG (2003) Statistical methods for engineers. Pacific Grove, CA, USA: Brooks/Cole Publishing Company. ISBN 0-534-23706-1
Wan N, Gu JD, Yan Y (2007) Degradation of p-nitrophenol by Achromobacter xylosoxidans Ns isolated from wetland sediment. Int Biodetrior Biodegrad 59:90–96
Xiarchos I, Jaworska A, Zakrzewska-Trznadel G (2008) Response surface methodology for the modeling of copper removal from aqueous solutions using micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration. J Membr Sci 321:222–231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salehi, Z., Vahabzadeh, F., Sohrabi, M. et al. Statistical medium optimization and biodegradative capacity of Ralstonia eutropha toward p-nitrophenol. Biodegradation 21, 645–657 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9332-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9332-5