Abstract
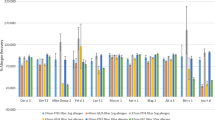
The Environmental Exposure Unit (EEU) is a 924 m3 facility (Kingston General Hospital, Ontario) in which uniform concentrations of various pollens in HEPA-filtered air at known rates of laminar airflow can be maintained. This facility provided a unique opportunity to compare several air samplers without the environmental variation inherent in outdoor comparisons. The purpose of this study was to conduct a quantitative comparison of pollen measurements using the Rotorod, Burkard™ Personal Volumetric Air Sampler, Air-O-Cell™ and a 37 mm open-faced filter cassette with a microporous filter in the EEU. Pollen samples were taken during clinical trials being conducted in the Unit. Raw pollen counts/m3 obtained using the different methods were corrected using published particle collection efficiencies for the particle size (∼ ∼20 μm) and airflow. Data were analyzed by ANOVA/Tukey HSD. No statistically significant differences were found between pollen concentrations determined by Rotorod, Air-O-Cell and filter cassette. Pollen levels determined by the Burkard were up to 2 times higher than the other sampling methods. Relative standard deviations were similar for the Rotorod, Burkard, and filter cassette and higher for the Air-O-Cell. This study demonstrated that, under our conditions, the Rotorod sampler provides consistent and reliable measurements of ragweed pollen concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AOC:
-
Air-O-Cell
- Burkard:
-
Burkard™ Personal Volumetric Air Sampler
- EEU:
-
Environmental Exposure Unit
- filter cassette:
-
37-mm open-faced filter cassette with a microporous filter
References
Aizenberg V., Reponen T., Grinshpun S.A. and Willeke K. (2000), Performance of Air-O-Cell, Burkard, and Button Samplers for total enumeration of airborne spores. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 61: 855–864
Anon. (1998), Users manual for the use of the Air-O-Cell air quality particle sampler. Zefon Analytical Accessories, St. Petersburg, FL
Buchan R.M., Soderholm S.C. and Tillery M.I. (1986), Aerosol sampling efficiency of 37 mm filter cassettes. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 47: 825–831
Coates F.A., Yang W.H. and Cakmak S. (2002), A comparison of aeroallergen data to investigate representative sampling radius. Can. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 7: 16–20
Day J.H., Briscoe M.P. (1999), Environmental exposure unit: a system to test anti-allergic treatment. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 83: 83–89
Day J.H., Briscoe M.P., Clark R.H., Ellis A.K. and Gervais P. (1997a), Onset of action and efficacy of terfenadine, astemizole, cetirizine, and loratadine for the relief of symptoms of allergic rhinitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 79: 163–172
Day J.H., Briscoe M.P., Welsh A., Smith J.N., Clark A., Ellis A.K. and Mason J. (1997b), Onset of action, efficacy, and safety of a single dose of fexofenadine hydrochloride for ragweed allergy using an environmental exposure unit. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 79: 533–540
Day J.H., Briscoe M.P., Rafeiro E., Ellis A.K., Pettersson E. and Akerlund A. (2000), Onset of action of intranasal budesonide (Rhinocort aqua) in seasonal allergic rhinitis studied in a controlled exposure model. J Allergy Clin. Immunol. 105: 489–494
Day J.H., Briscoe M., Rafeiro E., Chapman P. and Kramer B. (2001), Comparative onset of action and symptom relief with cetirizine, loratadine, or placebo in an environmental exposure unit in subjects with seasonal allergic rhinitis: Confirmation of a test system. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 87: 474–481
Di-Giovanni F. (1998), A review of the sampling efficiency of rotating-arm impactors used in aerobiological studies. Grana 37: 164–171
Dillon H.K., Heinsohn P.A. and Miller J.D. (1996), Field guide for the determination of biological contaminants in environmental samples. American Industrial Hygiene Association, Fairfax, VA, p. 120
Frenz D.A. (1999), Comparing pollen and spore counts collected with the Rotorod Sampler and Burkard spore trap. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 83: 341–347
Frenz D.A. (2000), The effect of windspeed on pollen and spore counts collected with the Rotorod Sampler and Burkard spore trap. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 85: 392–394
Frenz D.A. (2001), Interpreting atmospheric pollen counts for use in clinical allergy: allergic symptomology. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 86: 150–157
Frenz D.A., Lince N.L. (1997), A comparison of pollen recovery by three models of the Rotorod sampler. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 79: 256–258
Gagnon L., Comtois P. (1992), Peut-on comparer les resultats de differents types de capteurs polliniques? [Are sampling results from different pollen traps comparable?]. Grana 31: 125–130
Hirst J.M. (1952), An automatic volumetric spore trap. Ann. Appl. Biol. 39: 257–265
Linden G., Kenny L., Mark D. and Chalmers C. (1997), Sampling efficiency of the Swedish method for the sampling of total dust. Arbete och Hälsa 13: 1–17
Malone D.C., Lawson K.A., Smith D.H., Arrighi H.M. and Battista C. (1997), A cost of illness study of allergic rhinitis in the United States. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 99: 22–27
Nelson H.S., Solomon W.R. (2003), How ill the wind? Issues in aeroallergen sampling. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 112: 3–8
Ogden E.C., Raynor G.S. (1967), A new sampler for airborne pollen: the rotoslide. J. Allergy 40: 1–11
Portnoy J., Landuyt J., Pacheco F., Flappan S., Simon S. and Barnes C. (2000), Comparison of the Burkard and Allergenco MK-3 volumetric collectors. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 84: 19–24
Solomon W.R., Burge H.A., Boise J.R. and Becker M. (1980), Comparative particle recoveries by the retracting Rotorod, Rotoslide and Burkard spore trap sampling in a compact array. Int. J. Biometeorol. 24: 107–116
Watson H.H. (1954), Errors due to anisokinetic sampling of aerosols. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 15: 21–25
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Kingston General Hospital Allergy Research Fund. We thank Dr. Brian Flannigan, Scottish Centre for Pollen Studies, Napier University, Edinburgh and Mrs. Francis Coates, Aerobiology Research, Ottawa for helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heffer, M.J., Ratz, J.D., Miller, J.D. et al. Comparison of the Rotorod to other air samplers for the determination of Ambrosia artemisiifolia pollen concentrations conducted in the Environmental Exposure Unit. Aerobiologia 21, 233–239 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-005-9007-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-005-9007-6