Abstract
Background
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) occasionally induce small-bowel injury. However, the clinical features have only been partially clarified. The aim of this study was to clarify the clinical features of the disease and evaluate the effectiveness of endoscopic balloon dilation therapy for diaphragm disease, using double-balloon endoscopy (DBE).
Methods
This is a retrospective case study using our DBE database. Our inclusion criteria required patients to meet all the following criteria: (1) history of NSAID use; (2) endoscopic findings of erosion and/or ulcer and/or typical diaphragm-like strictures; (3) improvement in clinical findings (signs and symptoms) and/or endoscopic findings by cessation of NSAIDs, except for diaphragm disease; and (4) exclusion of other causes (e.g., malignant tumor, inflammatory bowel disease, and infectious disease). The clinical records of patients were investigated.
Results
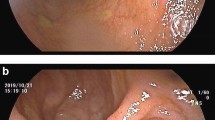
Eighteen patients were included. Sixteen patients showed ulcerative lesions, and the remaining 2 patients showed diaphragm diseases. For localized lesions, 12 patients evidenced lesions in the ileum, 5 patients had lesions in the duodenum and/or jejunum, and 1 had lesions in both intestines. The ulcerative lesions were multiple with various morphologies that were located unrelated to mesenteric or antimesenteric sides. The endoscopic balloon dilations were performed safely, and all patients improved with regard to their symptoms.
Conclusions
Symptomatic NSAID-induced small-bowel injuries exhibit a variety of patterns of ulcerative lesions as observed in the ileum in many cases. The endoscopic balloon dilation appears to be a safe and effective treatment for diaphragm disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjarnason I, Price AB, Zanelli G, Smethurst P, Burke M, Gumpel JM, et al. Clinicopathological features of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced small intestinal strictures. Gastroenterology 1988;94:1070–1074.
Lang J, Price AB, Levi AJ, Burke M, Gumpel JM, Bjarnason I. Diaphragm disease: pathology of disease of the small intestine induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Clin Pathol 1988;41:516–526.
Allison MC, Howatson AG, Torrance CJ, Lee FD, Russell RI. Gastrointestinal damage associated with the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. N Engl J Med 1992;327:749–754.
Iddan G, Meron G, Glukhovsky A, Swain P. Wireless capsule endoscopy. Nature (Lond) 2000;405:417.
Graham DY, Opekun AR, Willingham FF, Qureshi WA. Visible small-intestinal mucosal injury in chronic NSAID users. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005;3:55–59.
Goldstein JL, Eisen GM, Lewis B, Gralnek IM, Zlotnick S, Fort JG. Video capsule endoscopy to prospectively assess small bowel injury with celecoxib, naproxen plus omeprazole, and placebo. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005;3:133–141.
Maiden L, Thjodleifsson B, Theodors A, Gonzalez J, Bjarnason I. A quantitative analysis of NSAID-induced small bowel pathology by capsule enteroscopy. Gastroenterology 2005;128:1172–1178.
Maiden L, Thjodleifsson B, Seigal A, Bjarnason II, Scott D, Birgisson S, et al. Long-term effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cyclooxygenase-2 selective agents on the small bowel: a cross-sectional capsule enteroscopy study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:1040–1045.
Yamamoto H, Sekine Y, Sato Y, Higashizawa T, Miyata T, Iino S, et al. Total enteroscopy with a nonsurgical steerable double-balloon method. Gastrointest Endosc 2001;53:216–220.
Yamamoto H, Yano T, Kita H, Sunada K, Ido K, Sugano K. New system of double-balloon enteroscopy for diagnosis and treatment of small intestinal disorders. Gastroenterology 2003;125:1556;author reply 1557.
Yamamoto H, Kita H, Sunada K, Hayashi Y, Sato H, Yano T, et al. Clinical outcomes of double-balloon endoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of small-intestinal diseases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;2:1010–1016.
Moreels TG, Roth B, Vandervliet EJ, Parizel PM, Dutre J, Pelckmans PA. The use of the double-balloon enteroscope for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and biliary stent placement after Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy. Endoscopy 2007;39(suppl 1):E196–E197.
Emmett DS, Mallat DB. Double-balloon ERCP in patients who have undergone Roux-en-Y surgery: a case series. Gastrointest Endosc 2007;66:1038–1041.
Aabakken L, Bretthauer M, Line PD. Double-balloon enteroscopy for endoscopic retrograde cholangiography in patients with a Roux-en-Y anastomosis. Endoscopy 2007;39:1068–1071.
Sunada K, Yamamoto H, Hayashi Y, Sugano K. Clinical importance of the location of lesions with regard to mesenteric or antimesenteric side of the small intestine. Gastrointest Endosc 2007;66:S34–S38.
Kamata Y, Iwamoto M, Nara H, Kamimura T, Takayashiki N, Yamamoto H, et al. A case of rheumatoid arthritis with protein losing enteropathy induced by multiple diaphragmatic strictures of the small intestine: successful treatment by bougieing under double-balloon enteroscopy. Gut 2006;55:1372.
Matsuhashi N, Yamada A, Hiraishi M, Konishi T, Minota S, Saito T, et al. Multiple strictures of the small intestine after long-term nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy. Am J Gastroenterol 1992;87:1183–1186.
Kessler WF, Shires GT III, Fahey TJ III. Surgical complications of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced small bowel ulceration. J Am Coll Surg 1997;185:250–254.
Yen HH, Chen YY, Soon MS. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated ileal ulcers: an evaluation by double-balloon enteroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2006;63:328.
Manetas M, O’Loughlin C, Kelemen K, Barkin JS. Multiple small-bowel diaphragms: a cause of obscure GI bleeding diagnosed by capsule endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2004;60:848–851.
Hayashi Y, Yamamoto H, Kita H, Sunada K, Sato H, Yano T, et al. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced small bowel injuries identified by double-balloon endoscopy. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:4861–4864.
Somasundaram S, Sigthorsson G, Simpson RJ, Watts J, Jacob M, Tavares IA, et al. Uncoupling of intestinal mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and inhibition of cyclooxygenase are required for the development of NSAID-enteropathy in the rat. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000;14:639–650.
Reuter BK, Davies NM, Wallace JL. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug enteropathy in rats: role of permeability, bacteria, and enterohepatic circulation. Gastroenterology 1997;112:109–117.
Konaka A, Kato S, Tanaka A, Kunikata T, Korolkiewicz R, Takeuchi K. Roles of enterobacteria, nitric oxide and neutrophil in pathogenesis of indomethacin-induced small intestinal lesions in rats. Pharmacol Res 1999;40:517–524.
Watanabe T, Higuchi K, Kobata A, Nishio H, Tanigawa T, Shiba M, et al. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced small intestinal damage is Toll-like receptor 4 dependent. Gut 2008;57:181–187.
Robert A, Asano T. Resistance of germfree rats to indomethacin-induced intestinal lesions. Prostaglandins 1977;14:333–341.
Gorbach SL, Plaut AG, Nahas L, Weinstein L, Spanknebel G, Levitan R. Studies of intestinal microflora. II. Microorganisms of the small intestine and their relations to oral and fecal flora. Gastroenterology 1967;53:856–867.
Matsumoto T, Kudo T, Esaki M, Yano T, Yamamoto H, Sakamoto C, et al. Prevalence of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced enteropathy determined by double-balloon endoscopy: a Japanese multicenter study. Scand J Gastroenterol 2008;43:490–496.
Bjarnason I, Hayllar J, Smethurst P, Price A, Gumpel MJ. Metronidazole reduces intestinal inflammation and blood loss in non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug induced enteropathy. Gut 1992;33:1204–1208.
Leite AZ, Sipahi AM, Damiao AO, Coelho AM, Garcez AT, Machado MC, et al. Protective effect of metronidazole on uncoupling mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation induced by NSAID: a new mechanism. Gut 2001;48:163–167.
Bjarnason I, Hopkinson N, Zanelli G, Prouse P, Smethurst P, Gumpel JM, et al. Treatment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug induced enteropathy. Gut 1990;31:777–780.
Goldstein JL, Eisen GM, Lewis B, Gralnek IM, Aisenberg J, Bhadra P, et al. Small bowel mucosal injury is reduced in healthy subjects treated with celecoxib compared with ibuprofen plus omeprazole, as assessed by video capsule endoscopy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007;25:1211–1222.
Kelly ME, McMahon LE, Jaroszewski DE, Yousfi MM, De Petris G, Swain JM. Small bowel diaphragm disease: seven surgical cases. Arch Surg 2005;140:1162–1166.
Onwudike M, Sundaresan M, Melville D, Wood JJ. Diaphragm disease of the small-bowel: a case report and literature review. Dig Surg 2002;19:410–413.
Mehdizadeh S, Lo SK. Treatment of small-bowel diaphragm disease by using double-balloon enteroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2006;64:1014–1017.
Tanaka S, Mitsui K, Shirakawa K, Tatsuguchi A, Nakamura T, Hayashi Y, et al. Successful retrieval of video capsule endoscopy retained at ileal stenosis of Crohn’s disease using double-balloon endoscopy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;21:922–923.
Matsumoto T, Iida M, Matsui T, Yao T, Watanabe H, Okabe H. Non-specific multiple ulcers of the small intestine unrelated to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Clin Pathol 2004;57: 1145–1150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, Y., Yamamoto, H., Taguchi, H. et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced small-bowel lesions identified by double-balloon endoscopy: endoscopic features of the lesions and endoscopic treatments for diaphragm disease. J Gastroenterol 44 (Suppl 19), 57–63 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-008-2277-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-008-2277-3