Abstract
Eph receptors comprise the largest family of receptor tyrosine kinases consisting of eight EphA receptors (with five corresponding glycosyl-phosphatidyl-inositol-anchored ephrinA ligands) and six EphB receptors (with three corresponding transmembrane ephrinB ligands). Originally identified as neuronal pathfinding molecules, genetic loss of function experiments have identified EphB receptors and ephrinB ligands as crucial regulators of vascular assembly, orchestrating arteriovenous differentiation and boundary formation. Despite these clearly defined rate-limiting roles of the EphB/ephrinB system for developmental angiogenesis, the mechanisms of the functions of EphB receptors and ephrinB ligands in the cells of the vascular system are poorly understood. Moreover, little evidence can be found in the recent literature regarding complementary EphB and ephrinB expression patterns that occur in the vascular system and that may bring cells into juxtapositional contact to allow bi-directional signaling between neighboring cells. This review summarizes the current knowledge of the role of EphB receptors and ephrinB ligands during embryonic vascular assembly and discusses recent findings on EphB/ephrinB-mediated cellular functions pointing to the crucial role of the Eph/ephrin system in controlling vascular homeostasis in the adult.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RH (2002) Vascular patterning by Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and ephrins. Semin Cell Dev Biol 13:55–60
Adams RH, Wilkinson GA, Weiss C, Diella F, Gale NW, Deutsch U, Risau W, Klein R (1999) Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular development: demarcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular morphogenesis, and sprouting angiogenesis. Genes Dev 13:295–306
Adams RH, Diella F, Hennig S, Helmbacher F, Deutsch U, Klein R (2001) The cytoplasmic domain of the ligand ephrinB2 is required for vascular morphogenesis but not cranial neural crest migration. Cell 104:57–69
Batlle E, Henderson JT, Beghtel H, Born MM van den, Sancho E, Huls G, Meeldijk J, Robertson J, Wetering N van de, Pawson T, Clevers H (2002) Beta-catenin and TCF mediate cell positioning in the intestinal epithelium by controlling the expression of EphB/ephrinB. Cell 111:251–263
Brantley DM, Cheng N, Thompson EJ, Lin Q, Brekken RA, Thorpe PE, Muraoka RS, Cerretti DS, Pozzi A, Jackson D, Lin C, Chen J (2002) Soluble Eph A receptors inhibit tumor angiogenesis and progression in vivo. Oncogene 21:7011–7026
Burger PC, Chandler DB, Klintworth GK (1983) Corneal neovascularization as studied by scanning electron microscopy of vascular casts. Lab Invest 48:169–180
Carles-Kinch K, Kilpatrick KE, Stewart JC, Kinch MS (2002) Antibody targeting of the EphA2 tyrosine kinase inhibits malignant cell behavior. Cancer Res 62:2840–2847
Carter N, Nakamoto T, Hirai H, Hunter T (2002) EphrinA1-induced cytoskeletal re-organization requires FAK and p130(cas). Nat Cell Biol 4:565–573
Chen E, Xia G, Kundra A, Smith DL, Masood R, Gill P (2003) EphB4/ephrinB2 expression by malignant mesothelioma as a potential therapeutic target. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 44:475
Cheng N, Brantley DM, Chen J (2002) The ephrins and Eph receptors in angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13:75–85
Dodelet VC, Pasquale EB (2000) Eph receptors and ephrin ligands: embryogenesis to tumorigenesis. Oncogene 19:5614–5619
Flanagan JG, Vanderhaeghen P (1998) The ephrins and Eph receptors in neural development. Annu Rev Neurosci 21:309–345
Füller T, Korff T, Kilian A, Dandekar G, Augustin HG (2003) Forward EphB4 signaling in endothelial cells controls cellular repulsion and segregation from ephrinB2 positive cells. J Cell Sci 116:2461–2470
Gale NW, Baluk P, Pan L, Kwan M, Holash J, DeChiara TM, McDonald DM, Yancopoulos GD (2001) Ephrin-B2 selectively marks arterial vessels and neovascularization sites in the adult, with expression in both endothelial and smooth-muscle cells. Dev Biol 230:151–160
Gerety SS, Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ (1999) Symmetrical mutant phenotypes of the receptor EphB4 and its specific transmembrane ligand ephrin-B2 in cardiovascular development. Mol Cell 4:403–414
Gimbrone MA, Cotran RS, Leapman SB, Folkman J (1974) Tumor growth and neovascularization: an experimental model using the rabbit cornea. J Natl Cancer Inst 52:413–427
Hamada K, Oike Y Ito Y, Maekawa H, Miyata K, Shimomura T, Suda T (2003) Distinct roles of ephrin-B2 forward and EphB4 reverse signaling in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:190–197
Holmberg J, Clarke DL, Frisen J (2000) Regulation of repulsion versus adhesion by different splice forms of an Eph receptor. Nature 408:203–206
Holzman LB, Marks RM, Dixit VM (1990) A novel immediate-early response gene of endothelium is induced by cytokines and encodes a secreted protein. Mol Cell Biol 10:5830–5838
Huynh-Do U, Stein E, Lane AA, Liu H, Cerretti DP, Daniel TO (1999) Surface densities of ephrin-B1 determine EphB1-coupled activation of cell attachment through alphaVbeta3 and alpha5beta1 integrins. EMBO J 18:2165–2173
Kullander K, Klein R (2002) Mechanisms and functions of Eph and ephrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:475–486
Lawson ND, Weinstein BM (2002) Arteries and veins: making a difference with zebrafish. Nat Rev Genet 3:674–682
Liu W, Ahmad SA, Jung YD, Reinmuth N, Fan F, Bucana CD, Ellis LM (2002) Coexpression of ephrin-Bs and their receptors in colon carcinoma. Cancer 94:934–939
Luo H, Yu G, Wu Y, Wu J (2002) EphB6 crosslinking results in costimulation of T cells. J Clin Invest 110:1141–1150
Mukouyama YS, Shin D, Britsch S, Taniguchi M, Anderson DJ (2002) Sensory nerves determine the pattern of arterial differentiation and blood vessel branching in the skin. Cell 109:693–705
Munoz JJ, Alonso CL, Sacedon R, Crompton T, Vicente A, Jimenez E, Varas A, Zapata AG (2002) Expression and function of the Eph A receptors and their ligands ephrins A in the rat thymus. J Immunol 169:177–184
Nakamoto M, Bergemann AD (2002) Diverse roles for the Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases in carcinogenesis. Microsc Res Tech 59:58–67
Nikolova Z, Djonov V, Zuercher G, Andres AC, Ziemiecki A (1998) Cell-type specific and estrogen dependent expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphB4 and its ligand ephrin-B2 during mammary gland morphogenesis. J Cell Sci 111:2741–2751
Ogawa K, Pasqualini R, Lindberg RA, Kain R, Freeman AL, Pasquale EB (2000) The ephrin-A1 ligand and its receptor, EphA2, are expressed during tumor neovascularization. Oncogene 19:6043–6052
Oike Y, Ito Y, Hamada K, Zhang XQ, Miyata K, Arai F, Inada T, Araki K, Nakagata N, Takeya M, Kisanuki YY, Yanagisawa M, Gale NW, Suda T (2002) Regulation of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis by EphB/ephrin-B2 signaling between endothelial cells and surrounding mesenchymal cells. Blood 100:1326–1333
Othman-Hassan K, Patel K, Papoutsi M, Rodriguez-Niedenfuhr M, Christ B, Wilting J (2001) Arterial identity of endothelial cells is controlled by local cues. Dev Biol 237:398–409
Palmer A, Klein R (2003) Multiple roles of ephrins in morphogenesis, neuronal networking, and brain function. Genes Dev 17:(in press)
Palmer A, Zimmer M, Erdmann KS, Eulenburg V, Porthin A, Heumann R, Deutsch U, Klein R (2002) EphrinB phosphorylation and reverse signaling: regulation by Src kinases and PTP-BL phosphatase. Mol Cell 9:725–737
Pandey A, Shao H, Marks RM, Polverini PJ, Dixit VM (1995) Role of B61, the ligand for the Eck receptor tyrosine kinase, in TNF-alpha-induced angiogenesis. Science 268:567–569
Shin D, Garcia-Cardena G, Hayashi SI, Gerety S, Asahara T, Stavrakis G, Isner J, Folkman J, Gimbrone MA, Anderson DJ (2001) Expression of ephrinB2 identifies a stable genetic difference between arterial and venous vascular smooth muscle as well as endothelial cells, and marks subsets of microvessels at sites of adult neovascularization. Dev Biol 230:139–150
Stephenson SA, Slomka S, Douglas EL, Hewett PJ, Hardingham JE (2001) Receptor protein tyrosine kinase EphB4 is up-regulated in colon cancer. Bull Menninger Clin Mol Biol 2:15
Suenobu S, Takakura N, Inada T, Yamada Y, Yuasa H, Zhang XQ, Sakano S, Oike Y, Suda T (2002) A role of EphB4 receptor and its ligand, ephrin-B2, in erythropoiesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293:1124–1131
Takai N, Miyazaki T, Fujisawa K, Nasu K, Miyakawa I (2001) Expression of receptor tyrosine kinase EphB4 and its ligand ephrin-B2 is associated with malignant potential in endometrial cancer. Oncol Rep 8:567–573
Tang XX, Evans AE, Zhao H, Cnaan A, London W, Cohn SL, Brodeur GM, Ikegaki N (1999) High-level expression of EPHB6, EFNB2, and EFNB3 is associated with low tumor stage and high TrkA expression in human neuroblastomas. Clin Cancer Res 5:1491–1496
Tang XX, Zhao H, Robinson ME, Cohen B, Cnaan A, London W, Cohn SL, Cheung NK, Brodeur GM, Evans AE, Ikegaki N (2000) Implications of EPHB6, EFNB2, and EFNB3 expressions in human neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10936–10941
Vogt T, Stolz W, Welsh J, Jung B, Kerbel RS, Kobayashi H, Landthaler M, McClelland M (1998) Overexpression of Lerk-5/Eplg5 messenger RNA: a novel marker for increased tumorigenicity and metastatic potential in human malignant melanomas. Clin Cancer Res 4:791–797
Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ (1998) Molecular distinction and angiogenic interaction between embryonic arteries and veins revealed by ephrin-B2 and its receptor Eph-B4. Cell 93:741–753
Wilkinson DG (2001) Multiple roles of EPH receptors and ephrins in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:155–164
Zelinski DP, Zantek ND, Stewart JC, Irizarry AR, Kinch MS (2001) EphA2 overexpression causes tumorigenesis of mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res 61:2301–2306
Zhang XQ, Takakura N, Oike Y, Inada T, Gale NW, Yancopoulos GD, Suda T (2001) Stromal cells expressing ephrin-B2 promote the growth and sprouting of ephrin-B2(+) endothelial cells. Blood 98:1028–1037
Zhong TP, Childs S, Leu JP, Fishman MC (2001) Gridlock signalling pathway fashions the first embryonic artery. Nature 414:216–220
Zou JX, Wang B, Kalo MS, Zisch AH, Pasquale EB, Ruoslahti E (1999) An Eph receptor regulates integrin activity through R-Ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13813–13818
Acknowledgements
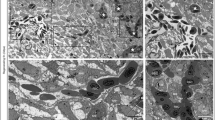
The authors thank Drs. Thomas Korff (Göttingen) and Tim Füller (Freiburg) for making the unpublished data in Fig. 3 available for this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Eph/ephrin work in the laboratory of the authors is supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Au83/3–2 within the SPP1069 "Angiogenesis")
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Augustin, H.G., Reiss, Y. EphB receptors and ephrinB ligands: regulators of vascular assembly and homeostasis. Cell Tissue Res 314, 25–31 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0770-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0770-9