Abstract
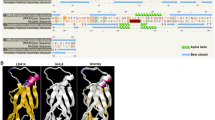
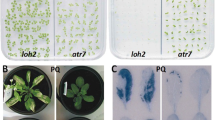
Phytic acid (inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate or InsP6) is the primary storage form of phosphorus in plant seeds. The rice OsLpa1 encodes a novel protein required for wild-type levels of seed InsP6 and was identified from a low phytic acid (lpa) mutant exhibiting a 45–50% reduction in seed InsP6. OsLpa1 is highly conserved in plants and Arabidopsis contains two OsLpa1-like genes, At3g45090 and At5g60760. Analysis of homozygous T-DNA insertion mutants of At5g60760 revealed significantly reduced levels of seed InsP6 while no changes were observed in seeds of At3g45090 mutants. A double knockout mutant of At5g60760 and At3g45090 was created and its seed InsP6 content was similar to that of the At5g60760 mutant indicating that At3g45090 does not provide functional redundancy. OsLpa1 was confirmed to be the ortholog of At5g60760 by complementation of a knockout mutant with a cDNA clone corresponding to the largest of three alternative transcripts of OsLpa1. The spatial and temporal expression of At5g60760 during seed development is consistent with its involvement in seed InsP6 biosynthesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- At :
-
Arabidopsis thaliana
- BLASTp:
-
Basic local alignment search tool protein–protein
- cDNA:
-
Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid
- DAF:
-
Days after fertilization
- GADPH:
-
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase
- HPIC:
-
High-performance ion chromatography
- InsP:
-
Inositol (poly)phosphate
- lpa :
-
Low phytic acid
- Os :
-
Oryza sativa
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- Pi:
-
Inorganic phosphate
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
- SAIL:
-
Syngenta Arabidopsis Insertion Lines
- SALK:
-
Salk Institute
- T-DNA:
-
Transfer DNA
References
Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, Gadrinab C, Heller C, Jeske A, Koesema E, Meyers CC, Parker H, Prednis L, Ansari Y, Choy N, Deen H, Geralt M, Hazari N, Hom E, Karnes M, Mulholland C, Ndubaku R, Schmidt I, Guzman P, Aguilar-Henonin L, Schmid M, Weigel D, Carter DE, Marchand T, Risseeuw E, Brogden D, Zeko A, Crosby WL, Berry CC, Ecker JR (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301:653–657
Brearley CA, Hanke DE (1996a) Inositol phosphates in the duckweed Spirodela polyrhiza L. Biochem J 314:215–225
Brearley CA, Hanke DE (1996b) Metabolic evidence for the order of addition of individual phosphate esters in the myo-inositol moiety of inositol hexakisphosphate in the duckweed Spirodela polyrhiza L. Biochem J 314:227–233
Brinch-Pedersen H, Sørensen LD, Holm PB (2002) Engineering crop plants: getting a handle on phosphate. Trends Plant Sci 7:118–125
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Cosgrove DJ (1980) Inositolhexakisphosphates. In: Cosgrove DJ (ed) Inositol Phosphates. Their Chemistry Biochemistry and Physiology. Elsevier, The Netherlands, pp 26–43
Cromwell GL, Coffey RD (1991) Phosphorus—a key essential nutrient yet a possible major pollutant—its central role in animal nutrition. In: Lyons TP (ed) Biotechnology in the Feed Industry. Alltech Publications, Nicholasville KY, pp 133–145
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Reptr 1:19–21
Fileppi M, Galasso I, Tagliabue G, Daminati MG, Campion B, Doria E, Sparvoli F (2010) Characterisation of structural genes involved in phytic acid biosynthesis in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Mol Breed 25:453–470
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Josefsen L, Bohn L, Sørensen MB, Rasmussen SK (2007) Characterization of a multifunctional inositol phosphate kinase from rice and barley belonging to the ATP-grasp superfamily. Gene 397:114–125
Kim S, Andaya C, Goyal S, Tai T (2008) The rice OsLpa1 gene encodes a novel protein involved in phytic acid metabolism. Theor Appl Genet 117:769–779
Larson SR, Rutger JN, Young KA, Raboy V (2000) Isolation and genetic mapping of a non-lethal rice (Oryza sativa L.) low phytic acid 1 mutation. Crop Sci 40:1397–1405
Lehmacher A, Hensel R (1994) Cloning sequencing and expression of the gene encoding 2-phosphoglycerate kinase from Methanothermus fervidus. Mol Gen Genet 242:163–168
Leipe DD, Koonin EV, Aravind L (2003) Evolution and classification of P-loop kinases and related proteins. J Mol Biol 333:781–815
Lott J, Greenwood J, Batten G (1995) Mechanisms and regulation of mineral nutrient storage during seed development. In: Kigel J, Galili G (eds) Seed Development and Germination. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 215–233
Majumder A, Biswas B (1973) Metabolism of inositol phosphates part V—biosynthesis of inositol phosphates during ripening of mung bean (Phaseolus aureus) seeds. Indian J Exp Biol 11:120–123
Mitsuhashi N, Ohnishi M, Sekiguchi Y, Kwon YU, Chang YT, Chung SK, Inoue Y, Reid RJ, Yagisawa H, Mimura T (2005) Phytic acid synthesis and vacuolar accumulation in suspension-cultured cells of Catharanthus roseus induced by high concentration of inorganic phosphate and cations. Plant Physiol 138:1607–1614
Mitsuhashi N, Kondo M, Nakaune S, Ohnishi M, Hayashi M, Hara-Nishimura I, Richardson A, Fukaki H, Nishimura M, Mimura T (2008) Localization of myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase to the endosperm in developing seeds of Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 59:3069–3076
Nagy R, Grob H, Weder B, Green P, Klein M, Frelet-Barrand A, Schjoerring JK, Brearley C, Martinoia E (2009) The Arabidopsis ATP-binding cassette protein AtMRP5/AtABCC5 is a high affinity inositol hexakisphosphate transporter involved in guard cell signaling and phytate storage. J Biol Chem 284:33614–33622
Odom AR, Stahlberg A, Wente SR, York JD (2000) A role for nuclear inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate kinase in transcriptional control. Science 287:2026–2029
Raboy V (1997) Accumulation and storage of phosphate and minerals. In: Larkins BA, Vasil IK (eds) Cellular and molecular biology of plant seed development. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 441–477
Raboy V (2001) Seeds for a better future: low phytate grains help to overcome malnutrition and reduce pollution. Trends Plant Sci 6:458–462
Raboy V (2003) myo-Inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate. Phytochem 64:1033–1043
Raboy V (2007) The ABCs of low-phytate crops. Nat Biotech 25:874–875
Raboy V, Gerbasi PF, Young KA, Stoneberg SD, Pickett SG, Bauman AT, Murthy PPN, Sheridan WF, Ertl DS (2000) Origin and seed phenotype of maize low phytic acid 1–1 and low phytic acid 2–1. Plant Physiol 124:355–368
Reddy NR, Sathe SK (2002) Food phytates. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Saiardi A, Caffrey JJ, Snyder SH, Shears SB (2000) Inositol polyphosphate multikinase (ArgRIII) determines nuclear mRNA export in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 468:28–32
Sessions A, Burke E, Presting G, Aux G, McElver J, Patton D, Dietrich B, Ho P, Bacwaden J, Ko C, Clarke JD, Cotton D, Bullis D, Snell J, Miguel T, Hutchison D, Kimmerly B, Mitzel T, Katagiri F, Glazebrook J, Law M, Goff SA (2002) A high-throughput arabidopsis reverse genetics system. Plant Cell 14:2985–2994
Shears SB (2004) How versatile are inositol phosphate kinases? Biochem J 377:265–280
Shi J, Wang H, Wu Y, Hazebroek J, Meeley RB, Ertl DS (2003) The maize low-phytic acid mutant lpa2 is caused by mutation in an inositol phosphate kinase gene. Plant Physiol 131:507–515
Shi JR, Wang HY, Hazebroek J, Ertl DS, Harp T (2005) The maize low-phytic acid 3 encodes a myo-inositol kinase that plays a role in phytic acid biosynthesis in developing seeds. Plant J 42:708–719
Shi J, Wang H, Schellin K, Li B, Faller M, Stoop JM, Meeley RB, Ertl DS, Ranch JP, Glassman K (2007) Embryo-specific silencing of a transporter reduces phytic acid content of maize and soybean seeds. Nat Biotech 25:930–937
Stephens LR, Irvine RF (1990) Stepwise phosphorylation of myo-inositol leading to myo-inositol hexakisphosphate in Dictyostelium. Nature 346:580–583
Stevenson-Paulik J, Odom AR, York JD (2002) Molecular and biochemical characterization of two plant inositol polyphosphate 6-/3-/5-kinases. J Biol Chem 277:42711–42718
Stevenson-Paulik J, Bastidas RJ, Chiou S-T, Frye RA, York JD (2005) Generation of phytate-free seeds in Arabidopsis through disruption of inositol polyphosphate kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:12612–12617
Suzuki M, Tanaka K, Kuwano M, Yoshida KT (2007) Expression pattern of inositol phosphate-related enzymes in rice (Oryza sativa L.): implications for the phytic acid biosynthetic pathway. Gene 405:55–64
Sweetman D, Johnson S, Caddick SEK, Hanke DE, Brearley CA (2006) Characterization of an Arabidopsis inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase (AtIPK1). Biochem J 394:95–103
Wilson MP, Majerus PW (1997) Characterization of a cDNA encoding Arabidopsis thaliana inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 232:678–681
York JD, Odom AR, Murphy R, Ives EB, Wente SR (1999) A phospholipase C-dependent inositol polyphosphate kinase pathway required for efficient messenger RNA export. Science 285:96–100
Zhao HJ, Liu QL, Ren XL, Wu DX, Shu QY (2008) Gene identification and allele-specific marker development for two allelic low phytic acid mutations in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 22:603–612
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by USDA Agricultural Research Service CRIS Project 5306-21000-016/017-00D (T.H.T.) and National Research Initiative Competitive Grant 2005-35301-15708 from the USDA Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service (T.H.T.). We are thankful to the UC Davis DANR Analytical Lab for assistance with HPIC analysis and to Victor Raboy, Cynthia Andaya, and Erin Easlon for critical reading of the manuscript and helpful suggestions for improvement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SI., Tai, T.H. Genetic analysis of two OsLpa1-like genes in Arabidopsis reveals that only one is required for wild-type seed phytic acid levels. Planta 232, 1241–1250 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1243-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1243-5