Abstract
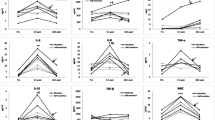
We investigated the effects of an ultra-marathon on cell-free plasma DNA as well as on mRNA expression of pro-apoptotic (Bax, Bad), anti-apoptotic (Bcl-2) and cell-protective (Hsp70, Hsp27 and Hsp32) genes in mononuclear blood cells (MNCs). Blood samples were drawn from 14 athletes before and immediately after 6-h run. In addition, blood samples were also collected and analyzed 2 and 24 h after the end of the run. Levels of plasma DNA were significantly increased immediately after the marathon (P < 0.001) and were still higher 2 h later (P < 0.005), but significantly lower than those immediately after the race (P < 0.05). Cell-free plasma DNA returned to pre-race levels 24 h after the run. mRNA expressions of Hsp70, Hsp32 and Bax significantly increased in MNCs after the race, whereas Hsp27 and Bad mRNA expression levels showed no significant changes. Bcl-2 expressions decreased immediately after the race (P < 0.001), but increased in the 24 h later (P < 0.05). We conclude that apoptotic ladders of cell-free DNA following exhaustive exercise originate from apoptotic cells and that not only skeletal muscle cells but also leukocytes contribute to this phenomenon.


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Arslan S, Erdem S, Sivri A, Hascelik Z, Tan E (2002) Exercise-induced apoptosis of rat skeletal muscle and the effect of meloxicam. Rheumatol Int 21:133–136. doi:10.1007/s00296-001-0156-9
Atamaniuk J, Ruzicka K, Stuhlmeier KM, Karimi A, Eigner M, Mueller MM (2006) Cell-free plasma DNA: a marker for apoptosis during hemodialysis. Clin Chem 52:523–526. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2005.058883
Atamaniuk J, Vidotto C, Tschan H, Bachl N, Stuhlmeier KM, Muller MM (2004) Increased concentrations of cell-free plasma DNA after exhaustive exercise. Clin Chem 50:1668–1670. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2004.034553
Chevion S, Moran DS, Heled Y, Shani Y, Regev G, Abbou B et al (2003) Plasma antioxidant status and cell injury after severe physical exercise. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5119–5123. doi:10.1073/pnas.0831097100
SL Dumke CL, Lind RH, Nieman DC (2006) Indirect calorimetry during ultradistance running: a case report. J Sports Sci Med 5(4):692–698
Febbraio MA, Koukoulas I (2000) HSP72 gene expression progressively increases in human skeletal muscle during prolonged, exhaustive exercise. J Appl Physiol 89:1055–1060
Fehrenbach E, Niess AM, Schlotz E, Passek F, Dickhuth HH, Northoff H (2000) Transcriptional and translational regulation of heat shock proteins in leukocytes of endurance runners. J Appl Physiol 89:704–710
Goodman C, Henry G, Dawson B, Gillam I, Beilby J, Ching S et al (1997) Biochemical and ultrastructural indices of muscle damage after a twenty-one kilometre run. Aust J Sci Med Sport 29:95–98
Lui YY, Dennis YM (2002) Circulating DNA in plasma and serum: biology, preanalytical issues and diagnostic applications. Clin Chem Lab Med 40:962–968. doi:10.1515/CCLM.2002.169
Maines MD (1997) The heme oxygenase system: a regulator of second messenger gases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 37:517–554. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.37.1.517
Marra S, Hoffman-Goetz L (2004) Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade during exercise decreases intestinal lymphocyte apoptosis but not cell loss in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 82:465–473. doi:10.1139/y04-072
Mars M, Govender S, Weston A, Naicker V, Chuturgoon A (1998) High intensity exercise: a cause of lymphocyte apoptosis? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 249:366–370. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9156
Mooren FC, Bloming D, Lechtermann A, Lerch MM, Volker K (2002) Lymphocyte apoptosis after exhaustive and moderate exercise. J Appl Physiol 93:147–153
Mooren FC, Lechtermann A, Volker K (2004) Exercise-induced apoptosis of lymphocytes depends on training status. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:1476–1483. doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000139897.34521.E9
Mosser DD, Caron AW, Bourget L, Denis-Larose C, Massie B (1997) Role of the human heat shock protein hsp70 in protection against stress-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 17:5317–5327
Niess AM, Passek F, Lorenz I, Schneider EM, Dickhuth HH, Northoff H et al (1999) Expression of the antioxidant stress protein heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in human leukocytes. Free Radic Biol Med 26:184–192. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00192-0
Nishimura G, Proske RJ, Doyama H, Higuchi M (2001) Regulation of apoptosis by respiration: cytochrome c release by respiratory substrates. FEBS Lett 505:399–404. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02859-9
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ (1993) Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 74:609–619. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90509-O
Pedersen BK, Hoffman-Goetz L (2000) Exercise and the immune system: regulation, integration, and adaptation. Physiol Rev 80:1055–1081
Plumier JC, Currie RW (1996) Heat shock-induced myocardial protection against ischemic injury: a role for Hsp70? Cell Stress Chaperones 1:13–17. doi:10.1379/1466-1268(1996)001<0013:HSIMPA>2.3.CO;2
Podhorska-Okolow M, Dziegiel P, Murawska-Cialowicz E, Krajewska B, Ciesielska U, Jethon Z et al (2004) Exercise-induced apoptosis in renal tubular cells of the rat. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 63:213–216
Pollack M, Leeuwenburgh C (2001) Apoptosis and aging: role of the mitochondria. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 56:B475–B482
Rauch HG, Hawley JA, Noakes TD, Dennis SC (1998) Fuel metabolism during ultra-endurance exercise. Pflugers Arch 436:211–219. doi:10.1007/s004240050624
Shastry S, Toft DO, Joyner MJ (2002) HSP70 and HSP90 expression in leucocytes after exercise in moderately trained humans. Acta Physiol Scand 175:139–146. doi:10.1046/j.1365-201X.2002.00979.x
Shephard RJ (2003) Adhesion molecules, catecholamines and leucocyte redistribution during and following exercise. Sports Med 33:261–284. doi:10.2165/00007256-200333040-00002
Simpson RJ, Florida-James GD, Whyte GP, Guy K (2006) The effects of intensive, moderate and downhill treadmill running on human blood lymphocytes expressing the adhesion/activation molecules CD54 (ICAM-1), CD18 (beta2 integrin) and CD53. Eur J Appl Physiol 97:109–121 Epub 28 February 2006
Siu PM, Bryner RW, Martyn JK, Alway SE (2004) Apoptotic adaptations from exercise training in skeletal and cardiac muscles. FASEB J 18:1150–1152 Epub 7 May 2004
Steensberg A, Morrow J, Toft AD, Bruunsgaard H, Pedersen BK (2002) Prolonged exercise, lymphocyte apoptosis and F2-isoprostanes. Eur J Appl Physiol 87:38–42 Epub 14 March 2002
Stuhlmeier KM, Pollaschek C (2004) Differential effect of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) on the genes encoding hyaluronan synthases and utilization of the p38 MAPK pathway in TGF-beta-induced hyaluronan synthase 1 activation. J Biol Chem 279:8753–8760 Epub 15 December 2003
Stupka N, Lowther S, Chorneyko K, Bourgeois JM, Hogben C, Tarnopolsky MA (2000) Gender differences in muscle inflammation after eccentric exercise. J Appl Physiol 89:2325–2332
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Brenner C, Larochette N et al (1999) Mitochondrial release of caspase-2 and -9 during the apoptotic process. J Exp Med 189:381–394. doi:10.1084/jem.189.2.381
Thompson D, Basu-Modak S, Gordon M, Poore S, Markovitch D, Tyrrell RM (2005) Exercise-induced expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human lymphocytes. Free Radic Res 39:63–69. doi:10.1080/10715760400022327
Willis D, Moore AR, Frederick R, Willoughby DA (1996) Heme oxygenase: a novel target for the modulation of the inflammatory response. Nat Med 2:87–90. doi:10.1038/nm0196-87
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atamaniuk, J., Stuhlmeier, K.M., Vidotto, C. et al. Effects of ultra-marathon on circulating DNA and mRNA expression of pro- and anti-apoptotic genes in mononuclear cells. Eur J Appl Physiol 104, 711–717 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0827-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0827-2