Abstract.
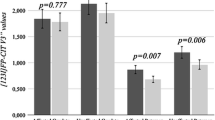
Levodopa pharmacokinetic-phamacodynamic (PK-PD) modeling may be able to test the functional integrity of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system in Parkinson’s disease (PD). [123I]-FP-CIT SPECT imaging of striatal dopamine transporters has also been introduced for the evaluation of presynaptic dopaminergic homeostasis. We aimed to assess the intrapatient relation between levodopa PK-PD and SPECT measures of dopaminergic function in PD. Thirty-five PD patients, 1 to 4 on the Hoehn and Yahr (H&Y) scale, enrolled in the study. Each patient was examined by levodopa PK-PD modeling and SPECT imaging. Primary measure outcomes were the levodopa half-life in the effect compartment (t1/2eq) for PKPD modeling and the ratio of specific to non specific (SP/NSP) tracer striatal uptake for SPECT. Levodopa t1/2eq was highly significantly correlated with H&Y scale (r = –0.815, p < 0.0001), Unified Parkinson’s disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) (r = –0.691, p < 0.0001) and PD symptom duration (r = –0.647, p < 0.0001). SPECT contralateral putamen SP/NSP ratio showed the most significant correlations with clinical indicators of disease severity: H&Y, r = –0.526, p < 0.002; UPDRS, r = –0.523, p < 0.002; symptom duration, r = –0.513, p < 0.002. Significant correlations were observed between levodopa t1/2eq and putamen SP/NSP ratios, yielding the closest correlation for the contralateral region (r = 0.522, p < 0.002). An indirect PK-PD dopaminergic functional variable and direct SPECT measures of presynaptic dopaminergic system homeostasis were in close agreement with clinical data and correlated to each other. Levodopa PK-PD modeling can be a practical clinical tool indirectly assessing the functional integrity of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system in PD patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Contin, M., Martinelli, P., Riva, R. et al. Assessing dopaminergic function in Parkinson’s disease: levodopa kinetic-dynamic modeling and SPECT. J Neurol 250, 1475–1481 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-003-0257-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-003-0257-3