Abstract
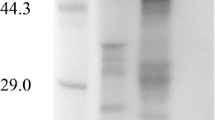
A novel intracellular glucosyltransferase (GTase) was isolated from cells of Actinoplanes sp. CKD485-16—acarbose-producing cells. The enzyme was purified by DEAE-cellulose and G75-40 Sephadex chromatography. The molecular mass of the enzyme was estimated to be 62 kDa by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and its isoelectric point (pI) was pH 4.3. The N-terminal sequence of the GTase consisted of NH2-Ser-Val-Pro-Leu-Ser-Leu-Pro-Ala-Glu-Trp. The optimum pH and temperature were 7.5 and 30°C. The enzyme was stable in a pH range of 5.5–9.0 and below 40°C. Enzymatic reactions were performed by incubating the GTase with various substrates. The GTase converted acarbose into component C, maltose into trehalose, and maltooligosaccharides into maltooligosyl trehaloses. The reactions were reversible. Various acarbose analogs were tested as inhibitors against the GTase as a means to suppress component C formation. Valienamine was the most potent, with an IC50 value of 2.4×10−3 mM and showed a competitive inhibition mode.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowers SG, Mahmud T, Floss HG (2002) Biosynthetic studies on the α-glucosidase inhibitor acarbose: the chemical synthesis of dTDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-α-d-glucose. Carbohydr Res 337:297–304
Choi BT, Shin CS (2003) Reduced formation of byproduct component C in acarbose fermentation by Actinoplanes sp. CKD485-16. Biotechnol Prog 19:1677–1682
Crueger A, Dellweg HG, Lenz JG, Schroder W, Pape H, Goeke K, Schaper B, Hemker M, Piepersberg W, Distler J, Stratmann A (1999) Processes for preparing acarviosyl transferase and for using it in the conversion of acarbose homologues into acarbose, for the preparation of acarbose homologues. US Patent 5 989 882
Degwert U, van Hulst R, Pape H, Herrold RE, Beale JM, Keller PJ, Lee JP, Floss HG (1987) Studies on the biosynthesis of the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor acarbose: valienamine, a m-C7N unit not derived from the shikimate pathway. J Antibiot 40:855–861
Dong H, Mahmud T, Tornus I, Lee S, Floss H (2001) Biosynthesis of the validamycins: identification of intermediates in the biosynthesis of validamycin A by Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. limoneus. J Am Chem Soc 123:2733–2742
Fillinger S, Chaveroche MK, van Dijck P, de Vries R, Ruijter G, Thevelein J, d’Enfert C (2001) Trehalose is required for the acquisition of tolerance to a variety of stresses in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Microbiology 147:1851–1862
Frommer W, Plus W, Schafer D, Schmidt D (1975) Glycoside-hydrolase enzyme inhibitors. US Patent 3 876 766
Hemker M, Stratmann A, Goeke K, Schroder W, Lenz J, Piepersberg W, Pape H (2001) Identification, cloning, expression, and characterization of the extracellular acarbose-modifying glycosyltransferase, AcbD, from Actinoplanes sp. strain SE50. J Bacteriol 183:4484–4492
Kato M (1999) Trehalose production with a new enzymatic system from Sulfolobus solfataricus KM1. J Mol Catal B 6:223–233
Kato M, Miura Y, Kettoku M, Komeda T, Iwamatsu A, Kobayashi K (1996) Reaction mechanism of a new glycosyltrehalose-hydrolyzing enzyme isolated from the hyperthermophilic archaeon, Sulfolobus solfataricus KM1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60:921–925
Kobayashi K, Kato M, Miura Y, Kettoku M, Komeda T, Iwamatsu A (1996) Gene analysis of trehalose-producing enzymes from hyperthermophilic archaea in Sulfolobales. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60:1720–1723
Lee S, Egelkrout E (1998) Biosynthetic studies on the α-glucosidase inhibitor acarbose in Actinoplanes sp.: glutamate is the primary source of the nitrogen in acarbose. J Antibiot 51:225–227
Lee S, Saueribrei B, Niggemann J, Egelkraut E (1997) Biosynthesic studies on the α-glucosidase inhibitor acarbose in Actinoplanes sp.: source of the maltose unit. J Antibiot 50:954–957
Maruta K, Nakada T, Kubota M, Chaen H, Sugimoto T, Kurimoto M, Tsujisaka Y (1995) Formation of trehalose from maltooligosaccharides by a novel enzymatic system. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59:1829–1834
Murao S, Ohyama K (1975) New amylase inhibitor (S-1) from Streptomyces diastaticus var. amylostaticus no. 2476. Agric Biol Chem 39:2271–2273
Nakada T, Maruta M, Tsusaki K, Kubota M, Chaen H, Fukuda S, Sugimoto T, Kurimoto M, Tsujisaka Y (1995) Purification and properties of a novel enzyme, maltooligosyl trehalose synthase, from Arthrobacter sp. Q36. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59:2210–2214
Nakada T, Ikegami S, Chaen H, Kubota M, Fukuda S, Sugimoto T, Kurimoto M, Tsujisaka Y (1996) Purification and characterization of thermostable maltooligosyl trehalose synthase from the thermophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60:263–266
Nishimoto T, Nakada T, Chaen H, Fukuda S (1996a) Purification and characterization of a thermostable trehalose synthesis from Thermus aquaticus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60:835–839
Nishimoto T, Nakano M, Nakada T, Chaen H, Fukuda S, Sugimoto T, Kurimoto M, Tsujisaka Y (1996b) Purification and properties of a novel enzyme, trehalose synthase, from Pimelobacter sp. R48. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60:640–644
de Pascale D, Sasso MP, Lernia I, Lazzaro AD, Furia A, Farina MC, Rossi M, Rosa MD (2001) Recombinant thermophilic enzymes for trehalose and trehalosyl dextrins production. J Mol Catal B 11:777–786
Schiraldi C, Lernia ID, Rosa MD (2002) Trehalose production: exploiting novel approaches. Trends Biotechnol 20:420–425
Stratmann A, Mahmud T, Lee S, Distler J, Floss HG, Piepersberg W (1999) The AcbC protein from Actinoplanes sp. is a C7-cyclitol synthase related to 3-dehydroquinate synthases and is involved in the biosynthesis of the α-glucosidase inhibitor acarbose. J Biol Chem 274:10889–10896
Truscheit E, Frommer W, Junge B, Muller L, Schmidt DD, Wingender W (1981) Chemistry and biochemistry of α-glucosidase inhibitors. Angew Chem Int Ed 20:744–761
Tsusaki K, Nishimoto T, Nakada T, Kubota M, Chaen H, Sugimoto T, Kurimoto M (1996) Cloning and sequencing of trehalose synthase gene from Pimelobacter sp. R48. Biochim Biophys Acta 1290:1–3
Tsusaki K, Nishimoto T, Nakada T, Kubota M, Chaen H, Fukuda S, Sugimoto T, Kurimoto M (1997) Cloning and sequencing of trehalose synthase gene from Thermus aquaticus ATCC33923. Biochim Biophys Acta 1334:28–32
Zhang CS, Stratmann A, Block O, Bruckner R, Podeschwa M, Altenbach HJ, Wehmeier UF, Piepersberg W (2002) Biosynthesis of the C(7)-cyclitol moiety of acarbose in Actinoplanes species SE50/110. 7-O-phosphorylation of the initial cyclitol precursor leads to proposal of a new biosynthetic pathway. J Biol Chem 277:22853–22862
Zhang CS, Podeschwa M, Altenbach HJ, Piepersberg W, Wehmeier UF (2003a) The acarbose-biosynthetic enzyme AcbO from Actinoplanes sp. SE 50/110 is a 2-epi-5-epi-valiolone-7-phosphate 2-epimerase. FEBS Lett 540:47–52
Zhang CS, Podeschwa M, Block O, Altenbach HJ, Piepersberg W, Wehmeier UF (2003b) Identification of a 1-epi-valienol 7-kinase activity in the producer of acarbose, Actinoplanes sp. SE50/110. FEBS Lett 540:53–57
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, B.T., Shin, C.S. Isolation and characterization of a novel intracellular glucosyltransferase from the acarbose producer Actinoplanes sp. CKD485-16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65, 273–280 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1639-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1639-x