Abstract
Introduction
Intracranial arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) display venous signals on arterial spin labeling (ASL) magnetic resonance (MR) imaging due to the presence of arteriovenous shunting. Our aim was to quantitatively correlate AVM signal intensity on ASL with the degree of arteriovenous shunting estimated on digital subtraction angiography (DSA) in AVMs.
Methods
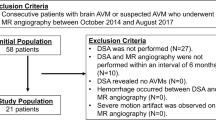
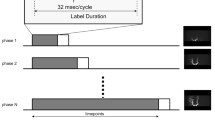
MR imaging including pseudo-continuous ASL at 3 T and DSA were obtained on the same day in 40 patients with intracranial AVMs. Two reviewers assessed the nidus and venous signal intensities on ASL images to determine the presence of arteriovenous shunting. Interobserver agreement on ASL between the reviewers was determined. ASL signal intensity of the AVM lesion was correlated with AVM size and the time difference between normal and AVM venous transit times measured from the DSA images.
Results
Interobserver agreement between two reviewers for nidus and venous signal intensities was excellent (κ = 0.80 and 1.0, respectively). Interobserver agreement regarding the presence of arteriovenous shunting was perfect (κ = 1.0). AVM signal intensity showed a positive relationship with the time difference between normal and AVM venous transit times (r = 0.638, P < 0.001). AVM signal intensity also demonstrated a positive relationship with AVM size (r = 0.561, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
AVM signal intensity on ASL in patients with AVM correlates well with the degree of early vein opacification on DSA, which corresponds to the degree of arteriovenous shunting.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hernesniemi JA, Dashti R, Juvela S, Vaart K, Niemela M, Laakso A (2008) Natural history of brain arteriovenous malformations: a long-term follow-up study of risk of hemorrhage in 238 patients. Neurosurgery 63:823–829
Crawford PM, West CR, Chadwick DW, Shaw MD (1986) Arteriovenous malformations of the brain: natural history in unoperated patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49:1–10
Ondra SL, Troupp H, George ED, Schwab K (1990) The natural history of symptomatic arteriovenous malformations of the brain: a 24-year follow-up assessment. J Neurosurg 73:387–391
Choi JH, Mohr JP (2005) Brain arteriovenous malformations in adults. Lancet Neurol 4:299–308
van Beijnum J, van der Worp HB, Buis DR et al (2011) Treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 306:2011–2019
Han JH, Kim DG, Chung HT et al (2008) Clinical and neuroimaging outcome of cerebral arteriovenous malformations after Gamma Knife surgery: analysis of the radiation injury rate depending on the arteriovenous malformation volume. J Neurosurg 109:191–198
Kaufmann TJ, Huston J 3rd, Mandrekar JN, Schleck CD, Thielen KR, Kallmes DF (2007) Complications of diagnostic cerebral angiography: evaluation of 19,826 consecutive patients. Radiology 243:812–819
Detre JA, Zhang W, Roberts DA et al (1994) Tissue specific perfusion imaging using arterial spin labeling. NMR Biomed 7:75–82
Kukuk GM, Hadizadeh DR, Bostrom A et al (2010) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations at 3.0 T: intraindividual comparative study of 4D-MRA in combination with selective arterial spin labeling and digital subtraction angiography. Investig Radiol 45:126–132
Wolf RL, Wang J, Detre JA, Zager EL, Hurst RW (2008) Arteriovenous shunt visualization in arteriovenous malformations with arterial spin-labeling MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:681–687
Pollock JM, Whitlow CT, Simonds J et al (2011) Response of arteriovenous malformations to gamma knife therapy evaluated with pulsed arterial spin-labeling MRI perfusion. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:15–22
Le TT, Fischbein NJ, Andre JB, Wijman C, Rosenberg J, Zaharchuk G (2012) Identification of venous signal on arterial spin labeling improves diagnosis of dural arteriovenous fistulas and small arteriovenous malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:61–68
Fernandez-Seara MA, Edlow BL, Hoang A, Wang J, Feinberg DA, Detre JA (2008) Minimizing acquisition time of arterial spin labeling at 3 T. Magn Reson Med 59:1467–1471
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (1986) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65:476–483
Hamilton MG, Spetzler RF (1994) The prospective application of a grading system for arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 34:2–6
Nornes H, Grip A, Wikeby P (1979) Intraoperative evaluation of cerebral hemodynamics using directional Doppler technique. Part 1: arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 50:145–151
Homan RW, Devous MD Sr, Stokely EM, Bonte FJ (1986) Quantification of intracerebral steal in patients with arteriovenous malformation. Arch Neurol 43:779–785
Nataf F, Meder JF, Roux FX et al (1997) Angioarchitecture associated with haemorrhage in cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a prognostic statistical model. Neuroradiology 39:52–58
Nornes H, Grip A (1980) Hemodynamic aspects of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 53:456–464
Norbash AM, Marks MP, Lane B (1994) Correlation of pressure measurements with angiographic characteristics predisposing to hemorrhage and steal in cerebral arteriovenous malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:809–813
Marks MP, Lane B, Steinberg GK, Chang PJ (1990) Hemorrhage in intracerebral arteriovenous malformations: angiographic determinants. Radiology 176:807–813
Kihlstrom L, Guo WY, Karlsson B, Lindquist C, Lindqvist M (1997) Magnetic resonance imaging of obliterated arteriovenous malformations up to 23 years after radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 86:589–593
Izawa M, Hayashi M, Chernov M et al (2005) Long-term complications after gamma knife surgery for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):34–37
Deibler AR, Pollock JM, Kraft RA, Tan H, Burdette JH, Maldjian JA (2008) Arterial spin-labeling in routine clinical practice, part 1: technique and artifacts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1228–1234
Ethical standards and patient consent
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by our Institutional Review Board and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that due to the retrospective nature of this study, informed consent was waived.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sunwoo, L., Sohn, CH., Lee, J.Y. et al. Evaluation of the degree of arteriovenous shunting in intracranial arteriovenous malformations using pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroradiology 57, 775–782 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1533-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1533-5