Abstract
Purpose
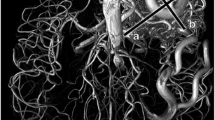
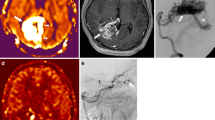
To evaluate the performance of acceleration-selective arterial spin labeling (AccASL) MR angiography in the visualization of brain arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) in comparison with digital subtraction angiography (DSA) and time-of-flight (TOF) MR angiography.
Methods
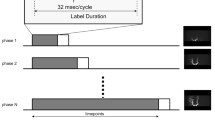
Twenty-one patients with brain AVM (mean age 31.1 ± 18.6 years; 11 males, 10 females) underwent TOF and AccASL MR angiography and DSA. Two neuroradiologists conducted an observer study for detection, nidus size, eloquence, venous drainage pattern, and Spetzler-Martin (SM) grade. The evaluations included the visualization of each AVM component with reference to DSA and assessments of contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR). The kappa statistic, repeated measures analysis of variance, Wilcoxon matched pairs test, and paired t test were used.
Results
Both observers detected more AVMs with AccASL (95.2%, 90.5% for Observers 1 and 2) than with TOF (76.2% and 71.4%, respectively). The inter-modality agreement between AccASL and DSA was almost perfect for the eloquence, venous drainage pattern, and SM grade for Observer 1 and moderate for the venous drainage pattern and substantial for the eloquence and SM grade for Observer 2. The visualization scores were higher with AccASL than with TOF for the feeding artery (AccASL, 4.5 ± 1.0 vs. TOF, 3.9 ± 1.5, p = 0.0214), nidus (4.6 ± 1.1 vs. 3.2 ± 1.5, p = 0.0006), and draining vein (4.6 ± 1.0 vs. 2.2 ± 1.1, p < 0.0001), respectively. The CNRs in the nidus were higher in AccASL than in TOF (29.9 ± 16.7 vs. 20.8 ± 16.5, p = 0.0002), as in the draining vein (23.2 ± 13.0 vs. 12.6 ± 12.0, p = 0.0010), respectively.
Conclusions
AccASL better visualized brain AVMs compared with TOF and was useful for grading without the use of contrast agents.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hernesniemi JA, Dashti R, Juvela S, Vaart K, Niemela M, Laakso A (2008) Natural history of brain arteriovenous malformations: a long-term follow-up study of risk of hemorrhage in 238 patients. Neurosurgery 63(5):823–829; discussion 829-831. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000330401.82582.5E
Laakso A, Dashti R, Juvela S, Isarakul P, Niemela M, Hernesniemi J (2011) Risk of hemorrhage in patients with untreated Spetzler-Martin grade IV and V arteriovenous malformations: a long-term follow-up study in 63 patients. Neurosurgery 68(2):372–377; discussion 378. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e3181ffe931
Morgan MK, Davidson AS, Assaad NNA, Stoodley MA (2017) Critical review of brain AVM surgery, surgical results and natural history in 2017. Acta Neurochir 159(8):1457–1478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3217-x
Marchal G, Bosmans H, Van Fraeyenhoven L, Wilms G, Van Hecke P, Plets C, Baert AL (1990) Intracranial vascular lesions: optimization and clinical evaluation of three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography. Radiology 175(2):443–448. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.175.2.2326471
Wilcock DJ, Jaspan T, Worthington BS (1995) Problems and pitfalls of 3-D TOF magnetic resonance angiography of the intracranial circulation. Clin Radiol 50(8):526–532
Huston J 3rd, Rufenacht DA, Ehman RL, Wiebers DO (1991) Intracranial aneurysms and vascular malformations: comparison of time-of-flight and phase-contrast MR angiography. Radiology 181(3):721–730. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.181.3.1947088
Priest AN, Taviani V, Graves MJ, Lomas DJ (2014) Improved artery-vein separation with acceleration-dependent preparation for non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography. Magn Reson Med 72(3):699–706. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.24981
Schmid S, Ghariq E, Teeuwisse WM, Webb A, van Osch MJ (2014) Acceleration-selective arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med 71(1):191–199. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.24650
Obara M, Togao O, Yoneyama M, Okuaki T, Shibukawa S, Honda H, Van Cauteren M (2016) Acceleration-selective arterial spin labeling for intracranial MR angiography with improved visualization of cortical arteries and suppression of cortical veins. Magn Reson Med 77:1996–2004. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26275
Togao O, Hiwatashi A, Obara M, Yamashita K, Kikuchi K, Kamei R, Nishimura A, Arimura K, Yoshimoto K, Iihara K, Van Cauteren M, Honda H (2017) Acceleration-selective arterial spin-labeling MR angiography used to visualize distal cerebral arteries and collateral vessels in moyamoya disease. Radiology:162279 286:611–621. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017162279
Akamine Y, Obara M, Togao O, Shibukawa S, Yoneyama M, Okuaki T, Van Cauteren M (2017) Robust visualization of MCA main trunk by improved acceleration-selective arterial spin labeling (iAccASL) for intracranial MR angiography. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med 25:361
Obara M, Togao O, Yoneyama M, Okuaki T, Shibukawa S, Honda H, Van Cauteren M (2017) Acceleration-selective arterial spin labeling for intracranial MR angiography with improved visualization of cortical arteries and suppression of cortical veins. Magn Reson Med 77(5):1996–2004. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26275
Togao O, Hiwatashi A, Obara M, Yamashita K, Kikuchi K, Kamei R, Nishimura A, Arimura K, Yoshimoto K, Iihara K, Van Cauteren M, Honda H (2018) Acceleration-selective arterial spin-labeling MR angiography used to visualize distal cerebral arteries and collateral vessels in moyamoya disease. Radiology 286(2):611–621. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017162279
Tsuchiya K, Kobayashi K, Nitatori T, Kimura T, Ikedo M, Takemoto S (2010) Hybrid of opposite-contrast MRA of the brain by combining time-of-flight and black-blood sequences: initial experience in major trunk stenoocclusive diseases. J Magn Reson Imaging 31(1):56–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.21997
Wu H, Block WF, Turski PA, Mistretta CA, Johnson KM (2013) Noncontrast-enhanced three-dimensional (3D) intracranial MR angiography using pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling and accelerated 3D radial acquisition. Magn Reson Med 69(3):708–715. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.24298
Kauczor HU, Engenhart R, Layer G, Gamroth AH, Wowra B, Schad LR, Semmler W, van Kaick G (1993) 3D TOF MR angiography of cerebral arteriovenous malformations after radiosurgery. J Comput Assist Tomogr 17(2):184–190
Ehricke HH, Schad LR, Gademann G, Wowra B, Engenhart R, Lorenz WJ (1992) Use of MR angiography for stereotactic planning. J Comput Assist Tomogr 16(1):35–40
Blatter DD, Parker DL, Ahn SS, Bahr AL, Robison RO, Schwartz RB, Jolesz FA, Boyer RS (1992) Cerebral MR angiography with multiple overlapping thin slab acquisition. Part II. Early clinical experience. Radiology 183(2):379–389. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.183.2.1561338
Duran M, Schoenberg SO, Yuh WT, Knopp MV, van Kaick G, Essig M (2002) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations: morphologic evaluation by ultrashort 3D gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography. Eur Radiol 12(12):2957–2964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-002-1418-y
Fujima N, Osanai T, Shimizu Y, Yoshida A, Harada T, Nakayama N, Kudo K, Houkin K, Shirato H (2016) Utility of noncontrast-enhanced time-resolved four-dimensional MR angiography with a vessel-selective technique for intracranial arteriovenous malformations. J Magn Reson Imaging 44(4):834–845. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25222
Raoult H, Bannier E, Robert B, Barillot C, Schmitt P, Gauvrit JY (2014) Time-resolved spin-labeled MR angiography for the depiction of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a comparison of techniques. Radiology 271(2):524–533. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13131252
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Yukiko N. Kami for useful discussions on the statistical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
MO and MVC are employees of Philips Japan.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Togao, O., Hiwatashi, A., Yamashita, K. et al. Acceleration-selective arterial spin labeling MR angiography for visualization of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology 61, 979–989 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02217-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02217-w