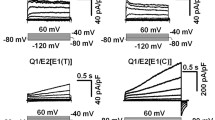
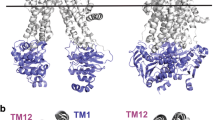
Abstract
KCNE1-KCNE5 are single membrane-spanning proteins that associate with voltage-gated potassium channels to diversify their function. Other than the KCNQ1/KCNE1 complex, little is known about how KCNE proteins work. We focus on KCNE2, which associates with KCNQ1 to form K channels critical for gastric acid secretion in parietal cells. We use cysteine (Cys)-scanning mutagenesis to probe the functional role of residues along the KCNE2 transmembrane domain (TMD) in modulating KCNQ1 function. There is an α-helical periodicity in how Cys substitutions along the KCNE2 TMD perturb KCNQ1 pore conductance/ion selectivity. However, positions where Cys substitutions perturb KCNQ1 gating kinetics cluster to the extracellular end and cytoplasmic half of the KCNE2 TMD. This is the first systematic perturbation analysis of a KCNE TMD. We propose that the KCNE2 TMD adopts an α-helical secondary structure with one face making intimate contact with the KCNQ1 pore domain, while the contacts with the KCNQ1 voltage-sensing domain appear more dynamic.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott GW, Goldstein SAN (1998) A superfamily of small potassium channel subunits: form and function of the MinK-related peptides (MiRPs). Q Rev Biophys 31:357–398
Abbott GW, Goldstein SAN (2002) Disease-associated mutations in KCNE potassium channel subunits (MiRPs) reveal promiscuous disruption of multiple currents and conservation of mechanism. FASEB J 16:390–400
Aggeli A, Bannister ML, Bell M, Boden N, Findlay JBC, Hunter M, Knowles PF, Yang J-C (1998) Conformation and ion-channeling activity of a 27-residue peptide modeled on the single-transmembrane segment of the IsK (minK) protein. Biochemistry 37:8121–8131
Bendahhou S, Marionneau C, Haurogne K, Larroque M-M, Derand R, Szuts V, Escande D, Demolombe S, Barhanin J (2005) In vitro molecular interactions and distribution of KCNE family with KCNQ1 in the human heart. Cardiovasc Res 67:529–538
Chandrasekhar KD, Bas T, Kobertz WR (2006) KCNE1 subunits require co-assembly with K+ channels for efficient trafficking and cell surface expression. J Biol Chem 281:40015–40023
Chen Y-H, Xu S-J, Bendahhou S, Wang X-L, Wang Y, Xu W-Y, Jin H-W, Sun H, Su X-Y, Zhuang Q-N, Yang Y-Q, Li Y-B, Liu Y, Xu H-J, Li X-F, Ma N, Mou C-P, Chen Z, Barhanin J, Huang W (2003) KCNQ1 gain-of-function mutation in familial atrial fibrillation. Science 299:251–254
Franqueza L, Lin M, Shen J, Keating MT, Sanguinetti MC (1999) Long QT syndrome-associated mutations in the S4-S5 linker of KvLQT1 potassium channels modify gating and interaction with minK subunits. J Biol Chem 274:21063–21070
Goldstein SAN, Miller C (1991) Site-specific mutations in a minimal voltage-dependent K+ channel alter ion selectivity and open-channel block. Neuron 7:403–408
Hong K, Piper DR, Diaz-Valdecantos A, Brugada J, Oliva A, Burashnikov E, Santos-de-Soto J, Grueso-Montero J, Diaz-Enfante E, Brugada P, Saches F, Sanguinetti MC, Brugada R (2005) De novo KCNQ1 mutation responsible for atrial fibrillation and short QT syndrome in utero. Cardiovasc Res 68:433–440
Isbrandt D, Friederich P, Solth A, Haverkamp W, Ebneth A, Borggrefe M, Funke H, Sauter K, Breithardt G, Pongs O, Schulze-Bahr E (2002) Identification and functional characterization of a novel KCNE2 (MiRP1) mutation that alters HERG channel kinetics. J Mol Med 80:524–532
LeMasurier M, Heginbotham L, Miller C (2001) KcsA: it’s a potassium channel. J Gen Physiol 118:303–313
Lerche C, Seebohm G, Wagner C, Scherer CR, Dehmelt L, Abitbol I, Gerlach U, Brendel J, Attali B, Busch AE (2000) Molecular impact of minK on the enantiospecific block of I Ks by chromanols. Br J Pharmacol 131:1503–1506
Liu J, Zhang M, Jiang M, Tseng G-N (2002) Structural and functional role of the extracellular S5-P linker in the HERG potassium channel. J Gen Physiol 120:723–737
Long SB, Campbell EB, MacKinnon R (2005) Voltage sensor of Kv1.2: structural basis of electromechanical coupling. Science 309:903–908
Lu Z, Klem AM, Ramu Y (2002) Coupling between voltage sensors and activation gate in voltage-gated K+ channels. J Gen Physiol 120:663–676
Melman YF, Demenech A, de la Luna S, McDonald TV (2001) Structural determinants of KvLQT1 control by the KCNE1 family of proteins. J Biol Chem 276:6439–6444
Melman YF, Krumerman A, McDonald TV (2002) A single transmembrane site in the KCNE-encoded proteins controls the specificity of KvLQT1 channel gating. J Biol Chem 277:25187–25194
Morais Cabral JH, Zhou Y, MacKinnon R (2001) Energetic optimization of ion conduction rate by the K+ selectivity filter. Nature 414:37–42
Popot J-L, Engelman DM (2000) Helical membrane protein folding, stability, and evolution. Annu Rev Biochem 69:881–922
Roepke TK, Anantharam A, Kirchhof P, Busque SM, Young JB, Geibel JP, Lerner DJ, Abbott GW (2006) The KCNE2 potassium channel ancillary subunit is essential for gastric acid secretion. J Biol Chem 281:23740–23747
Sanguinetti MC, Curran ME, Zou A, Shen J, Spector PS, Atkinson DL, Keating MT (1996) Coassembly of KvLQT1 and minK (IsK) proteins to form cardiac I Ks potassium channel. Nature 384:80–83
Schreibmayer W, Lester HA, Dascal N (1994) Voltage clamping of Xenopus laevis oocytes utilizing agarose-cushion electrodes. Pfluegers Archiv 426:453–458
Sesti F, Goldstein SAN (1998) Single-channel characteristics of wild-type I Ks channels and channels formed with two minK mutants that cause long QT syndrome. J Gen Physiol 112:651–663
Tai KK, Goldstein SAN (1998) The conduction pore of a cardiac potassium channel. Nature 391:605–608
Takumi T, Moriyoshi K, Aramori I, Ishii T, Oiki S, Okada Y, Ohkubo H, Nakanishi S (1991) Alteration of channel activities and gating by mutations of slow I SK potassium channel. J Biol Chem 266:22192–22198
Tapper AR, George AL Jr (2000) MinK subdomains that mediate modulation of and association with KvLQT1. J Gen Physiol 116:379–390
Tapper AR, George AL Jr (2001) Location and orientation of minK within the I Ks potassium channel complex. J Biol Chem 276:38249–38254
Teng S, Ma L, Zhen Y, Lin C-X, Bahring R, Vardanyan V, Pongs O, Hui R (2003) Novel gene hKCNE4 slows the activation of the KCNQ1 channel. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:808–813
Wang K-W, Tai KK, Goldstein SAN (1996) MinK residues line a potassium channel pore. Neuron 16:571–577
Wilson GG, Sivaprasadarao A, Findlay JBC, Wray D (1994) Changes in activation gating of I sK potassium currents brought about by mutations in the transmembrane sequence. FEBS Lett 353:251–254
Wu D-M, Jiang M, Zhang M, Liu X-S, Korolkova YV, Tseng G-N (2006a) KCNE2 is colocalized with KCNQ1 and KCNE1 in cardiac myocytes and may function as a negative modulator of I Ks current amplitude in the heart. Heart Rhythm 3:1469–1480
Wu D-M, Lai L-P, Zhang M, Wang H-L, Jiang M, Liu X-S, Tseng G-N (2006b) Characterization of an LQT5-related mutation in KCNE1, Y81C: implications for a role of KCNE1 cytoplasmic domain in I Ks channel function. Heart Rhythm 3:1031–1040
Zhang M, Jiang M, Tseng G-N (2001) MinK-related peptide 1 associates with Kv4.2 and modulates its gating function. A potential role as ß subunit of cardiac transient outward channel. Circ Res 88:1012–1019
Zhang M, Liu J, Jiang M, Wu DM, Sonawane K, Guy HR, Tseng G-N (2005) Interactions between charged residues in the transmembrane segments of voltage-sensing domain of the hERG channel. J Membr Biol 207:169–181
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by HL 67840 and HL 46451 from National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health (to G. N. T.) and a grant-in-aid award from American Heart Association/Mid-Atlantic Affiliate (to M. Z.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, XS., Zhang, M., Jiang, M. et al. Probing the Interaction Between KCNE2 and KCNQ1 in Their Transmembrane Regions. J Membrane Biol 216, 117–127 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-007-9047-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-007-9047-7