Abstract
Rationale
Illicit drugs such as methamphetamine are commonly abused drugs that have also been observed to be prevalent in drivers injured in road accidents. The exact effect of methamphetamine or its specific isomers on driving and driving behaviour have yet to be thoroughly investigated.
Methods
Twenty healthy recreational illicit stimulant users (ten males, ten females), aged between 21 and 34 years (mean = 24.3 years, SD = 3.4 years), attended two testing sessions involving oral consumption of 0.42 mg/kg d,l-methamphetamine or a matching placebo. The drug administration was counterbalanced, double-blind, and medically supervised. At each session, driving performance was assessed 2.5 h post-drug administration.
Results
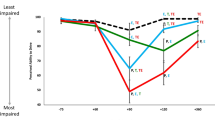
Mean blood and saliva d,l-methamphetamine concentrations of approximately 90 and 400 ng/ml, respectively, at 2 h and 95 and 475 ng/ml at 3 h were observed. These levels of d,l-methamphetamine were found not to significantly impair, or improve, driving performance at the 2.5-h post-drug administration time point.
Conclusions
The findings of this study illustrate that d,l-methamphetamine has no significant effect on simulated driving performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angrist B, Corwin J, Bartlik B, Cooper T (1987) Early pharmacokinetics and clinical effects of oral d-amphetamine in normal subjects. Biological Psychiatry 22:1357–1368
Brauer LH, Ambre J, de Wit H (1996) Acute tolerance to subjective but not cardiovascular effects of d-amphetamine in normal healthy men. J Clin Psychopharmacol 16(1):72–76
Brookhuis KA, De Waard D, Samyn N (2004) Effects of MDMA (ecstasy), and multiple drugs use on (simulated) driving performance and traffic safety. Psychopharmacology 173(3–4):440–445
Dastrup E, Lees MN, Bechara A, Dawson JD, Rizzo M (2010) Risky car following in abstinent users of MDMA. Accid Anal Prev 42(3):867–873
Drummer OH, Gerostamoulos D, Chu M, Swann P, Boorman M, Cairns I (2007) Drugs in oral fluid in randomly selected drivers. Forensic Sci Int 170(2–3):105–110
Drummer OH, Gerostamoulos J, Batziris H, Chu M, Caplehorn J, Robertson MD, Swann P (2004) The involvement of drugs in drivers of motor vehicles killed in Australian road traffic crashes. Accid Anal Prev 36:239–248
Drummer OH, Gerostamoulos J, Batziris H, Chu M, Caplehorn JRM, Robertson MD et al (2003) The incidence of drugs in drivers killed in Australian road traffic crashes. Forensic Sci Int 134(2–3):154–162
Drummer OH, Kourtis I, Beyer J, Tayler P, Boorman M, and Gerostamoulos D (2011) The prevalence of drugs in injured drivers. Forensic Sci Int. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2011.01.040
Hardman JG, Limbird LE (1996) Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 9th edn. McGraw-Hill Companies, New York, USA
Kupietz SS, Bartlik B, Angrist B, Winsberg BG (1985) Psychostimulant plasma concentration and learning performance. J Clin Psychopharmacol 5(5):293–295
Kuypers KPC, Samyn N, Ramaekers JG (2006) MDMA and alcohol effects, combined and alone, on objective and subjective measures of actual driving performance and psychomotor function. Psychopharmacology 187(4):467–475
Lacey JH, Kelley-Baker T, Furr-Holden D, Voas RB, Romano E, Ramirez A et al (2009) 2007 national roadside survey of alcohol and drug use by drivers: drug results. National Highway Safety Administration, Washington DC
Lemos NP (2009) Methamphetamine and driving. Sci Justice 49(4):247–249
Logan BK (2002) Methamphetamine - effects on human performance and behaviour. Forensic Sci Rev 14(1/2):133–151
Logan BK (2001) Amphetamines: an update on forensic issues. J Anal Toxicol 25(5):400–404
Logon BK, Schwilke EW (1996) Drug and alcohol use in fatally injured drivers in Washington State. J Forensic Sci 41(3):505–510
Mitler MM, Hajdukovic R, Erman MK (1993) Treatment of narcolepsy with methamphetamine. Sleep 16(4):306–317
Moeller MR, Kraemer T (2002) Drugs of abuse monitoring in blood for control of driving under the influence of drugs. Ther Drug Monit 24(2):210–221
Ogden EJD, Moskowitz H (2004) Effects of alcohol and other drugs on driver performance. Traffic Inj Prev 5(3):185–198
Papafotiou K, Carter JD, Stough C (2005) An evaluation of the sensitivity of the Standardised Field Sobriety Tests (SFSTs) to detect impairment due to marijuana intoxication. Psychopharmacology 180(1):107–114
Ramaekers JG, Kuypers KPC, Samyn N (2006) Stimulant effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) 75 mg and methylphenidate 20 mg on actual driving during intoxication and withdrawal. Addiction 101(11):1614–1621
Schwilke EW, Sampaio Dos Santos MI, Logan BK (2006) Changing patterns of drug and alcohol use in fatally injured drivers in Washington State. J Forensic Sci 51(5):1191–1198
Senna MC, Augsburger M, Aebi B, Briellmann TA, Donzé N, Dubugnon JL et al (2010) First nationwide study on driving under the influence of drugs in Switzerland. Forensic Sci Int 198(1–3):11–16
Silber BY, Croft RJ, Papafotiou K, Stough C (2006) The acute effects of d-amphetamine and methamphetamine on attention and psychomotor performance. Psychopharmacology 187(2):154–169
Silber BY, Papafotiou K, Croft RJ, Ogden E, Swann P, Stough C (2005) The effects of dexamphetamine on simulated driving performance. Psychopharmacology 179(3):536–543
Walsh JM, De Gier JJ, Christopherson AS, Verstraete AG (2004) Drugs and driving. Traffic Inj Prev 5(3):241–253
Acknowledgements
This research was partially funded by a grant from VicRoads, Melbourne, Australia, and an Australian Research Council Discovery grant (DP0772762) to Professor Con Stough, Katherine Papafotiou and Edward Ogden.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silber, B.Y., Croft, R.J., Downey, L.A. et al. The effect of d,l-methamphetamine on simulated driving performance. Psychopharmacology 219, 1081–1087 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2437-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2437-7