Abstract.
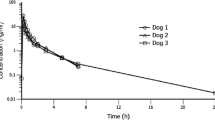
We examined the effect of intracisternal application of endothelin-1 (ET-1) on the permeability of fluorescein into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in beagle dogs in order to evaluate its role in disruption of blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability seen in the subarachnoid hemorrhage animal model. Intracisternal application of their autologous blood for producing a canine two-hemorrhage model revealed an enhanced fluorescein permeability into the CSF together with the development of cerebral vasospasm. A single dose of ET-1 (40 pmol/animal) significantly increased penetration of fluorescein compared with that in normal dogs. Although its magnitude was much less than that in the two-hemorrhage model after the first administration of ET-1, the second challenge of the same dose of ET-1 with a 48-h interval produced marked disruption of BBB permeability similar to those in the animal model. Moreover, the ET-1-induced enhancement of fluorescein permeability into the CSF was completely prevented by intracisternal pretreatment with an endothelin ETA-receptor selective antagonist, S-0139 (0.03 mg/kg), as were the ET-1-induced cerebral vasoconstriction and behavioral changes as previously reported. Thus, we conclude that ET-1 acting on the adventitial site of brain in dogs contributes to the disruption of BBB permeability via endothelin ETA-receptor mediation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narushima, I., Kita, T., Kubo, K. et al. Contribution of endothelin-1 to disruption of blood-brain barrier permeability in dogs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 360, 639–645 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002109900137
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002109900137