Abstract
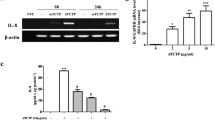
Translationally controlled tumor protein (TCTP) is believed to be involved in a variety of inflammatory processes: secretion of histamine and cytokines such as IL-4, IL-8, IL-13, and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor; chemoattraction for eosinophils; augmentation of B cell proliferation; and immunoglobulin production, thereby potentially regulating allergic phenomena. In a previous study, we showed that the cytokine-releasing activity of extracellular TCTP is generated only when TCTP dimerizes via the intermolecular disulfide bond of NH2-terminal truncated TCTP implying that the dimerized TCTP (dTCTP) promotes the inflammatory phenomena. Modulation of dTCTP, thus, may offer a strategy for the treatment of chronic allergic diseases. In this study, we searched for dTCTP-binding peptides (dTBPs) by screening a phage-displayed 7-mer peptide library. We identified one peptide in the library, designated as dTBP2, which showed higher affinity to dTCTP than to full-length, monomeric TCTP. dTBP2 inhibited the induction of IL-8 by dTCTP from BEAS-2B cells. dTBP2 also reduced symptom score and eosinophil infiltration in a mouse rhinitis model. This study suggests that the dTBP2 binding to dTCTP modulates the release of inflammatory mediators of dTCTP. This result may provide a rational strategy for the treatment of allergic diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calderon MA, Lozewicz S, Prior A, Jordan S, Trigg CJ, Davies RJ (1994) Lymphocyte infiltration and thickness of the nasal mucous membrane in perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 93:635–643
Borish L, Rosenwasser LJ (1996) Update on cytokines. J Allergy Clin Immunol 97:719–733, quiz 734
Bascom R, Wachs M, Naclerio RM, Pipkorn U, Galli SJ, Lichtenstein LM (1988) Basophil influx occurs after nasal antigen challenge: effects of topical corticosteroid pretreatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol 81:580–589
Bochner BS, Schleimer RP (1994) The role of adhesion molecules in human eosinophil and basophil recruitment. J Allergy Clin Immunol 94:427–438, quiz 439
Borish LC, Nelson HS, Corren J, Bensch G, Busse WW, Whitmore JB, Agosti JM (2001) Efficacy of soluble IL-4 receptor for the treatment of adults with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 107:963–970
Sun Q, Jones K, McClure B, Cambareri B, Zacharakis B, Iversen PO, Stomski F, Woodcock JM, Bagley CJ, D’Andrea R et al (1999) Simultaneous antagonism of interleukin-5, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and interleukin-3 stimulation of human eosinophils by targeting the common cytokine binding site of their receptors. Blood 94:1943–1951
Lack G, Bradley KL, Hamelmann E, Renz H, Loader J, Leung DY, Larsen G, Gelfand EW (1996) Nebulized IFN-gamma inhibits the development of secondary allergic responses in mice. J Immunol 157:1432–1439
Schwarze J, Hamelmann E, Cieslewicz G, Tomkinson A, Joetham A, Bradley K, Gelfand EW (1998) Local treatment with IL-12 is an effective inhibitor of airway hyperresponsiveness and lung eosinophilia after airway challenge in sensitized mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol 102:86–93
Shields RL, Whether WR, Zioncheck K, O’Connell L, Fendly B, Presta LG, Thomas D, Saban R, Jardieu P (1995) Inhibition of allergic reactions with antibodies to IgE. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 107:308–312
Corne J, Djukanovic R, Thomas L, Warner J, Botta L, Grandordy B, Gygax D, Heusser C, Patalano F, Richardson W et al (1997) The effect of intravenous administration of a chimeric anti-IgE antibody on serum IgE levels in atopic subjects: efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics. J Clin Invest 99:879–887
Ciprandi G, Tosca MA, Cosentino C, Riccio AM, Passalacqua G, Canonica GW (2003) Effects of fexofenadine and other antihistamines on components of the allergic response: adhesion molecules. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112:S78–S82
MacDonald SM, Rafnar T, Langdon J, Lichtenstein LM (1995) Molecular identification of an IgE-dependent histamine-releasing factor. Science 269:688–690
Schroeder JT, Lichtenstein LM, MacDonald SM (1997) Recombinant histamine-releasing factor enhances IgE-dependent IL-4 and IL-13 secretion by human basophils. J Immunol 159:447–452
Bheekha-Escura R, MacGlashan DW, Langdon JM, MacDonald SM (2000) Human recombinant histamine-releasing factor activates human eosinophils and the eosinophilic cell line, AML14-3D10. Blood 96:2191–2198
Yoneda K, Rokutan K, Nakamura Y, Yanagawa H, Kondo-Teshima S, Sone S (2004) Stimulation of human bronchial epithelial cells by IgE-dependent histamine-releasing factor. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286:L174–L181
Kang HS, Lee MJ, Song H, Han SH, Kim YM, Im JY, Choi I (2001) Molecular identification of IgE-dependent histamine-releasing factor as a B cell growth factor. J Immunol 166:6545–6554
Kim M, Min HJ, Won HY, Park H, Lee JC, Park HW, Chung J, Hwang ES, Lee K (2009) Dimerization of translationally controlled tumor protein is essential for its cytokine-like activity. PLoS ONE 4:e6464
Teshima S, Rokutan K, Nikawa T, Kishi K (1998) Macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates synthesis and secretion of a mouse homolog of a human IgE-dependent histamine-releasing factor by macrophages in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol 161:6356–6366
Gnanasekar M, Rao KV, Chen L, Narayanan RB, Geetha M, Scott AL, Ramaswamy K, Kaliraj P (2002) Molecular characterization of a calcium binding translationally controlled tumor protein homologue from the filarial parasites Brugia malayi and Wuchereria bancrofti. Mol Biochem Parasitol 121:107–118
Li F, Zhang D, Fujise K (2001) Characterization of fortilin, a novel antiapoptotic protein. J Biol Chem 276:47542–47549
Gachet Y, Tournier S, Lee M, Lazaris-Karatzas A, Poulton T, Bommer UA (1999) The growth-related, translationally controlled protein P23 has properties of a tubulin binding protein and associates transiently with microtubules during the cell cycle. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 8):1257–1271
Kim M, Jung Y, Lee K, Kim C (2000) Identification of the calcium binding sites in translationally controlled tumor protein. Arch Pharm Res 23:633–636
Bommer UA, Thiele BJ (2004) The translationally controlled tumour protein (TCTP). Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:379–385
Norzila MZ, Fakes K, Henry RL, Simpson J, Gibson PG (2000) Interleukin-8 secretion and neutrophil recruitment accompanies induced sputum eosinophil activation in children with acute asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161:769–774
Moqbel R, Levi-Schaffer F, Kay AB (1994) Cytokine generation by eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 94:1183–1188
Clutterbuck EJ, Hirst EM, Sanderson CJ (1989) Human interleukin-5 (IL-5) regulates the production of eosinophils in human bone marrow cultures: comparison and interaction with IL-1, IL-3, IL-6, and GMCSF. Blood 73:1504–1512
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs (A090030), Mid-career Research Program through NRF grant funded by the MEST (R01-2007-000-20263-0), Seoul R&BD Program (ST090801), and the NCRC program of MOST/KOSEF (R15-2006-020) to Kyunglim Lee, Ewha Womans University (2010) to Miyoung Kim, and William F. Milton Fund to Guido Guidotti.
Disclosures
M. Kim and K. Lee have submitted an application for a patent on the use of the peptides to treat allergic diseases.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 31 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M., Chung, J., Lee, C. et al. A peptide binding to dimerized translationally controlled tumor protein modulates allergic reactions. J Mol Med 89, 603–610 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0740-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0740-8