Summary
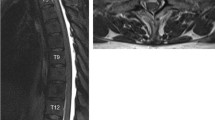
A hydrocephalic-hydromyelic condition was induced in adult cats by causing the closure of the lateral apertures with intracisternal injections of kaolin. After displaying the symptoms characteristic of increased intracranial pressure, which lasted about 10–14 days but varied somewhat in intensity from animal to animal, the cats recovered. From approximately the 2nd post-operative week onward, a distended central canal was revealed by ventriculography; subsequently cavities developed in the tissue of the cord that communicated with the canal. Most cavities were located dorsal to the canal. The surfaces of the distended canal and the cavities showed that in ventral areas the ependyma streched but remained intact, whereas in dorsal areas it ruptured, exposing the nerve fibers to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). In cats which had been hydrocephalic for up to 2 years the walls of the cavities were covered by gliotic scar tissue; the nerve fibers were no longer exposed directly to the CSF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker DP, Wilson JA, Watson GW (1972) The spinal cord central canal: response to experimental hydrocephalus and canal occlusion. J Neurosurg 36:416–424
Bleier R, Albrecht R, Cruce J (1975) Supraependymal cells of hypothalamic third ventricle: identification as resident phagocytes of the brain. Science 189:299–301
Booz KH, Faulhauer K, Donauer E, Nieland F (1979) Morphologische Veränderungen am Zentralkanal der Katze nach Kaolin-Injektion in der Cisterna magna. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 93:643–661
Brocklehurst G, Dolman GS, Hochwald GM (1977) Serial section study of the terminal spinal cord in the normal and the kaolin hydrocephalic cat. Z Kinderchir 22:553–560
Clark RG, Milhorat TH (1970) Experimental hydrocephalus. Part 3. Light microscopic findings in acute and subacute obstructive hydrocephalus in the monkey. J Neurosurg 32:400–413
Clementi F, Marini D (1972) The surface fine structure of the walls of the cerebral ventricles and choroid plexus in the cat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 123:82–95
Dohrmann GJ (1972) Cervical spinal cord in experimental hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 37:538–542
Eisenberg HM, McLennan JE, Welch K, Treves S (1974a) Radioisotope ventriculography in cats with kaolin-induced hydrocephalus. Radiology 110:399–402
Eisenberg HM, McLennan JE, Welch K (1974b) Ventricular perfusion in cats with kaolin-induced hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 41:20–28
Faulhauer K, Donauer E (1985) Experimental hydrocephalus and hydrosyringomyelia in the cat. Radiological findings. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 74:72–80
Flor WJ, James AE, Ribas JL, Parker JL, Sickel WL (1979) Ultrastructure of the ependyma in the lateral ventricles of primates with experimental communicating hydrocephalus. Scan Electron Microsc 3:47–54
Gardner WJ (1965) Hydrodynamic mechanism of syringomyelia: its relationship to myeloceie. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 28:247–259
Garfia A, Mestres P, Rascher K (1980) Trinitrophenol lesions of the ventricular wall: A SEM-TEM study. Scan Electron Microsc 3:449–456
Go KG, Stokroos I, Blaauw EH, Zuiderveen F, Molenaar I (1976) Changes of the ventricular ependyma and choroid plexus in experimental hydrocephalus, as observed by scanning electron microscopy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 34:55–64
Gonzalez-Darder J, Barbera J, Cerda-Nicolas M, Segura D, Broseta J, Barcia-Salorio JL (1984) Sequential morphological and funcitional changes in kaolin-induced hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 61:918–924
Hall PV, Muller J, Campbell RL (1975) Experimental hydrosyringomyelia, ischemic myelopathy, and syringomyelia. J Neurosurg 43:464–470
Hall PV, Godersky J, Campbell R, Kalsbeck J (1977) A study of experimental syringomyelia by scanning electron microscopy. Neurosurgery 1:41–47
Hamilton WJ, Mossman HW (1972) Spinal Cord. In: Human embryology. Prenatal development of form and function. Heffer and Sons, Cambridge, pp 448–453
Hochwald GM, Nakamura S, Camins MB (1981) The rat in experimental obstructive hydrocephalus. Z Kinderchir 34:403–410
James AE, Flor WJ, Noak GR, Strecker E-P, Burns B (1978) Evaluation of the central canal of the spinal cord in experimentally induced hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 48:970–974
Leslie RA, Gwyn DG, Morrison CM (1978) The fine structure of the ventricular surface of the area postrema of the cat, with particular reference to supraependymal structures. Am J Anat 153:173–290
Lindberg LA, Vasenius L, Talanti S (1977) The surface fine structure of the ependymal lining of the lateral ventricles in rats with hereditary hydrocephalus. Cell Tissue Res 179:121–129
McLaurin RL, Baily OT, Schurr PH, Ingraham FD (1954) Myelomalacia and multiple cavitations of spinal cord secondary to adhesive arachnoiditis. Arch Pathol 57:138–146
Mestres P, Breipohl W (1976) Morphology and distribution of supraependymal cells in the third ventricle of the albino rat. Cell Tissue Res 168:303–314
Nakamura S, Camins MB, Hochwald GM (1983) Pressureabsorption responses to the infusion of fluid into the spinal cord central canal of kaolin-hydrocephalic cats. J Neurosurg 58:198–203
Netsky MG (1953) Syringomyelia. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 70:741–777
Nielson SL, Gauger GE (1974) Experimental hydrocephalus: surface alterations of the lateral ventricle. Scanning electron microscope studies. Lab Invest 30:618–625
Ogata J, Hochwald GM, Cravioto H, Ranshoff J (1972) Light and electron microscopic studies of experimental hydrocephalus. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 21:213–223
Page R (1975) Scanning electron microscopy of the ventricular system in normal and hydrocephalic rabbits. J Neurosurg 42:646–664
Rascher K, Mestres P (1980) Reaction of the hypothalamic ventricular lining following systemic administration of MSG. Scan Electron Microsc 3:451–464
Rascher K, Booz KH, Nacimiento AC, Donauer E (1985) The ependyma of the cat central canal, with particular reference to its mitochondria-containing bulbs. Scan Electron Microsc 1:231–238
Schlesinger EB, Antunes JL, Michlsen WJ, Louis KM (1981) Hydromyelia: clinical presentation and comparison of modalities of treatment. Neurosurgery 9:356–365
Torvik A, Stenwig AE (1977) The pathology of experimental obstructive hydrocephalus. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 38:21–26
Torvik A, Murthy VS (1977) the spinal cord central canal in kaolin-induced hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 47:397–402
Williams B (1969) The distending force in the production of “communicating syringomyelia”. Lancet ii:189–193
Williams B, Fahy G (1983) A critical appraisal of “terminal ventriculostomy” for the treatment of syringomyelia. J Neurosurg 58:188–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rascher, K., Booz, K.H., Donauer, E. et al. Structural alterations in the spinal cord during progressive communicating syringomyelia. An experimental study in the cat. Acta Neuropathol 72, 248–255 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691097
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691097