Abstract
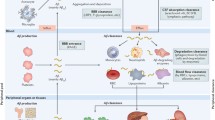
With the advent of novel therapies for Alzheimer’s disease, there is a pressing need for biomarkers that are easy to monitor, such as the amyloid-beta (Aβ) levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma. To gain a better understanding of the explanatory power of these biomarkers, we formulate and analyze a compartmental mathematical model for the Aβ accumulation in the brain, CSF and plasma, throughout the course of Alzheimer’s treatment. Our analysis reveals that the total Aβ burden in the brain is dictated by a unitless quantity called the polymerization ratio, which is the product of the production and elongation rates divided by the product of the fragmentation and loss rates. In this ratio, the production rate and loss rate include a source and sink term, respectively, related to the intercompartmental transport. Our results suggest that production inhibitors are likely to reduce the Aβ levels in all three compartments. In contrast, agents that ingest monomers off of polymers, or that increase fragmentation or block elongation, may also reduce Aβ burden in the brain, but may produce little change in—or even transiently increase—CSF and plasma Aβ levels. Hence, great care must be taken when interpreting these biomarkers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ard, M. D., G. M. Cole, J. Wei, A. P. Mehrle and J. D. Fratkin (1996). Scavenging of Alzheimer’s amyloid β-protein by microglia in culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 43, 190–202.
Arriagada, P. V., J. H. Growdon, E. T. Hedley-Whyte and B. T. Hyman (1992). Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 42, 631–639.
Bard, F. et al. (2000). Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid β-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat. Med. 6, 916–919.
Berg, L., D. W. McKeel, J. P. Miller, J. Baty and J. C. Morris (1993). Neuropathological indexes of Alzheimer’s disease in demented and nondemented persons aged 80 years and older. Arch. Neurol. 50, 349–358.
Betz, A. L., G. W. Goldstein and R. Katzman (1989). Blood-brain-cerebrospinal fluid barriers, Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular, and Medical Aspects, Chap. 30, 4th edn, G. J. Siegel (Ed.), New York: Raven Press Ltd.
Biere, A. L., B. Ostaszewski, E. R. Stimson, B. T. Hyman, J. E. Maggio and D. J. Selkoe (1996). Amyloid β-peptide is transported on lipoproteins and albumin in human plasma. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 32916–32922.
Calhoun, M. E., P. Burgermeister, A. L. Phinney, M. Stalder, M. Tolnay, K.-H. Wiederhold, D. Abramowski, C. Sturchler-Pierrat, B. Sommer, M. Staufenbiel and M. Jucker (1999). Neurol overexpression of mutant amyloid pre-cursor protein results in prominent deposition of cerebrovascular amyloid. Neurobiology 96, 14088–14093.
Chauhan, V. P. S., I. Ray, A. Chauhan and H. M. Wisniewski (1999). Binding of gelsolin, a secretory protein, to amyloid β-protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 258, 241–246.
Come, J. H., P. E. Fraser and P. T. Lansbury (1993). A kinetic model for amyloid formation in the prion diseases: importance of seeding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 5959–5963.
Craft, D. L., L. M. Wein and D. J. Selkoe (2001). The impact of novel treatments on Aβ burden in Alzheimer’s disease: insights from a mathematical model. Submitted for publication.
Cruz, L., B. Urbanc, S. V. Buldyrev, R. Christie, T. Gomez-Isla, S. Havlin, M. McNamara, H. E. Stanley and B. T. Hyman (1997). Aggregation and disaggregation of senile plaques in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 7612–7616.
DeMattos, R. B., K. R. Bales, D. J. Cummins, J.-C. Dodart, S. M. Paul and D. M. Holtzman (2001). Peripheral anti-Aβ antibody alters CNS and plasma Aβ clearance and decreases brain Aβ burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 8850–8855.
DeMattos, R. B., K. R. Bales, J.-C. Cummins, S. M. Paul and D. M. Holtzman (2002). Brain to plasma amyloid-β efflux: a measure of brain amyloid burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Science 295, 2264–2267.
Esler, W. P., E. R. Stimson, J. M. Jennings, H. V. Vinters, J. R. Ghilardi, J. P. Lee, P. W. Mantyh and J. E. Maggio (2000). Alzheimer’s disease amyloid propogation by a template-dependent dock-lock mechanism. Biochemistry 39, 6288–6295.
Felsenstein, K. M. (2000). The next generation of AD therapeutics: the future is now. Abstracts from the 7th Annual Conference on Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders, Abstract 613.
Flory, P. J. (1953). Principles of Polymer Chemistry, Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Galasko, D. et al. (1998). High cerebrospinal fluid tau and low amyloid β42 levels in the clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer disease and relation to Apolipoprotein E genotype. Arch. Neurol. 55, 937–945.
Ghersi-Egea, J.-F., P. D. Gorevic, J. Ghiso, B. Frangione, C. S. Patlak and J. D. Fenstermacher (1996). Fate of cerebrospinal fluid-borne amyloid β-peptide: rapid clearance into blood and appreciable accumulation by cerebral arteries. J. Neurochem. 166, 880–883.
Gravina, S. A., L. Ho, C. B. Eckman, K. E. Long, L. Otvos Jr., L. H. Younkin, N. Suzuki and S. C. Younkin (1995). Amyloid β (Aβ) in Alzheimer’s disease brain: biochemical and immunocytochemical analysis with antibodies specific for forms ending at Aβ40 or Aβ42 (43). J. Biochem. 270, 7013–7016.
Harper, J. D. and P. T. Lansbury (1997). Models of amyloid seeding in Alzheimer’s disease and scrapie: mechanistic truths and physiological consequences of the time-dependent solubility of amyloid proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 66, 385–407.
Harper, J. D., S. S. Wong, C. M. Lieber and P. T. Lansbury Jr (1999). Assembly of Aβ Amyloid protofibrils: an in vitro model for a possible early event in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry 38, 8972–8980.
Ho, D. D., A. U. Neumann, A. S. Perelson, W. Chen, J. M. Leonard and M. Markowitz (1995). Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature 373, 123–126.
Hyman, B. T., K. Marzloff and P. V. Arriagada (1993). The lack of accumulation of senile plaques or amyloid burden in Alzheimer’s disease suggests a dynamic balance between amyloid deposition and resolution. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 52, 594–600.
Hyman, B. T., H. L. West, G. W. Rebeck, S. V. Buldyrev, R. N. Mantegna, M. Ukleja, S. Havlin and H. E. Stanley (1995). Quantitative analysis of senile plaques in Alzheimer disease: observation of log-normal size distribution and molecular epidemiology of differences associated with apolipoprotein E genotype and trisomy 21 (Down syndrome). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 3586–3590.
Inouye, H. and D. A. Kirschner (2000). Aβ fibrillogenesis: kinetic parameters for fibril formation from Congo red binding. J. Struct. Biol. 130, 123–129.
Jackson, J. (1957). Networks of waiting lines. Operations Res. 5, 518–521.
Janus, C. et al. (2000). Aβ peptide immunization reduces behavioral impairment and plaques in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 408, 979–982.
Kuo, Y.-M., M. R. Emmerling, H. C. Lampert, S. R. Hempelman, T. A. Kokjohn, A. S. Woods, R. J. Cotter and A. E. Roher (1999). High levels of circulating Aβ42 are sequestered by plasma proteins in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 257, 787–791.
Lemere, C. A., J. K. Blusztajn, H. Yamaguchi, T. Wisniewski, T. C. Saido and D. J. Selkoe (1996). Sequence of deposition of heterogeneous amyloid β-peptides and APO E in Down syndrome: implications for initial events in amyloid plaque formation. Neurobiol. Disord. 3, 6–12.
Lomakin, A., D. S. Chung, G. B. Benedek, D. A. Kirschner and D. B. Teplow (1996). On the nucleation and growth of amyloid β-protein fibrils: detection of nuclei and quantitation of rate constants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 1125–1129.
Lomakin, A., D. B. Teplow, D. A. Kirschner and G. B. Benedek (1997). Kinetic theory of fibrillogenesis of amyloid β-protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 7942–7947.
Lu, L.-F., Y.-M. Kuo, A. E. Roher, L. Brachova, Y. Shen, L. Sue, T. Beach, J. H. Kurth, R. E. Rydel and J. Rogers (1999). Soluble amyloid β peptide concentration as a predictor of synaptic change in Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Pathol. 155, 853–862.
Lutz, R. J., R. L. Dedrick and D. S. Zaharko (1980). Physiological pharmacokinetics: an in vivo approach to membrane transport. Pharmacol. Ther. 11, 559–592.
Mackic, J. B., M. H. Weiss, W. Miao, E. Kirkman, J. Ghiso, M. Calero, J. Bading, B. Frangione and B. V. Zlokovic (1998). Cerebrovascular accumulation and increased blood-brain barrier permeability to circulating Alzheimer’s amyloid β peptide in aged squirrel monkey with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. J. Neurochem. 70, 210–215.
Martel, C. L., J. B. Mackic, J. G. McComb, J. Ghiso and B. V. Zlokovic (1996). Blood-brain barrier uptake of the 40 and 42 amino acid sequences of circulating Alzheimer’s amyloid β in guinea pigs. Neurosci. Lett. 206, 157–160.
Masel, J. and V. A. A. Jansen (2000). Designing drugs to stop the formation of prions and other amyloids. Biophys. Chem. 88, 47–59.
McLean, C. A., R. A. Cherny, F. W. Fraser, S. J. Fuller, M. J. Smith, K. Beyreuther, A. I. Bush and C. L. Masters (1999). Soluble pool of Aβ amyloid as a determinant of severity of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 46, 860–866.
Naiki, H., K. Hasegawa, I. Yamaguchi, H. Nakamura, F. Gejyo and K. Nakakuki (1998). Apolipoprotein E and antioxidants have different mechanisms of inhibiting Alzheimer’s β-amyloid fibril formulation in vitro. Biochemistry 37, 17882–17889.
Naiki, H., K. Higuchi, K. Nakakuki and T. Takeda (1991). Kinetic analysis of amyloid fibril polymerization in vitro. Lab. Invest. 65, 104–110.
Naiki, H. and K. Nakakuki (1996). First-order kinetic model of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid fibril extension in vitro. Lab. Invest. 74, 374–383.
Näslund, J., V. Haroutunian, R. Mohs, K. L. Davis, P. Davies, P. Greengard and J. D. Buxbaum (2000). Correlation between elevated levels of amyloid β-peptide in the brain and cognitive decline. JAMA 283, 1571–1577.
Oosawa, F. and M. A. Kasai (1962). A theory of linear and helical aggregations of macromolecules. J. Mol. Biol. 44, 10–21.
Oyler, G. A., R. B. Duckrow and R. A. Hawkins (1992). Computer simulation of the blood-brain barrier: a model including two membranes, blood flow, facilitated and nonfacilitated diffusion. J. Neurosci. Methods 44, 179–196.
Poduslo, J. F., G. L. Curran, J. J. Haggard, A. L. Biere and D. J. Selkoe (1997). Permeability and residual plasma volume of human, Dutch variant, and rat amyloid β-protein 1–40 at the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol. Disord. 4, 27–34.
Schenk, D. et al. (1999). Immunization with amyloid-β attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature 400, 173–177.
Scheuner, D. et al. (1996). Nat. Med. 2, 864–870.
Selkoe, D. J. (1999). Translating cell biology into therapeutic advances in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 399(Suppl.), A23–31.
Shibata, M., S. Yamada, S. R. Kumar, M. Calero, J. Bading, B. Frangione, D. M. Holzman, C. A. Miller, D. K. Strickland, J. Ghiso and B. V. Zlokovic (2000). Clearance of Alzheimer’s amyloid-ss (1–40) peptide from brain by LDL receptor-related protein-1 at the blood-brain barrier. J. Clin. Invest. 106(12), 1489–1499.
Tseng, B. P., W. P. Esler, C. B. Clish, E. R. Stimson, J. R. Ghilardi, H. V. Vinters, P. W. Mantyh, J. P. Lee and J. E. Maggio (1999). Deposition of monomeric, not oligomeric, Aβ mediates growth of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid plaques in human brain preparations. Biochemistry 38, 10424–10431.
Urbanc, B., L. Cruz, S. V. Buldyrev, S. Havlin, H. E. Stanley and B. T. Hyman (1999). Dynamics of plaque formation in Alzheimer’s disease. Biophys. J. 76, 1330–1334.
von Smoluchowski, M. (1916). Drei vorträge über diffusion, brownsche bewegung und koagulation von kolloidteilchen. Z. Phys. 17, 557–585.
von Smoluchowski, M. (1917). Versuch einer mathematischen theorie der koagulationskinetic kolloider lösungen. Z. Phys. 92, 129–168.
Walsh, D. M., A. Lomakin, G. B. Benedek, M. M. Condron and D. Teplow (1997). Amyloid β-protein fibrillogenesis: detection of a protofibrillar intermediate. J. Biochem. 272, 22364–22372.
Walsh, D. M., B. P. Tsang, R. E. Rydel, M. B. Podlisny and D. J. Selkoe (2000). The oligomerization of amyloid β-protein begins intracellularly in cells derived from human brain. Biochemistry 39, 10831–10839.
Wang, J., D. W. Dickson, J. Q. Trojanowski and V. M.-Y. Lee (1999). The levels of soluble versus insoluble brain Aβ distinguish Alzheimer’s disease from normal and pathologic aging. Exp. Neurol. 158, 328–337.
Wei, X., S. K. Ghosh, M. E. Taylor, V. A. Johnson, E. A. Emini, P. Deutsch, J. D. Lifson, S. Bonhoffer, M. A. Nowak, B. H. Hahn and G. Shaw (1995). Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature 373, 117–123.
Weiner, H. L., C. A. Lemere, R. Maron, E. T. Spooner, T. F. Grenfell, C. Mori, S. Issazadeh, W. W. Hancock and D. J. Selkoe (2000). Nasal administration of amyloid-beta peptide decreases cerebral amyloid burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 48, 567–579.
Wolfe, M. S., W. Xia, C. L. Moore, D. D. Leatherwood, B. L. Ostaszewski, T. Rahmati, I. O. Donkor and D. J. Selkoe (1999). Peptidomimetic probes and molecular modeling suggest Alzheimer’s γ-secretase is an intramembrane-cleaving aspartyl protease. Biochemistry 38, 4720–4727.
Wolfe, M. S., W Xia, B. L. Ostaszewski, T. S. Diehl, W. T. Kimberley and D. J. Selkoe (1999). Two transmembrane aspartates in presenilin-1 required for presenilin endoproteolysis and γ-secretase activity. Nature 398, 513–517.
Ye, Y., N. Lukinova and M. N. Fortini (1999). Neurogenic phenotypes and altered Notch processing in drosophila presinilin mutants. Nature 398, 525–529.
Zlokovic, B. V., J. Ghiso, J. B. Mackic, J. G. McComb, M. H. Weiss and B. Frangione (1993). Blood-brain barrier transport of circulating Alzheimer’s amyloid β. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 197, 1034–1040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Craft, D.L., Wein, L.M. & Selkoe, D.J. A mathematical model of the impact of novel treatments on the Aβ burden in the Alzheimer’s brain, CSF and plasma. Bull. Math. Biol. 64, 1011–1031 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2002.0304
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2002.0304