Abstract
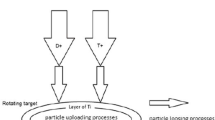
A high-intensity compact D–D/D–T neutron generator with a thick adsorption target is designed with an intensity of 1012 n/s. In this work, a radio-frequency (RF) ion source ignited by an internal antenna is designed with magnetic mirror fields in both axial and radial directions, which can facilitate the confinement of high-density plasma and prolong the service life of the ion source. According to the finite element method software COMSOL Multiphysics, a high-current low-energy D+ beam transport line is simulated and designed with the deuterium beam of 200 keV/6 mA. In particular, the adsorption target is fixed at an angle of 45° with respect to the beam direction, which is beneficial to reduce the beam power density of the target. The simulation results show that the maximum temperature of the target surface is 171.0 °C, which would reduce deuterium or tritium release from the adsorption target. According to the Multi-layer computing model, neutron energy spectra, angular distributions and integrated yields of the compact D–D/D–T neutron generator are calculated and evaluated, corresponding to a thick adsorption target at the deuterium beam of 200 keV/6 mA. The compact D–D/D–T neutron generator can produce quasi-mono-energetic neutrons with energy of 2.45 or 14.1 MeV, respectively, corresponding to the neutron yields up to 6.06 × 109 and 1.18 × 1012 n/s.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Authors’ comment: All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.]
Change history
02 February 2024
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/s10050-023-01211-4
References
S.Y. Zhang, X. Yang, Y.X. Wang, X.H. Bai et al., Eur. Phys. J. A 59, 5 (2023)
R.R. Greenberg, P. Bode, E.A. De Nadai Fernandes, Spectrochim. Acta B At. Spectrosc. 66(3), 193–241 (2011)
J.H. Vainionpaa et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 350, 88–93 (2015)
E. Lehmann, G. Frei, A. Nordlund et al., IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 52(1), 389–393 (2005)
C.S. Lim, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 262(2), 525–532 (2004)
B.D. Sowerby, Appl. Radiat. Isot. 67(9), 1638–1643 (2009)
D. Koltick, Y. Kim, S. Mcconchie et al., Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. B 261(1–2), 277–280 (2007)
T. Misawai, Y. Yamaguchi, T. Yagi, et al., Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC), 2012 IEEE. IEEE (2012)
J.H. Vainionpaa et al., Phys. Proc. 60, 203–211 (2014)
J.H. Vainionpaa, J.L. Harris, M.A. Piestrup, et al., High Yield Neutron Generators Using The DD Reaction. International Conference Application of Accelerators in Research and Industry (2013)
J. Reijonen, Proceedings of the 2005 Particle Accelerator Conference. IEEE (2005)
D.L. Williams, et al., AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1099(1). American Institute of Physics (2009)
Z.-W. Huang et al., J. Instrum. 13(1), P01013 (2018)
Z.-W. Huang et al., Nucl. Sci. Techn. 30(5), 86 (2019)
Z. Huang et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equipment 904, 107–112 (2018)
J. Reijonen et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71(2), 1134–1136 (2000)
P. Yubo, N. Zhanqi, W. Xuezhi et al., At. Energy Sci. Technol. 3, 193–197 (1993). (in Chinese)
S. Biehe, C. Qin, Nucl. Tech. 14, 731 (1991). (in Chinese)
Z. Yu, Research on D–T/D–D neutron generator technology (Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, 2011). (in Chinese)
J. Reijonen, et al., Charged Particle Detection, Diagnostics, and Imaging, vol 4510. SPIE (2001)
J. Reijonen, K.N. Leung, G. Jones, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 73(2), 934–936 (2002)
K.-N. Leung, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 69(2), 998–1002 (1998)
J. Hopwood et al., J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vacuum Surf. Films 11(1), 152–156 (1993)
H. Muta et al., Surf. Coat. Technol. 174, 152–156 (2003)
D. Wutte et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 142(3), 409–416 (1998)
S.K. Hahto et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75(2), 355–359 (2004)
M. Hosseinzadeh, H. Afarideh, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equipment 735, 416–421 (2014)
B.A. Ludewigt, R.P. Wells, J. Reijonen, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 261(1–2), 830–834 (2007)
J. Kim, Nucl. Inst. Methods 145(1), 9–17 (1977)
Z. Wei et al., Eur. Phys. J. A 55(9), 162 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (12075105, U2167203) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (lzujbky-2022-kb07, lzujbky-2023-stlt01, lzujbky-2022-ey14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Navin Alahari
The original online version of this article was revised: In this article S.Y. Zhang was incorrectly denoted as the corresponding author but it should have been Y. Zhang.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, X.H., Wei, Z., Wu, K. et al. Physical design of a high-intensity compact D–D/D–T neutron generator based on the internal antenna RF ion source. Eur. Phys. J. A 59, 284 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/s10050-023-01177-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/s10050-023-01177-3