Abstract
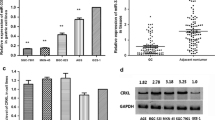
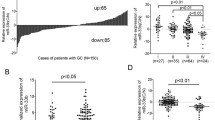
MicroRNA-219-1 (miR-219-1) acts as a tumor suppressor in a variety of cancers but, the regulatory epigenetic mechanism involved in its gene expression level has not been studied. Using real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR) and bisulfite genomic sequencing technology, promoter methylation level of miR-219-1 and gene expression levels of miR-219-5p and miR-219-1-3p were determined respectively, in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) (n = 31), their adjacent normal tissues (n = 31), and GBM U87 cell line. Following treatment of GBM U87 cells with 5-aza-2′-deoxycitidine (5-aza-dC), miR-219-1 promoter methylation, their target mRNA, and protein levels were determined by genomic bisulfite modification, real-time-PCR, and ELISA techniques, respectively. Our results showed that gene expression levels of miR-219-5p and miR-219-1-3p were significantly lower in GBM patients relative to their adjacent normal tissues (p < 0.01). MiR-219-1 promoter had a high level of methylation in GBM tissues (p < 0.01) and a negative correlation was observed between the miRNAs gene expression and methylation levels in GBM tissues (p < 0.01). Treatment of GBM U87 cells by 5-aza-dC decreased the level of miR-219-1 methylation, amount of target mRNA, and levels of cyclin A2 and mucin 4 (MUC4) proteins, and increased the expression levels of miR-219-5p and miR-219-1-3p (p < 0.01). Using external miR-219-5p and miR-219-1-3p, the expression of cyclin A2 and MUC4 were suppressed and proliferative activity of the U87MG cell line was reduced (p < 0.01). These findings suggested that DNA methylation has a crucial role in the regulation of miR-219-1 gene expression and that hypermethylated miR-219-1 may be involved in GBM pathogenesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 5-aza-dC:
-
5-aza-2′-deoxycitidine
- DMED:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- GBM:
-
glioblastoma multiforme
- miRNA:
-
microRNA
- MUC4:
-
mucin 4
- real-time PCR:
-
real time polymerase chain reaction
References
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). GLOBOCAN 2008. Estimated Incidence, Mortality and 5-Year Prevalence: Both Sexes. Available online: http://globocan.iarc.fr (accessed on 16 October 2013).
Dolecek, T. A., Propp, J. M., Stroup, N. E., and Kruchko, C. (2012) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005-2009, Neuro Oncol., 14, v1-v49.
Louis, D. N., Ohgaki, H., Wiestler, O. D., Cavenee, W. K., Burger, P. C., et al. (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system, Acta Neuropathol., 114, 97-109.
Wen, P. Y., and Kesari, S. (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults, N. Engl. J. Med., 359, 492-507.
Bartel, D. (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function, Cell, 116, 281-297.
Vidigal, J. A., and Ventura, A. (2015) The biological functions of miRNAs: lessons from in vivo studies, Trends Cell. Biol., 25, 137-147.
Reddy, K. B. (2015) MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer, Cancer Cell Int., 15, 38.
Liu, X., Chen, X., Yu, X., Tao, Y., Bode, A. M., et al. (2013) Regulation of microRNAs by epigenetics and their interplay involved in cancer, J. Exp. Clin. Cancer. Res., 32, 96.
Konno, M., Koseki, J., Asai, A., Yamagata, A., Shimamura, T., et al. (2019) Distinct methylation levels of mature microRNAs in gastrointestinal cancers, Nat. Commun., 10, 3888.
Jiang, B., Li, M., Ji, F., and Nie, Y. (2017) MicroRNA-219 exerts a tumor suppressive role in glioma via targeting Sal-like protein 4, Exp. Ther. Med., 14, 6213-6221.
Ma, Q. (2019) MiR-219-5p suppresses cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting CCNA2, Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett., 24, 4.
Lahdaoui, F., Delpu, Y., Vincent, A., Renaud, F., Messager, M., et al. (2015) miR-219-1-3p is a negative regulator of the mucin MUC4 expression and is a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer, Oncogene, 34, 780-788.
Lee, R. S., Sohn, S., Shin, K. H., Kang, M. K., Park, N. H., and Kim, R. H. (2017) Bisphosphonate inhibits the expression of cyclin A2 at the transcriptional level in normal human oral keratinocytes, Int. J. Mol. Med., 40, 623-630.
Piwecka, M., Rolle, K., Belter, A., Barciszewska, A. M., Żywicki, M., et al. (2015) Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression profile in malignant glioma tissues, Mol. Oncol., 9, 1324-1340.
Ondracek, J., Fadrus, P., Sana, J., Besse, A., Loja, T., et al. (2017) Global microRNA expression profiling identifies unique microRNA pattern of radioresistant glioblastoma cells, Anticancer Res., 37, 1099-1104.
Rao, S. A. M., Arimappamagan, A., Pandey, P., Santosh, V., Hegde, A. S., et al. (2013) miR-219-5p inhibits receptor tyrosine kinase pathway by targeting EGFR in glioblastoma, PLoS One, 8, e63164, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063164.
Guo, M., Peng, Y., Gao, A., Du, C., and Herman, J. G. (2019) Epigenetic heterogeneity in cancer, Biomark Res., 7, 23.
Ghasemi, A., Fallah, S., and Ansari, M. (2016) MiR-153 as a tumor suppressor in glioblastoma multiforme is downregulated by DNA methylation, Clin. Lab., 62, 573-580.
Wang, L. Q., and Chim, C. S. (2015) DNA methylation of tumor-suppressor miRNA genes in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Epigenomics, 7, 461-473.
Serra, P. L., and Esteller, M. (2012) DNA methylation-associated silencing of tumor-suppressor microRNAs in cancer, Oncogene, 31, 1609-1622.
Pan, Z., Zhu, L. J., Li, Y. Q., Hao, L. Y., Yin, C., et al. (2014) Epigenetic modification of spinal miR-219 expression regulates chronic inflammation pain by targeting CaMKIIγ, J. Neurosci., 16, 9476-9483.
Shi, F., Chen, X., Fu, A., Hansen, J., Stevens, R., et al. (2013) Aberrant DNA methylation of miR-219 promoter in long-term night shiftworkers, Environ. Mol. Mutagen, 54, 406-413.
Malumbres, M., and Barbacid, M. (2009) Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 9, 153-166.
Xia, P., Choi, A. H., Deng, Z., Yang, Y., Zhao, J., and Wang, Y. (2017) Cell membrane-anchored MUC4 promotes tumorigenicity in epithelial carcinomas, Oncotarget, 8, 14147-14157.
Egger, G., Liang, G., Aparicio, A., and Jones, P. A. (2004) Epigenetics in human disease and prospects epigenetic therapy, Nature, 429, 457-463.
De Sousa Abreu, R., Penalva, L. O., Marcotte, E., and Vogel, C. (2009) Global signatures of protein and mRNA expression levels, Mol. Biosyst., 5, 1512-1526.
Svoronos, A. A., Engelman, D. M., and Slack, F. J. (2016) OncomiR or tumor suppressor? The duplicity of MicroRNAs in cancer, Cancer Res., 76, 3666-3670.
Funding
This work was supported by the IRNA University of Medical Sciences (IUMS) [project no. 24756].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in financial or any other sphere. All procedures performed in present study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2021, Vol. 86, No. 4, pp. 496-510, https://doi.org/10.31857/S0320972521040047.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi, A., Mohammadi, A. & Fallah, S. Epigenetic Modification of MicroRNA-219-1 and Its Association with Glioblastoma Multiforme. Biochemistry Moscow 86, 420–432 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297921040040
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297921040040