Abstract
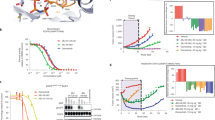
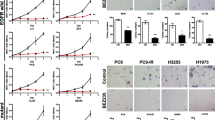
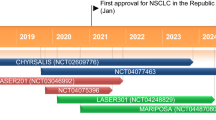
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death. Although docetaxel has been used as a second- or third-line treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the objective response rate is less than 10%. Hence, there is a need to improve the clinical efficacy of docetaxel monotherapy; combination therapy should be considered. Here, we show that CKD-516, a vascular disruption agent, can be combined with docetaxel to treat epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-resistant NSCLC. CKD-516 was orally bioavailable; neither CKD-516 nor docetaxel affected the mean plasma concentration–time profile or pharmacokinetic parameters of the other drug. CKD-516 and docetaxel synergistically inhibited the growth of H1975 (with an L858R/T790M double mutation of EGFR) and A549 (with a KRAS mutation) lung cancer cell lines. In addition, docetaxel plus CKD-516 delayed tumor growth in—and extended the lifespan of—tumor-bearing mice. Thus, combination CKD-516 and docetaxel therapy could be used to treat EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- BA:
-
Bioavailability
- BSC:
-
Best supportive care
- CD31:
-
Cluster of differentiation 31
- CDK:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase
- CYP:
-
Cytochrome P450
- DC:
-
Dendritic cell
- DCE:
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced
- DDI:
-
Drug-drug interaction
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- FACS:
-
Fluorescence activated cell sorting
- IACUC:
-
Institutional animal care and use committee
- ICI:
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor
- i.p. :
-
Intraperitoneal
- i.v. :
-
Intravenous
- JNK:
-
C-Jun N-terminal kinase
- KRAS:
-
Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog
- LC–MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- n.c.:
-
Not calculated
- n.d.:
-
Not determined
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- ORR:
-
Objective response rate
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PK:
-
Pharmacokinetics
- p.o. :
-
Per os
- q.d. :
-
Quaque die
- SD:
-
Sprague–Dawley
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- VDA:
-
Vascular disrupting agent
References
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C (2018) The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553:446–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25183
Alexander M, Kim SY, Cheng H (2020) Update 2020: Management of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung 198:897–907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-020-00407-5
Shepherd FA, Dancey J, Ramlau R, Mattson K, Gralla R, O’Rourke M, Levitan N, Gressot L, Vincent M, Burkes R, Coughlin S, Kim Y, Berille J (2000) Prospective randomized trial of docetaxel versus best supportive care in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 18:2095–2103. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2000.18.10.2095
Weiss JM, Stinchcombe TE (2013) Second-Line Therapy for Advanced NSCLC. Oncologist 18:947–953. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0096
Hinnen P, Eskens FA (2007) Vascular disrupting agents in clinical development. Br J Cancer 96:1159–1165. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6603694
Hollebecque A, Massard C, Soria JC (2012) Vascular disrupting agents: a delicate balance between efficacy and side effects. Curr Opin Oncol 24:305–315. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCO.0b013e32835249de
Mita MM, Sargsyan L, Mita AC, Spear M (2013) Vascular-disrupting agents in oncology. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 22:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.2013.759557
Kim SJ, Jegal KH, Im JH, Park G, Kim S, Jeong HG, Cho IJ, Kang KW (2020) Involvement of ER stress and reactive oxygen species generation in anti-cancer effect of CKD-516 for lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04043-x
Smolarczyk R, Czapla J, Jarosz-Biej M, Czerwinski K, Cichon T (2021) Vascular disrupting agents in cancer therapy. Eur J Pharmacol 891:173692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173692
Kim KW, Lee JM, Jeon YS, Lee IJ, Choi Y, Park J, Kiefer B, Kim C, Han JK, Choi BI (2013) Vascular disrupting effect of CKD-516: preclinical study using DCE-MRI. Invest New Drugs 31:1097–1106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-012-9915-6
Oh DY, Kim TM, Han SW, Shin DY, Lee YG, Lee KW, Kim JH, Kim TY, Jang IJ, Lee JS, Bang YJ (2016) Phase I study of CKD-516, a novel vascular disrupting agent, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Res Treat 48:28–36. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.258
Marcath LA, Coe TD, Hoylman EK, Redman BG, Hertz DL (2018) Prevalence of drug-drug interactions in oncology patients enrolled on national clinical trials network oncology clinical trials. BMC Cancer 18:1155. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5076-0
Royer I, Monsarrat B, Sonnier M, Wright M, Cresteil T (1996) Metabolism of docetaxel by human cytochromes P450: interactions with paclitaxel and other antineoplastic drugs. Cancer Res 56:58–65. PMID: 8548776. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8548776
Engels FK, Ten Tije AJ, Baker SD, Lee CK, Loos WJ, Vulto AG, Verweij J, Sparreboom A (2004) Effect of cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition on the pharmacokinetics of docetaxel. Clin Pharmacol Ther 75:448–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clpt.2004.01.001
Mhaidat NM, Zhang XD, Jiang CC, Hersey P (2007) Docetaxel-induced apoptosis of human melanoma is mediated by activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and inhibited by the mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway. Clin Cancer Res 13:1308–1314. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2216
Moon CH, Lee SJ, Lee HY, le Dung TK, Cho WJ, Cha H, Park JW, Min YJ (2014) CKD-516 displays vascular disrupting properties and enhances anti-tumor activity in combination with chemotherapy in a murine tumor model. Invest New Drugs 32:400–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-013-0043-8
Onodera K, Sakurada A, Notsuda H, Watanabe T, Matsuda Y, Noda M, Endo C, Okada Y (2018) Growth inhibition of KRAS and EGFRmutant lung adenocarcinoma by cosuppression of STAT3 and the SRC/ARHGAP35 axis. Oncol Rep 40:1761–1768. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6536
Wang ES, Pili R, Seshadri M (2012) Modulation of chemotherapeutic efficacy by vascular disrupting agents: optimizing the sequence and schedule. J Clin Oncol 30:760–761; author reply 761–763. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.39.3934
Clemenson C, Chargari C, Deutsch E (2013) Combination of vascular disrupting agents and ionizing radiation. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 86:143–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2012.10.002
Schwartz GK, Shah MA (2005) Targeting the cell cycle: a new approach to cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 23:9408–9421. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.01.5594
Nehme A, Varadarajan P, Sellakumar G, Gerhold M, Niedner H, Zhang Q, Lin X, Christen RD (2001) Modulation of docetaxel-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by all- trans retinoic acid in prostate cancer cells. Br J Cancer 84:1571–1576. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2001.1818
Singh AV, Bandi M, Raje N, Richardson P, Palladino MA, Chauhan D, Anderson KC (2011) A novel vascular disrupting agent plinabulin triggers JNK-mediated apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis in multiple myeloma cells. Blood 117:5692–5700. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-12-323857
Chen DS, Mellman I (2013) Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 39:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012
Kashyap AS, Fernandez-Rodriguez L, Zhao Y, Monaco G, Trefny MP, Yoshida N, Martin K, Sharma A, Olieric N, Shah P, Stanczak M, Kirchhammer N, Park SM, Wieckowski S, Laubli H, Zagani R, Kasenda B, Steinmetz MO, Reinecker HC, Zippelius A (2019) GEF-H1 signaling upon microtubule destabilization is required for dendritic cell activation and specific anti-tumor responses. Cell Rep 28(3367–3380):e3368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.057
Kim SJ, Kim HK, Ryu KH, Hong CI (2019) Abstract 3216: CKD-516, a novel vascular disrupting agent, enhances anticancer activity of anti-PD-1 antibody in SMAD4-deficient colon cancer model. Can Res 79:3216–3216. https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445.AM2019-3216
Spear MA, LoRusso P, Mita A, Mita M (2011) Vascular disrupting agents (VDA) in oncology: advancing towards new therapeutic paradigms in the clinic. Curr Drug Targets 12:2009–2015. https://doi.org/10.2174/138945011798829366
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant 2021R1A2C2093196.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Soo Jin Kim, Kyunghyeon Lee, U Ji Kim, Se-mi Kim and Keun Ho Ryu works in CKD Research Institution, Chong Kun Dang Pharmacuetical Corporation.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.J., Lee, K., Park, J. et al. CKD-516 potentiates the anti-cancer activity of docetaxel against epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant lung cancer. Toxicol Res. 39, 61–69 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43188-022-00146-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43188-022-00146-0