Abstract
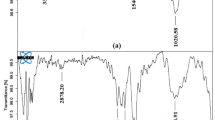
The chitosan biopolymer was impregnated with quaternary ammonium salt tetrabutylammonium bromide to enhance adsorption capacity of the material. The synthesized material, tetrabutylammonium impregnated chitosan (TIC) was characterized using various spectral techniques such as Fourier Transform Infra-red spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) along with energy dispersive X-ray spectrum for elemental composition (EDAX), Thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA-DTA) and pH point of zero charge (pHPZC). The pHPZC of the material was found to be 8.2 which indicated that both anionic as well as cationic dyes can be adsorbed on its surface. Thus TIC was employed as adsorbent for the removal of two dyes namely, malachite green (MG) and methylene blue (MB). The effects of operational parameters such as pH of dye solution, contact time, adsorbent dose, adsorbate concentration and temperature on the adsorption process were studied using batch adsorption method. The adsorption process was found to follow Freundlich isotherm model and maximum adsorption capacities were found to be 56.1 mg g−1 and 30.5 mg g−1 for MG and MB respectively at pH 8.5. Pseudo-second order kinetic model was found to be the best-fit model and thermodynamic studies showed that the process of adsorption is spontaneous and enthalpy driven in nature.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Yaseen DA, Scholz M (2019) Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: a critical review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:1193–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2130-z
Routoula E, Patwardhan SV (2020) Degradation of anthraquinone dyes from effluents: a review focusing on enzymatic dye degradation with industrial potential. Environ Sci Technol 54:647–664
Popli S, Patel UD (2015) Destruction of azo dyes by anaerobic–aerobic sequential biological treatment: a review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:405–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0499-x
Ho YS, Chiang CC (2001) Sorption studies of acid dye by mixed sorbents. Adsorption 7:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011652224816
Khattab TA, Abdelrahman MS, Rehan M (2020) Textile dyeing industry: environmental impacts and remediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:3803–3818
Lellis B, Fávaro-Polonio CZ, Pamphile JA, Polonio JC (2019) Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnol Res Innov 3:275–290
Holkar CR, Jadhav AJ, Pinjari DV, Mahamuni NM, Pandit AB (2016) A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: possible approaches. J Environ Manage 182:351–366
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour Technol 97:1061–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/jbiortech200505001
Kushwaha A, Gupta N, Chattopadhyaya M (2014) Removal of cationic methylene blue and malachite green dyes from aqueous solution by waste materials of Daucus carota. J Saudi Chem Soc 18:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjscs201106011
Crini G, Badot PM (2008) Application of chitosan, a natural aminopolysaccharide, for dye removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption processes using batch studies: a review of recent literature. Prog Polym Sci 33:399–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.11.001
Kellner-Rogers JS, Taylor JK, Masud AM, Aich N, Pinto AH (2019) Kinetic and thermodynamic study of methylene blue adsorption onto chitosan: insights about metachromasy occurrence on wastewater remediation. Energ Ecol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-019-00116-7
Meng R, Liu L, Jin Y, Zhenze L, Gao H, Yao J (2019) Recyclable carboxylated cellulose beads with tunable pore structure and size for highly efficient dye removal. Cellulose 26:8963–8969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02733-1
Córdova BM, Venâncio T, Olivera M (2020) Xanthation of alginate for heavy metal ions removal. Characterization of xanthate-modified alginates and its metal derivatives. Int J Bio Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.022
Zhao X, Wang X, Lou T (2020) Preparation of fibrous chitosan/sodium alginate composite foams for the adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124054
Ravi PL (2018) Enhanced adsorption capacity of designed bentonite and alginate beads for the effective removal of methylene blue. Appl Clay Sci 169:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.12.019
Kausar A, Iqbal M, Javed A, Aftab K, Nazli ZH, Bhatti HN, Nouren S (2018) Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: a review. J Mol Liq 256:395–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.034
Hassan MM, Carr CM (2018) A critical review on recent advancements of the removal of reactive dyes from dye house effluent by ion-exchange adsorbents. Chemosphere 209:201–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.043
Junejo R, Jalbani NS, Kaya S, Serdaroglu G, Şimşek S, Memon S (2021) Experimental and DFT modeling studies for the adsorptive removal of reactive dyes from wastewater. Sep Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2021.1900252
Junejo R, Memon S, Kaya S (2020) Effective removal of the Direct Black-38 dye from wastewater using a new silica-modified resin: equilibrium and thermodynamics modeling studies. J Chem Eng Data 65:4805–4814. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.0c00292
Jeyaseelan C, Chaudhary N, Jugade R (2018) Sulphate-crosslinked chitosan as an adsorbent for the removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution. Air Soil Water Res 11:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178622118811680
Jabeen S, Lone M, Afzal S, Kour P, Shaheen A, Ahanger F, Rathera G, Dar A (2020) Effect of single and binary mixed surfactant impregnation on the adsorption capabilities of chitosan hydrogel beads toward rhodamine B. New J Chem 44:12216–12226. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ02496A
Vithalkar S, Jugade R (2020) Adsorptive removal of crystal violet from aqueous solution by cross-linked chitosan coated bentonite. Mater Today Proc 29:1025–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/jmatpr202004705
Karimi-Maleh H, Ranjbari S, Tanhaei B, Ayati A, Orooji Y, Alizadeh M, Karimi F, Sadegh Salmanpour S, Rouhi J, Sillanpää M, Sen F (2021) Novel 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide impregnated chitosan hydrogel beads nanostructure as an efficient nanobio-adsorbent for cationic dye removal: kinetic study. Environ Res 195:110809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.110809
Zhang J, Guan G, Lou T, Wang X (2021) Preparation and flocculation property of cationic chitosan-DADMAC-β-cyclodextrin copolymer. Starch 73:2100047. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.202100047
Guo L-Y, Lu H-Q, Rackemann D, Shi C, Li W, Li K, Doherty W (2021) Quaternary ammonium-functionalized magnetic chitosan microspheres as an effective green adsorbent to remove high-molecular-weight invert sugar alkaline degradation products (HISADPs). Chem Eng J 416:129084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129084
Shekhawat A, Kahu S, Saravanan D, Jugade R (2015) Synergistic behaviour of ionic liquid impregnated sulphate-crosslinked chitosan towards adsorption of Cr(VI). Int J Biol Macromol 80:615–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/jijbiomac201507035
Kahu S, Shekhawat A, Saravanan D, Jugade R (2016) Two-fold modified chitosan for enhanced adsorption of hexavalent chromium from simulated wastewater and industrial effluents. Carbohydr Polym 146:264–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/jcarbpol201603041
Kahu S, Shekhawat A, Saravanan D, Jugade R (2016) Ionic solid-impregnated sulphate-crosslinked chitosan for effective adsorption of hexavalent chromium from effluents. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:2269–2282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1059-3
Naseeruteen F, Hamid N, Suah F, Ngah W (2017) Adsorption of malachite green from aqueous solution by using novel chitosan ionic liquid beads. Int J Biol Macromol 107:1270–1277. https://doi.org/10.1016/jijbiomac201709111
Sadiq A, Rahim N, Suah F (2020) Adsorption and desorption of malachite green by using chitosan-deep eutectic solvents beads. Int J Biol Macromol 164:3965–3973. https://doi.org/10.1016/jijbiomac202009029
Kumar ASK, Sharma S, Reddy RS, Barathi M, Rajesh N (2015) Comprehending the interaction between chitosan and ionic liquid for the adsorption of palladium. Int J Biol Macromol 72:633–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.09.002
Kumar ASK, Kumar CU, Rajesh V, Rajesh N (2014) Microwave assisted preparation of n-butylacrylate grafted chitosan and its application for Cr (VI) adsorption. Int J Biol Macromol 66:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.02.007
Kumar ASK, Gupta T, Kakan SS, Kalidhasan S, Manasi RV, Rajesh N (2012) Effective adsorption of hexavalent chromium through a three center (3c) co-operative interaction with an ionic liquid and biopolymer. J Hazard Mater 239–240:213–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.08.065
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plain surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Freundlich H (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. Z Phys Chem 57:385–470
Temkin M (1941) Adsorption equilibrium and the kinetics of processes on nonhomogeneous surfaces and in the interaction between adsorbed mols. J Phys Chem (USSR) 15:296–332
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K Sven Vetenskapsakad Handl 24:1–39
Annadurai G, Krishnan MRV (1997) Adsorption of acid dye from aqueous solution by chitin: equilibrium studies. Indian J Chem Technol 4:217–222
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1964) Equilibria and capacities for adsorption on carbon. J Sanit Eng Div 90:79–108
Queiroz M, Melo K, Sabry D, Sassaki G, Rocha H (2014) Does the use of chitosan contribute to oxalate kidney stone formation? Mar Drugs 13:141–158. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13010141
Kahu S, Shekhawat A, Saravanan D, Jugade RM (2017) Stannic chloride impregnated chitosan for defluoridation of water. Int J Biol Macromol 104:1528–1538. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjbiomac201702101
Fan C, Sun T, Luo J, Liu H, Zhou X (2020) Effect of introduction of tetrabutylammonium bromide on properties of poly (lactic acid) tubular scaffold prepared by electrospinning. Micro Nano Lett 15:277–282. https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl20190544
Vafakish B, Wilson L (2019) Surface-modified chitosan: an adsorption study of a “Tweezer-like” biopolymer with fluorescein. Surfaces 2:468–484. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2030035
Postek MT, Vladár AE (2015) Does your SEM really tell the truth?—how would you know? Part 4: charging and its mitigation. In: Proceedings of SPIE—the international society for optical engineering, vol 9636, p 963605. https://doi.org/10.1117/122195344
Salazar-Rabago J, Leyva-Ramos R, Rivera-UtrillaJ O-P, Cerino-Cordova F (2017) Biosorption mechanism of Methylene Blue from aqueous solution onto White Pine (Pinus durangensis) sawdust: effect of operating conditions. Sustain Environ Res 27:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/jserj201611009
Mckay G, Blair HS, Gardner JR (1982) Adsorption of dyes on chitin: equilibrium studies. J Appl Polym Sci 27:3043–3057. https://doi.org/10.1002/app1982070270827
Shekhawat A, Kahu S, Saravanan D, Jugade R (2017) Tin (IV) cross-linked chitosan for the removal of As (III). Carbohydr Polym 172:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/jcarbpol201705038
Muinde V, Onyari J, Wamalwa B, Wabomba J (2020) Adsorption of malachite green dye from aqueous solutions using mesoporous chitosan–zinc oxide composite material. J Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 2:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/jenceco202007005
Adeyi A, Jamil S, Abdullah L, Choong T, Lau K, Alias N (2020) Simultaneous adsorption of malachite green and methylene blue dyes in a fixed-bed column using poly(acrylonitrile-co-acrylic acid) modified with thiourea. Molecules 25:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112650
Arumugam TK, Krishnamoorthy P, Rajagopalan NR, Nanthini S, Vasudevan D (2019) Removal of malachite green from aqueous solutions using a modified chitosan composite. Int J Biol Macromol 128:655–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/jijbiomac201901185
Thabede PM, Shooto ND, Naidoo EB (2020) Removal of methylene blue dye and lead ions from aqueous solution using activated carbon from black cumin seeds. South Afri J Chem Eng 33:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2020.04.002
Awwad NS, El-Jahhar AA, Alasmary JAM (2020) Removal of methylene blue dyes from aqueous system using composite polymeric-apatite resins. Chem Technol Nat Synth Dyes Pigm. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.92048
Dehghani M, Dehghan A, Alidadi H, Dolatabadi M, Mehrabpour M, Converti A (2017) Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions by a new chitosan/zeolite, composite from shrimp waste: kinetic and equilibrium study. Korean J Chem Eng 34:1699–1707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-017-0077-2
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge UGC, New Delhi for funding under UGC-SAP, DST, New Delhi for funding under DST-FIST program and RTM Nagpur University for University Research Project Dev/2117. One of the authors MK acknowledges Department of Science and Technology for fellowship under DST INSPIRE Fellowship Program vide sanction order number [DST/INSPIRE Fellowship 2017/IF170496, Dt. Feb. 13, 2020].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khapre, M.A., Jugade, R.M. Tetrabutylammonium Impregnated Chitosan for Adsorptive Removal of Harmful Carcinogenic Dyes from Water-Bodies. Chemistry Africa 4, 993–1005 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-021-00281-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-021-00281-5