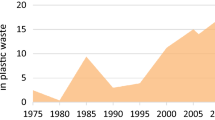
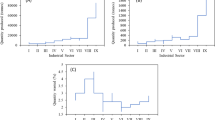
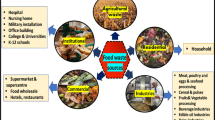
Abstract
Food waste reduction is an essential solution to guarantee food security and to achieve sustainable development goals, especially promoting sustainable consumption and production patterns that lead to attainment of the twelfth Sustainable Development Goal. Although a number of quantitative studies have explored food wastage, few have focused on analysing the main factors contributing to the issue. Given that Morocco, as a member of the United Nations, is committed to halving the per capita food waste at the consumer level by 2030, designing a lever for action to reduce food waste at the household level is crucial and is a top priority. So, many questions, such as the following, need to be answered: What are drivers of food waste generation? How could they influence food habits? Does being aware of the importance of sustainable consumption influence households to change their behaviour? The aim of this study is to analyse food waste rates associated with seven commodity groups among 256 Moroccan households. Results indicated that the most influential food waste generation driver was social class. Moreover, it was noted that consumers wasted food even if they were aware of the problem, and even if they mentioned adopting good eating habits. We therefore proposed an innovative environmental policy integration, named “Culture of Personal Food Governance”, that was based on three levels of action: regulating, raising awareness and monitoring. The results obtained will guide the scientific community, decision-makers and civil society to establish training and awareness protocols adapted to the Mediterranean context, or even to devise an international multi-stakeholder strategy against household food wastage.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are fully available upon request. Please, fell free to contact the corresponding author for any data.
References
Abouabdillah A, Capone R, El Youssfi L, Debs P, Harraq A, El Bilali H, El Amrani M, Bottalico F, Driouech N (2015) Household food waste in Morocco: an exploratory survey. In: Book of Proceedings of the VI International Scientific Agriculture Symposium-Agrosym, pp. 1353–1360
African Development Bank Group (2019) Country results brief 2019 – Morocco. https://www.afdb.org/sites/all/libraries/pdf.js/web/viewer.html?file=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.afdb.org%2FsitFs%2Fdefault%2Ffiles%2Fdocuments%2Fpublications%2Fcrb_morocco_en.pdf. Accessed 5 April 2023
Agapios A, Andreas V, Marinos S, Katerina M, Antonis ZA (2020) Waste aroma profile in the framework of food waste management through household composting. J Clean Prod 257:120340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120340
Ardra S, Barua MK (2022) Halving food waste generation by 2030: the challenges and strategies of monitoring UN Sustainable Development Goal target 12.3. J Clean Prod 380:135042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135042
Aschemann-Witzel J, De Hooge I, Amani P, Bech-Larsen T, Oostindjer M (2015) Consumer-related food waste: causes and potential for action. Sustainability 7(6):6457–6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7066457
Brook L, Cox J, Downing P (2007) Food behaviour consumer research: quantitative phase. WRAP-Waste Reduction Awards Program, London
Cappellini B, Parsons E (2012) Practising thrift at dinnertime: mealtime leftovers, sacrifice and family membership. Sociol Rev 60(2_suppl):121–134. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-954X.12041
Carlsen L, Bruggemann R (2022) The 17 United Nations’ sustainable development goals: a status by 2020. Int J Sust Dev World 29(3):219–229. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2021.1948456
Cattaneo A, Federighi G, Vaz S (2021) The environmental impact of reducing food loss and waste: a critical assessment. Food Policy 98:101890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2020.101890
Chan S, Weitz N, Persson Å, Trimmer C (2018) SDG 12: Responsible consumption and production. A Review of Research Needs. Technical annex to the Formas report Forskning för Agenda2030: Översikt av forskningsbehov och vägar framåt. Environment Insitute, Stockholm
Chan S, Weitz N, Persson Å, Trimmer C (2018) SDG 12: Responsible consumption and production. A Review of Research Needs Technical annex to the Formas report Forskning för Agenda 2030
Comber R, Hoonhout J, Van Halteren A, Moynihan P, Olivier P (2013) Food practices as situated action: exploring and designing for everyday food practices with households. In: Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems, 2457‑2466. https://doi.org/10.1145/2470654.2481340
Elhamdouni D, Arioua A, Karaoui I, Ait Ouhamchich K, Faouzi E, Aba B (2022) The multi-criteria analysis (AHP) method use for the environmental problems management: case of the household waste in Morocco. Euro-Mediterranean J Environ Integr 7(1):13–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-022-00293-8
Falissard B, Falissard MB (2022) Package ‘Psy’. Measurements 20:37–46. https://archive.linux.duke.edu/cran/web/packages/psy/psy.pdf. Accessed 28 January 2023
FAO (2011) Global food losses and food waste – extent, causes and prevention. Food and Agricultural Organisation of the United Nations, Rome
FAO (2019) The state of food and agriculture 2019. Moving forward on food loss and waste reduction 2–13. Food and Agricultural Organisation of the United Nations, Rome
Farr-Wharton G, Foth M, Choi JH-J (2014) Identifying factors that promote consumer behaviours causing expired domestic food waste. J Consum Behav 13(6):393–402. https://doi.org/10.1002/cb.1488
Field A, Miles J, Field Z (2012) Discovering statistics using R. Sage, New York
Ganglbauer E, Fitzpatrick G, Comber R (2013) Negotiating food waste: using a practice lens to inform design. ACM Trans Comput-Hum Interact 20(2):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1145/2463579.2463582
Graham-Rowe E, Jessop DC, Sparks P (2014) Identifying motivations and barriers to minimising household food waste. Resour Conserv Recycl 84:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.12.005
Grandhi B, Appaiah Singh J (2016) What a waste! A study of food wastage behavior in Singapore. J Food Prod Market 22(4):471–485. https://doi.org/10.1080/10454446.2014.885863
Gustavsson J (2011) Global food losses and food waste: extent, causes and prevention; study conducted for the International Congress Save Food! at Interpack 2011, [16–17 May]. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Düsseldorf
Hebrok M, Boks C (2017) Household food waste: drivers and potential intervention points for design – an extensive review. J Clean Prod 151:380–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.069
High Commission for Planning of Morocco (2022) Les indicateurs sociaux du Maroc. https://www.hcp.ma/Les-Indicateurs-sociaux-du-Maroc-Edition-2022_a3192.html. Accessed 15 Jan 2023
High Level Panel of Experts (2014) Food losses and waste in the context of sustainable food systems. Committee on World Food Security, Rome
Hirvonen K, de Brauw A, Abate GT (2021) Food consumption and food security during the COVID-19 pandemic in Addis Ababa. Am J Agr Econ 103(3):772–789. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajae.12206
Husson F, Josse J, Le S, Mazet J (2013) FactoMineR: multivariate exploratory data analysis and data mining with R. R package version 1(1.29)
Jribi S, Ben Ismail H, Doggui D, Debbabi H (2020) COVID-19 virus outbreak lockdown: what impacts on household food wastage? Environ Dev Sustain 22(5):3939–3955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00740-y
Kassambara A, Mundt F (2017) Factoextra: extract and visualize the results of multivariate data analyses. R Package Version 1(5):337–354
Khan J, Khurshid S, Sarwar A, Aziz T, Naveed M, Ali U et al. (2022) Enhancing bread quality and shelf life via glucose oxidase immobilized on zinc oxide nanoparticles – a sustainable approach towards food safety. Sustainability 14(21):14255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114255
Koivupuro H-K, Hartikainen H, Silvennoinen K, Katajajuuri J-M, Heikintalo N, Reinikainen A, Jalkanen L (2012) Influence of socio-demographical, behavioural and attitudinal factors on the amount of avoidable food waste generated in Finnish households. Int J Consum Stud 36(2):183–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1470-6431.2011.01080.x
Kuiper M, Cui H (2020) Using food loss reduction to reach food security and environmental objectives – a search for promising leverage points. Food Policy 98:101915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2020.101915
Liu G (2014) Food losses and food waste in China: a first estimate. OCDE. https://doi.org/10.1787/5jz5sq5173lq-en
Melbye EL, Onozaka Y, Hansen H (2017) Throwing it all away: exploring affluent consumers’ attitudes toward wasting edible food. J Food Prod Mark 23(4):416–429. https://doi.org/10.1080/10454446.2015.1048017
Ministry of National Territorial Planning, Urban Planning, Housing and City Policy – Morocco (2014) Recensement general de la population et de l’habitat. https://rgph2014.hcp.ma/. Accessed 23 June 2022
Parfitt J, Barthel M, Macnaughton S (2010) Food waste within food supply chains: quantification and potential for change to 2050. Philos Trans R Soc Bibiological Sci 365(1554):3065–3081. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2010.0126
Parizeau K, Von Massow M, Martin R (2015) Household-level dynamics of food waste production and related beliefs, attitudes, and behaviours in Guelph, Ontario. Waste Manag 35:207–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.09.019
Porpino G, Parente J, Wansink B (2015) Food waste paradox: antecedents of food disposal in low income households. Int J Consum Stud 39(6):619–629. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12207
Principato L, Ruini L, Guidi M, Secondi L (2019) Adopting the circular economy approach on food loss and waste: the case of Italian pasta production. Resour Conserv Recycl 144:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.01.025
Quested T, Ingle R, Parry A (2013) Household food and drink waste in the United Kingdom. Waste & Resources Action Programme (WRAP), Banbury
Reich A, Foley J (2014) Food loss and waste in the US: the science behind the supply chain. Institute on the Environment, The Food Policy Research Center, University of Minnesota
Rodrigues ER, Bortoleto AP (2022) Analyzing waste prevention behaviors by applying an ABMS framework. Detritus 21:3. https://doi.org/10.31025/2611-4135/2022.17226
Schanes K, Dobernig K, Gözet B (2018) Food waste matters – a systematic review of household food waste practices and their policy implications. J Clean Prod 182:978–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.030
Secondi L, Principato L, Laureti T (2015) Household food waste behaviour in EU-27 countries: a multilevel analysis. Food Policy 56:25–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2015.07.007
Shouket S, Khan J, Batool R, Sarwar A, Aziz T, Alhomrani M et al. (2023) Enhancement of shelf-life of food items via immobilized enzyme nanoparticles on varied supports. A sustainable approach towards food safety and sustainability. Food Res Int 169:112940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112940
Silvennoinen K, Katajajuuri J-M, Hartikainen H, Heikkilä L, Reinikainen A (2014) Food waste volume and composition in Finnish households. Br Food J. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-12-2012-0311
Song G, Semakula HM, Fullana-i-Palmer P (2018) Chinese household food waste and its’ climatic burden driven by urbanization: a Bayesian Belief Network modelling for reduction possibilities in the context of global efforts. J Clean Prod 202:916–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.233
Spratt O, Suri R, Deutsch J (2021) Defining upcycled food products. J Culin Sci Technol 19(6):485–496. https://doi.org/10.1080/15428052.2020.1790074
Springmann M, Clark M, Mason-D’Croz D, Wiebe K, Bodirsky BL, Lassaletta L, de Vries W, Vermeulen SJ, Herrero M, Carlson KM, Jonell M, Troell M, DeClerck F, Gordon LJ, Zurayk R, Scarborough P, Rayner M, Loken B, Fanzo J, Willett W (2018) Options for keeping the food system within environmental limits. Nature 562(7728):519–525. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0594-0
Stefan V, van Herpen E, Tudoran AA, Lähteenmäki L (2013) Avoiding food waste by Romanian consumers: the importance of planning and shopping routines. Food Qual Prefer 28(1):375–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2012.11.001
Sullivan GM, Artino AR Jr (2013) Analyzing and interpreting data from Likert-type scales. J Grad Med Educ 5(4):541–542. https://doi.org/10.4300/JGME-5-4-18
Team R (2015) RStudio: integrated development for R, vol 700. RStudio. Inc, Boston, p 879
Tsangas M, Gavriel I, Doula M, Xeni F, Zorpas AA (2020) Life cycle analysis in the framework of agricultural strategic development planning in the Balkan region. Sustainability 12(5):1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051813
United Nations (2019) World population Prospects 2019: Highlights. Population Division, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, United Nations, New York
Vicki Mavrakis BA (2014) The generative mechanisms of ‘food waste’in South Australian household settings. Thesis – Flinders University, Adelaide
Vilariño MV, Franco C, Quarrington C (2017) Food loss and waste reduction as an integral part of a circular economy. Front Environ Sci 5:21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2017.00021
Visschers VH, Wickli N, Siegrist M (2016) Sorting out food waste behaviour: a survey on the motivators and barriers of self-reported amounts of food waste in households. J Environ Psychol 45:66–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2015.11.007
Waitt G, Phillips C (2016) Food waste and domestic refrigeration: a visceral and material approach. Soc Cult Geogr 17(3):359–379. https://doi.org/10.1080/14649365.2015.1075580
Watson M, Meah A (2012) Food, waste and safety: negotiating conflicting social anxieties into the practices of domestic provisioning. Sociol Rev 60:102–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-954X.12040
Wei T, Simko V, Levy M, Xie Y, Jin Y, Zemla J (2017) Package “Corrplot.” Statistician 56(316):e24
Wickham H, Wickham MH (2020) Package ‘Plyr’. Obtenido Httpscran Rproject Orgwebpackagesdplyrdplyr Pdf. https://cran.r-hub.io/web/packages/dplyr/dplyr.pdf. Accessed 28 Jan 2023
Xulu TM, Mkhize NM, Iwarere SA, Nkomo SL (2022) Life cycle and end-of-life waste management of disposable diapers: a mini-review. Detritus 22:86. https://doi.org/10.31025/2611-4135/2022.17238
Zorpas AA (2020) Strategy development in the framework of waste management. Sci Total Environ 716:137088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137088
Zorpas AA, Lasaridi K, Pociovalisteanu DM, Loizia P (2018) Monitoring and evaluation of prevention activities regarding household organics waste from insular communities. J Clean Prod 172:3567–3577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.155
Zorpas AA, Navarro-Pedreño J, Jeguirim M, Dimitriou G, Almendro Candel MB, Argirusis C et al. (2021) Crisis in leadership vs waste management. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-021-00284-1
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to all the people behind this satisfying achievement. We gratefully acknowledge the efforts of our survey respondents. We are thankful for their patience, time, and effort. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Antonis Zorpas.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zoubi, A., Hallouti, A., El Mderssa, M. et al. Household food wastes in Morocco: extent of, drivers of and environmental policy integration for sustainable consumption. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-024-00517-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-024-00517-z