Abstract
Purpose
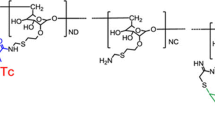
99mTc-tilmanocept is the first mannose-containing, receptor-directed, radiopharmaceutical for molecular imaging and mapping of sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) in solid tumor staging. This review focuses on the approved and innovative clinical application of 99mTc-tilmanocept.
Results and conclusion
99mTc-Tilmanocept is a new-generation radiotracer designed to overcome certain limitations of the conventionally used radiocolloids. The superior efficacy profile of 99mTc-tilmanocept has been demonstrated in several preclinical and clinical studies based on its specific properties like rapid injection site clearance, high uptake in the first node, and low distal node accumulation. The capability of 99mTc-tilmanocept for selective molecular imaging of the CD206 receptor may be used for diagnosis and treatment of several macrophage mediated diseases, including autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases (HIV and tuberculosis), neurodegenerative disorders (dementias) and cardiovascular disease (vulnerable plaque and atherosclerosis).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vera DR, Wallace AM, Hoh CK et al (2001) A synthetic macromoleculefor sentinel node detection: 99mTc-DTPA-mannosyl-dextran. J Nucl Med 42(951–9):28
Wallace AM, Hoh CK, Vera DR et al (2003) Lymphoseek: a molecular radiopharmceutical for sentinel node detection. Ann Surg Oncol 10(531–8):29
Torrelles JB, Azad AK, Henning LC et al (2008) Role of C-type lectins in mycobacterial infections. Curr Drug Targets 9:102–112
Stahl P, Schlesinger PH, Sigardson E et al (1980) Receptor-mediated pinocytosis of mannose glycoconjugates by macrophages: characterization and evidence for receptor recycling. Cell 19(1):207
Irache JM, Salman HH, Gamazo C et al (2008) Mannose-targeted systems for the delivery of therapeutics. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 5(6):703–724
Cabanas RM (1977) An approach for the treatment of penile carcinoma. Cancer 39(456–66):24
Morton DL, Wen DR, Wong JH et al (1992) Technicaldetails of intraoperative lymphatic mapping for early stage melanoma. ArchSurg 127(392–9):3
Méndez J, Wallace AM, Hoh CK et al (2003) Detection of gastric and colonic sentinel nodes through endoscopic administration of 99mTc-DTPA-mannosyl-dextran in pigs. J Nucl Med 44(10):1677–1681
Ellner SJ, Hoh CK, Vera DR et al (2003) Dose-dependent biodistribution of 99mTc DTPA-mannosyl-dextran for breast cancer sentinel lymph node mapping. Nucl Med Biol 30(8):805–810
Giuliano AE, Kirgan DM, Guenther JM et al (1994) Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymphadenectomy for breast cancer. Ann Surg 220:391–398
Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Galimberti V et al (1997) Sentinel-node biopsy to avoid axillary dissection in breast cancer with clinically negative lymph nodes. Lancet 349:1864–1867
Krag D, Weaver D, Ashikaga T et al (1998) The sentinel node in breast cancer – a multicenter validation study. N Engl J Med 339(14):941–946
McMasters KM, Tuttle TM, Carlson DJ et al (2000) Sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer: a suitable alternative to routine axillary dissection in multi-institutional practice when optimal technique is used. J Clin Oncol 18(13):2560–2566
Wallace AM, Han LK, Povoski SP et al (2013) Comparative evaluation of 99mTcTilmanocept for sentinel lymph node map-ping in breast cancer patients: results of two phase 3 trials. Ann Surg Oncol 20(2590–9):33
Baker JL, Pu M, Tokin CA, Hoh CK, Vera DR, Messer K et al (2015) Comparison of 99mTc-tilmanocept and filtered 99mTc sulfur colloid for identification of SLNs in breastcancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol 22(40–5):4
Tokin CA, Cope FO, Metz WL et al (2012) The efficacy of Tilmanocept in sentinel lymph mode mapping and identification in breast cancer patients: a comparative review and meta-analysis of the 99mTc-labeled nanocolloid human serum albumin standard of care. Clin Exp Metastasis 29(7):681–686
Unkart JT, Proudfoot J, Wallace AM (2018) Outcomes of “one-day” vs “two-day” injec-tion protocols using Tc-99m tilmanocept for sentinel lymph node biopsy inbreast cancer. Breast J 24(526–30):48
Morton DL, Thompson JF, Cochran AJ et al (2014) Final trial report of sentinel-node biopsy versus nodal observation in melanoma. N Engl J Med 370(7):599–609
Sondak VK, King DW, Zager JS et al (2013) Combined analysis of phase III trials evaluating 99mTc tilmanocept and vital blue dye for identification of sentinel lymph nodes in clinically node-negative cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol 20(2):680–688
Leong SP, Kim J, Ross MI et al (2011) A phase 2 study of 99mTc-tilmanocept in the detection of sentinel lymph nodes in melanoma and breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 18:961–969
Liu M, Wang SJ, Yang X et al (2017) Diagnostic efficacy of sentinel lymph node biopsyin early oral squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis of 66 studies. PLoS ONE 12:00170322
Civantos FJ, Zitsch RP, Schuller DE et al (2010) Sentinellymph node biopsy accurately stages the regional lymph nodes for T1–T2 oralsquamous cell carcinomas: results of a prospective multi-institutional trial. J Clin Oncol 28(1395–400):53
Marcinow AM, Hall N, Byrum E et al (2013) Use of a novelreceptor-targeted (CD206) radiotracer, 99mTc-tilmanocept, and SPECT/CT forsentinel lymph node detection in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: initial institutional report in an ongoing phase 3 study. JAMA Otolaryngol Head NeckSurg 139:895–902
Agrawal A, Civantos FJ, Brumund KT et al (2015) 99mTcTilmanocept accurately detects sentinel lymph nodes and predicts node pathology status in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: results of a phase III multi-institutional trial. Ann Surg Oncol 22:3708–3715
den Toom IJ, Mahieu R, van Rooij R et al (2020) Sentinel lymph node detection in oral cancer: a within-patient comparison between 99mTc-tilmanocept and 99mTc-nanocolloid. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-020-04984-8
Trials CU. U.S National Institutes of Health. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/ show/NCT03157167
Cope FO, Abbruzzese B, Sanders J et al (2016) The inextricable axis of targeted diagnostic imaging and therapy: An immunological natural history approach. Nucl Med Biol 43(3):215–2525
Varasteh Z, Hyafil F, Anizan N et al (2017) Targeting mannose receptor expression on macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques of apolipoprotein E-knockout mice using 111In-tilmanocept. EJNMMI Res 7(1):40
Zanni MV, Toribio M, Wilks MQ et al (2017) Application of a Novel CD206+ Macrophage-Specific Arterial Imaging Strategy in HIV-Infected Individuals. J Infect Dis 215(8):1264–1269
Trials CU. U.S National Institutes of Health. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/ show/ NCT02865434
Qin Z, Hoh CK, Olson ES et al (2019) Molecular Imaging of the Glomerulus via Mesangial Cell Uptake of Radiolabeled Tilmanocept. J Nucl Med. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.118.223727
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Alice Lorenzoni, Mario Santinami and Marco Maccauro declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights disclosure
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lorenzoni, A., Santinami, M. & Maccauro, M. Clinical applications of receptor-binding radiopharmaceutical 99mTc-Tilmanocept: sentinel node biopsy and beyond. Clin Transl Imaging 8, 413–418 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-020-00399-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-020-00399-5