Abstract
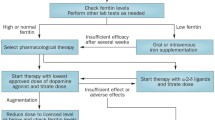
Restless legs syndrome (RLS; also known as Willis-Ekbom disease) is a common neurological, sensorimotor disorder. RLS is initially managed with lifestyle modifications, elimination of possible iatrogenic contributors and maintenance of normal-high peripheral iron stores. Moderate-to-severe RLS may be treated with pharmacological therapy, which generally involves the use of α-2-δ ligands (e.g. gabapentin enacarbil, pregabalin, gabapentin) and dopamine agonists (e.g. pramipexole, rotigotine, ropinirole), as well as opioids for treatment-resistant RLS. The chosen drug class/specific drug depends on patient factors (e.g. the most prominent symptoms, comorbidities, age-related issues, preferences) and drug factors (e.g. tolerability profile, augmentation risk).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
During EH, Winkelman JW. Drug treatment of restless legs syndrome in older adults. Drugs Aging. 2019;36(10):939–46.
Gonzalez-Latapi P, Malkani R. Update on restless legs syndrome: from mechanisms to treatment. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19(8):54.
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Restless legs syndrome fact sheet: NIH publication no. 17-4847. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Health; 2017.
Allen RP, Picchietti DL, Garcia-Borreguero D, et al. Restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease diagnostic criteria: updated International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (IRLSSG) consensus criteria–history, rationale, description, and significance. Sleep Med. 2014;15(8):860–73.
Cochen De Cock V. Therapies for restless legs in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2019;21(11):56.
Allen RP, Picchietti DL, Auerbach M, et al. Evidence-based and consensus clinical practice guidelines for the iron treatment of restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease in adults and children: an IRLSSG task force report. Sleep Med. 2018;41:27–44.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Silber MH, Winkelman JW, et al. Guidelines for the first-line treatment of restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease, prevention and treatment of dopaminergic augmentation: a combined task force of the IRLSSG, EURLSSG, and the RLS-foundation. Sleep Med. 2016;21:1–11.
Winkelman JW, Armstrong MJ, Allen RP, et al. Practice guideline summary: treatment of restless legs syndrome in adults: report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2016;87(24):2585–93.
Horizant® (gabapentin enacarbil) extended-release tablets: US prescribing information. Atlanta: Arbor Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2020.
Buchfuhrer MJ. Strategies for the treatment of restless legs syndrome. Neurotherapeutics. 2012;9(4):776–90.
Mirapex® (pramipexole dihydrochloride) tablets: US prescribing information. Ridgefield: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2020.
Requip® (ropinirole) tablets: US prescribing information. Research Triangle Park: GlaxoSmithKline; 2020.
Neupro® (rotigotine transdermal system): US prescribing information. Smyrna: UCB, Inc.; 2020.
Allen RP, Ondo WG, Ball E, et al. Restless legs syndrome (RLS) augmentation associated with dopamine agonist and levodopa usage in a community sample. Sleep Med. 2011;12(5):431–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Authorship and Conflict of interest
E.S. Kim is a contracted employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. K.A. Lyseng-Williamson is a salaried employee of Adis International/Springer Nature, is an editor of Drugs & Therapy Perspectives, was not involved in any publishing decision for the manuscript, and has no other conflicts of interest to declare. Both authors contributed to the review and are responsible for the article content.
Ethics approval, Consent to participate, Consent for publication, Availability of data and material, Code availability
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, E.S., Lyseng-Williamson, K.A. Choose treatment for restless legs syndrome based on patient and drug characteristics. Drugs Ther Perspect 36, 435–439 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-020-00773-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-020-00773-3