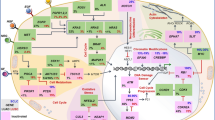
Abstract
Central nervous system (CNS) metastases most commonly arise from lung cancer, with the majority of patients affected during their disease course. The prognosis for patients with untreated brain metastases is poor, with surgical resection and/or radiotherapy as classic therapeutic options. However, the value of systemic therapy in the management of CNS metastases from lung cancer is growing. Novel targeted agents for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have demonstrated activity in treating patients with CNS involvement, and are potential alternatives to radiation and surgery. These agents include anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors such as alectinib, crizotinib, ceritinib, lorlatinib, and others; epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors, including the recently developed third-generation inhibitor osimertinib, and even immune checkpoint inhibitors such as nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and atezolizumab. This review summarizes current activity of systemic agents in the management of CNS metastases from NSCLC, as well as potential mechanisms of action of these small and large molecules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fox BD, Cheung VJ, Patel AJ, Suki D, Rao G. Epidemiology of metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2011;22(1):1–6, v.
Al-Shamy G, Sawaya R. Management of brain metastases: the indispensable role of surgery. J Neurooncol. 2009;92(3):275–82.
Bernardo G, Cuzzoni Q, Strada MR, Bernardo A, Brunetti G, Jedrychowska I, et al. First-line chemotherapy with vinorelbine, gemcitabine, and carboplatin in the treatment of brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase II study. Cancer Invest. 2002;20(3):293–302.
Reck M, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, Hui R, Csoszi T, Fulop A, et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(19):1823–33.
Arrieta O, Villarreal-Garza C, Zamora J, Blake-Cerda M, de la Mata MD, Zavala DG, et al. Long-term survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and synchronous brain metastasis treated with whole-brain radiotherapy and thoracic chemoradiation. Radiat Oncol. 2011;6:166.
Chao JH, Phillips R, Nickson JJ. Roentgen-ray therapy of cerebral metastases. Cancer. 1954;7(4):682–9.
Hubbs JL, Boyd JA, Hollis D, Chino JP, Saynak M, Kelsey CR. Factors associated with the development of brain metastases: analysis of 975 patients with early stage nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2010;116(21):5038–46.
Senan S, Brade A, Wang LH, Vansteenkiste J, Dakhil S, Biesma B, et al. PROCLAIM: randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed-cisplatin or etoposide-cisplatin plus thoracic radiation therapy followed by consolidation chemotherapy in locally advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(9):953–62.
Guerin A, Sasane M, Zhang J, Culver KW, Dea K, Nitulescu R, et al. Brain metastases in patients with ALK+ non-small cell lung cancer: clinical symptoms, treatment patterns and economic burden. J Med Econ. 2015;18(4):312–22.
Doebele RC, Lu X, Sumey C, Maxson DA, Weickhardt AJ, Oton AB, et al. Oncogene status predicts patterns of metastatic spread in treatment-naive nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2012;118(18):4502–11.
Stanic K, Zwitter M, Hitij NT, Kern I, Sadikov A, Cufer T. Brain metastases in lung adenocarcinoma: impact of EGFR mutation status on incidence and survival. Radiol Oncol. 2014;48(2):173–83.
Hsu F, De Caluwe A, Anderson D, Nichol A, Toriumi T, Ho C. EGFR mutation status on brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2016;96:101–7.
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(4):419–25.
Sperduto PW, Yang TJ, Beal K, Pan H, Brown PD, Bangdiwala A, et al. Estimating survival in patients with lung cancer and brain metastases: an update of the graded prognostic assessment for lung cancer using molecular markers (Lung-molGPA). JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(6):827–31.
Paget S. The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. 1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989;8(2):98–101.
Bos PD, Zhang XH, Nadal C, Shu W, Gomis RR, Nguyen DX, et al. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Nature. 2009;459(7249):1005–9.
Grinberg-Rashi H, Ofek E, Perelman M, Skarda J, Yaron P, Hajduch M, et al. The expression of three genes in primary non-small cell lung cancer is associated with metastatic spread to the brain. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(5):1755–61.
Kim JB, Islam S, Kim YJ, Prudoff RS, Sass KM, Wheelock MJ, et al. N-Cadherin extracellular repeat 4 mediates epithelial to mesenchymal transition and increased motility. J Cell Biol. 2000;151(6):1193–206.
Yoo JY, Yang SH, Lee JE, Cho DG, Kim HK, Kim SH, et al. E-cadherin as a predictive marker of brain metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer, and its regulation by pioglitazone in a preclinical model. J Neurooncol. 2012;109(2):219–27.
Shintani Y, Higashiyama S, Ohta M, Hirabayashi H, Yamamoto S, Yoshimasu T, et al. Overexpression of ADAM9 in non-small cell lung cancer correlates with brain metastasis. Cancer Res. 2004;64(12):4190–6.
Lin CY, Chen HJ, Huang CC, Lai LC, Lu TP, Tseng GC, et al. ADAM9 promotes lung cancer metastases to brain by a plasminogen activator-based pathway. Cancer Res. 2014;74(18):5229–43.
Brastianos PK, Carter SL, Santagata S, Cahill DP, Taylor-Weiner A, Jones RT, et al. Genomic characterization of brain metastases reveals branched evolution and potential therapeutic targets. Cancer Discov. 2015;5(11):1164–77.
Deeken JF, Loscher W. The blood-brain barrier and cancer: transporters, treatment, and Trojan horses. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(6):1663–74.
Delattre JY, Krol G, Thaler HT, Posner JB. Distribution of brain metastases. Arch Neurol. 1988;45(7):741–4.
Gleissner B, Chamberlain MC. Neoplastic meningitis. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5(5):443–52.
Reese TS, Karnovsky MJ. Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1967;34(1):207–17.
Liu X, Ide JL, Norton I, Marchionni MA, Ebling MC, Wang LY, et al. Molecular imaging of drug transit through the blood-brain barrier with MALDI mass spectrometry imaging. Sci Rep. 2013;3:2859.
Hawkins BT, Davis TP. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57(2):173–85.
Pardridge WM. CNS drug design based on principles of blood-brain barrier transport. J Neurochem. 1998;70(5):1781–92.
Zeng YD, Liao H, Qin T, Zhang L, Wei WD, Liang JZ, et al. Blood-brain barrier permeability of gefitinib in patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer before and during whole brain radiation therapy. Oncotarget. 2015;6(10):8366–76.
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF, Dempsey RJ, Mohiuddin M, Kryscio RJ, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. JAMA. 1998;280(17):1485–9.
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, Dempsey RJ, Maruyama Y, Kryscio RJ, et al. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med. 1990;322(8):494–500.
Kamp MA, Dibue-Adjei M, Cornelius JF, Slotty PJ, Steiger HJ, Ahmadi SA, et al. Is it all a matter of size? Impact of maximization of surgical resection in cerebral tumors. Neurosurg Rev. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-018-0963-z (Epub 20 Mar 2018).
Pessina F, Navarria P, Cozzi L, Ascolese AM, Maggi G, Rossi M, et al. role of surgical resection in patients with single large brain metastases: feasibility, morbidity, and local control evaluation. World Neurosurg. 2016;94:6–12.
Muacevic A, Wowra B, Siefert A, Tonn JC, Steiger HJ, Kreth FW. Microsurgery plus whole brain irradiation versus Gamma Knife surgery alone for treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized controlled multicentre phase III trial. J Neurooncol. 2008;87(3):299–307.
Qin H, Wang C, Jiang Y, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Ruan Z. Patients with single brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer equally benefit from stereotactic radiosurgery and surgery: a systematic review. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:144–52.
Paek SH, Audu PB, Sperling MR, Cho J, Andrews DW. Reevaluation of surgery for the treatment of brain metastases: review of 208 patients with single or multiple brain metastases treated at one institution with modern neurosurgical techniques. Neurosurgery. 2005;56(5):1021–34 (discussion 34).
Tsao MN, Lloyd N, Wong RK, Chow E, Rakovitch E, Laperriere N, et al. Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;4:CD003869.
Soffietti R, Kocher M, Abacioglu UM, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, et al. A European organisation for research and treatment of cancer phase iii trial of adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation in patients with one to three brain metastases from solid tumors after surgical resection or radiosurgery: quality-of-life results. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(1):65–72.
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, et al. Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(2):134–41.
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(11):1037–44.
Mulvenna P, Nankivell M, Barton R, Faivre-Finn C, Wilson P, McColl E, et al. Dexamethasone and supportive care with or without whole brain radiotherapy in treating patients with non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases unsuitable for resection or stereotactic radiotherapy (QUARTZ): results from a phase 3, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10055):2004–14.
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T, Akabane A, Higuchi Y, Kawagishi J, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(4):387–95.
Banfill KE, Bownes PJ, St Clair SE, Loughrey C, Hatfield P. Stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastases: impact of cerebral disease burden on survival. Br J Neurosurg. 2012;26(5):674–8.
Tsao M, Xu W, Sahgal A. A meta-analysis evaluating stereotactic radiosurgery, whole-brain radiotherapy, or both for patients presenting with a limited number of brain metastases. Cancer. 2012;118(9):2486–93.
Morris PG, Reiner AS, Szenberg OR, Clarke JL, Panageas KS, Perez HR, et al. Leptomeningeal metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer: survival and the impact of whole brain radiotherapy. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;7(2):382–5.
Robinet G, Thomas P, Breton JL, Lena H, Gouva S, Dabouis G, et al. Results of a phase III study of early versus delayed whole brain radiotherapy with concurrent cisplatin and vinorelbine combination in inoperable brain metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer: Groupe Francais de Pneumo-Cancerologie (GFPC) Protocol 95-1. Ann Oncol. 2001;12(1):59–67.
Barlesi F, Gervais R, Lena H, Hureaux J, Berard H, Paillotin D, et al. Pemetrexed and cisplatin as first-line chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with asymptomatic inoperable brain metastases: a multicenter phase II trial (GFPC 07-01). Ann Oncol. 2011;22(11):2466–70.
Fang L, Sun X, Song Y, Zhang Y, Li F, Xu Y, et al. Whole-brain radiation fails to boost intracerebral gefitinib concentration in patients with brain metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a self-controlled, pilot study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015;76(4):873–7.
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I, et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101(36):13306–11.
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304(5676):1497–500.
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(21):2129–39.
Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S, Srinivasan S, Tsai CM, Khoa MT, et al. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9(2):154–62.
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(3):239–46.
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(10):947–57.
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(25):2380–8.
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(2):121–8.
Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, et al. Final overall survival results from a randomised, phase III study of erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802). Ann Oncol. 2015;26(9):1877–83.
Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, O’Byrne K, Hirsh V, Mok T, et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(27):3327–34.
Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, Feng J, Lu S, Huang Y, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(2):213–22.
Wu YL, Zhou C, Liam CK, Wu G, Liu X, Zhong Z, et al. First-line erlotinib versus gemcitabine/cisplatin in patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: analyses from the phase III, randomized, open-label, ENSURE study. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(9):1883–9.
Yang JC, Wu YL, Schuler M, Sebastian M, Popat S, Yamamoto N, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(2):141–51.
Zhao D, Chen X, Qin N, Su D, Zhou L, Zhang Q, et al. The prognostic role of EGFR-TKIs for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40374.
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(2):113–25.
Heon S, Yeap BY, Britt GJ, Costa DB, Rabin MS, Jackman DM, et al. Development of central nervous system metastases in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and somatic EGFR mutations treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(23):5873–82.
Eichler AF, Kahle KT, Wang DL, Joshi VA, Willers H, Engelman JA, et al. EGFR mutation status and survival after diagnosis of brain metastasis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Neuro Oncol. 2010;12(11):1193–9.
Jackman DM, Holmes AJ, Lindeman N, Wen PY, Kesari S, Borras AM, et al. Response and resistance in a non-small-cell lung cancer patient with an epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and leptomeningeal metastases treated with high-dose gefitinib. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(27):4517–20.
Clarke JL, Pao W, Wu N, Miller VA, Lassman AB. High dose weekly erlotinib achieves therapeutic concentrations in CSF and is effective in leptomeningeal metastases from epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung cancer. J Neurooncol. 2010;99(2):283–6.
Huang Q, Li J, Sun Y, Wang R, Cheng X, Chen H. Efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the adjuvant treatment for operable non-small cell lung cancer by a meta-analysis. Chest. 2016;149(6):1384–92.
Riely GJ, Politi KA, Miller VA, Pao W. Update on epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(24):7232–41.
Bronte G, Rolfo C, Giovannetti E, Cicero G, Pauwels P, Passiglia F, et al. Are erlotinib and gefitinib interchangeable, opposite or complementary for non-small cell lung cancer treatment? Biological, pharmacological and clinical aspects. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014;89(2):300–13.
Ballard P, Yates JW, Yang Z, Kim DW, Yang JC, Cantarini M, et al. Preclinical comparison of osimertinib with other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant NSCLC brain metastases models, and early evidence of clinical brain metastases activity. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(20):5130–40.
Chen Y, Wang M, Zhong W, Zhao J. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of Gefitinib in a mouse model of non-small-cell lung carcinoma with brain metastasis. Lung Cancer. 2013;82(2):313–8.
Elmeliegy MA, Carcaboso AM, Tagen M, Bai F, Stewart CF. Role of ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier transporters in erlotinib CNS penetration and intracellular accumulation. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(1):89–99.
Togashi Y, Masago K, Masuda S, Mizuno T, Fukudo M, Ikemi Y, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of gefitinib and erlotinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012;70(3):399–405.
Heon S, Yeap BY, Lindeman NI, Joshi VA, Butaney M, Britt GJ, et al. The impact of initial gefitinib or erlotinib versus chemotherapy on central nervous system progression in advanced non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR mutations. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(16):4406–14.
Li MX, He H, Ruan ZH, Zhu YX, Li RQ, He X, et al. Central nervous system progression in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations in response to first-line treatment with two EGFR-TKIs, gefitinib and erlotinib: a comparative study. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):245.
Masuda T, Hattori N, Hamada A, Iwamoto H, Ohshimo S, Kanehara M, et al. Erlotinib efficacy and cerebrospinal fluid concentration in patients with lung adenocarcinoma developing leptomeningeal metastases during gefitinib therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;67(6):1465–9.
Lee E, Keam B, Kim DW, Kim TM, Lee SH, Chung DH, et al. Erlotinib versus gefitinib for control of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8(8):1069–74.
Ota K, Shiraishi Y, Harada T, Himeji D, Kitazaki T, Ebi N, et al. OA08. 02 Phase II study of erlotinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with leptomeningeal metastasis (LOGIK1101). J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12(1):S271–2.
Grommes C, Oxnard GR, Kris MG, Miller VA, Pao W, Holodny AI, et al. “Pulsatile” high-dose weekly erlotinib for CNS metastases from EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Neuro Oncol. 2011;13(12):1364–9.
Kuiper JL, Smit EF. High-dose, pulsatile erlotinib in two NSCLC patients with leptomeningeal metastases—one with a remarkable thoracic response as well. Lung Cancer. 2013;80(1):102–5.
Jackman DM, Cioffredi LA, Jacobs L, Sharmeen F, Morse LK, Lucca J, et al. A phase I trial of high dose gefitinib for patients with leptomeningeal metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(6):4527–36.
Li D, Ambrogio L, Shimamura T, Kubo S, Takahashi M, Chirieac LR, et al. BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor highly effective in preclinical lung cancer models. Oncogene. 2008;27(34):4702–11.
Zhang SR, Zhu LC, Jiang YP, Zhang J, Xu RJ, Xu YS, et al. Efficacy of afatinib, an irreversible ErbB family blocker, in the treatment of intracerebral metastases of non-small cell lung cancer in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017;38(2):233–40.
Hoffknecht P, Tufman A, Wehler T, Pelzer T, Wiewrodt R, Schutz M, et al. Efficacy of the irreversible ErbB family blocker afatinib in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-pretreated non-small-cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases or leptomeningeal disease. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10(1):156–63.
Schuler M, Wu YL, Hirsh V, O’Byrne K, Yamamoto N, Mok T, et al. First-line afatinib versus chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and common epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations and brain metastases. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11(3):380–90.
Tamiya ATM, Nishihara T, et al. Efficacy and cerebrospinal fluid concentration of afatinib in NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation developing leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12:S273.
Zhou L, He J, Xiong W, Liu Y, Xiang J, Yu Q, et al. Impact of whole brain radiation therapy on CSF penetration ability of Icotinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: Results of phase I dose-escalation study. Lung Cancer. 2016;96:93–100.
Yang JJ, Zhou C, Huang Y, Feng J, Lu S, Song Y, et al. Icotinib versus whole-brain irradiation in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer and multiple brain metastases (BRAIN): a multicentre, phase 3, open-label, parallel, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5(9):707–16.
Gong L, Xiong M, Huang Z, Miao L, Fan Y. Icotinib might be effective for the treatment of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in non-small cell lung cancer with sensitive EGFR mutations. Lung Cancer. 2015;89(3):268–73.
Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, Eberlein C, Nebhan CA, Spitzler PJ, et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014;4(9):1046–61.
Vansteenkiste J ea. CNS response to osimertinib vs. standard-of-care EGFR-TKI as first-line treatment in patients with egfrm advanced NSCLC: FLAURA [abstract no. LBA5]. Presented at the ESMO Asia 2017 Congress; 17–19 Nov 2017: Singapore.
Mok TS, Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Kim HR, Ramalingam SS, et al. Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(7):629–40.
Goss G, Tsai CM, Shepherd FA, Ahn MJ, Bazhenova L, Crino L, et al. CNS response to osimertinib in patients with T790M-positive advanced NSCLC: pooled data from two Phase II trials. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(3):687–93.
Ahn MJ, Kim DW, Cho BC, Kim SW, Lee JS, Ahn JS, et al. Phase I study (BLOOM) of AZD3759, a BBB penetrable EGFR inhibitor, in patients with TKI-naïve, EGFRm NSCLC with CNS metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(15 Suppl):2006.
Nanjo S, Hata A, Okuda C, Kaji R, Okada H, Tamura D, et al. Standard-dose osimertinib for refractory leptomeningeal metastases in T790M-positive EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2018;118(1):32–7.
Yang JCH, Cho BC, Kim DW, Kim SW, Lee JS, Su WC, et al. Osimertinib for patients (pts) with leptomeningeal metastases (LM) from EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): updated results from the BLOOM study. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(15 Suppl):2020.
Magnuson WJ, Lester-Coll NH, Wu AJ, Yang TJ, Lockney NA, Gerber NK, et al. Management of brain metastases in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-naive epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective multi-institutional analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(10):1070–7.
Jiang T, Su C, Li X, Zhao C, Zhou F, Ren S, et al. EGFR TKIs plus WBRT demonstrated no survival benefit other than that of TKIs alone in patients with NSCLC and EGFR mutation and brain metastases. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11(10):1718–28.
Johung KL, Yao X, Li F, Yu JB, Gettinger SN, Goldberg S, et al. A clinical model for identifying radiosensitive tumor genotypes in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(19):5523–32.
Soon YY, Leong CN, Koh WY, Tham IW. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors versus cranial radiation therapy for EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 2015;114(2):167–72.
Luo S, Chen L, Chen X, Xie X. Evaluation on efficacy and safety of tyrosine kinase inhibitors plus radiotherapy in NSCLC patients with brain metastases. Oncotarget. 2015;6(18):16725–34.
Jiang T, Min W, Li Y, Yue Z, Wu C, Zhou C. Radiotherapy plus EGFR TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: an update meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2016;5(6):1055–65.
Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, Seto T, Crino L, Ahn MJ, et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(25):2385–94.
Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa K, Mekhail T, et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(23):2167–77.
Gainor JF, Ou SH, Logan J, Borges LF, Shaw AT. The central nervous system as a sanctuary site in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8(12):1570–3.
Remon J, Le Rhun E, Besse B. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients: a continuing challenge in the personalized treatment era. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;53:128–37.
Rangachari D, Yamaguchi N, VanderLaan PA, Folch E, Mahadevan A, Floyd SR, et al. Brain metastases in patients with EGFR-mutated or ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancers. Lung Cancer. 2015;88(1):108–11.
Iwahara T, Fujimoto J, Wen D, Cupples R, Bucay N, Arakawa T, et al. Molecular characterization of ALK, a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed specifically in the nervous system. Oncogene. 1997;14(4):439–49.
Johung KL, Yeh N, Desai NB, Williams TM, Lautenschlaeger T, Arvold ND, et al. Extended survival and prognostic factors for patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer and brain metastasis. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(2):123–9.
Tang SC, Nguyen LN, Sparidans RW, Wagenaar E, Beijnen JH, Schinkel AH. Increased oral availability and brain accumulation of the ALK inhibitor crizotinib by coadministration of the P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) inhibitor elacridar. Int J Cancer. 2014;134(6):1484–94.
Costa DB, Kobayashi S, Pandya SS, Yeo WL, Shen Z, Tan W, et al. CSF concentration of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor crizotinib. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(15):e443–5.
Solomon BJ, Cappuzzo F, Felip E, Blackhall FH, Costa DB, Kim DW, et al. Intracranial efficacy of crizotinib versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: results from proFILE 1014. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2858–65.
Costa DB, Shaw AT, Ou SH, Solomon BJ, Riely GJ, Ahn MJ, et al. Clinical experience with crizotinib in patients with advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer and brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(17):1881–8.
Weickhardt AJ, Scheier B, Burke JM, Gan G, Lu X, Bunn PA Jr, et al. Local ablative therapy of oligoprogressive disease prolongs disease control by tyrosine kinase inhibitors in oncogene-addicted non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;7(12):1807–14.
Soria JC, Tan DSW, Chiari R, Wu YL, Paz-Ares L, Wolf J, et al. First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2017;389(10072):917–29.
Crino L, Ahn MJ, De Marinis F, Groen HJ, Wakelee H, Hida T, et al. Multicenter phase II study of whole-body and intracranial activity with ceritinib in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy and crizotinib: results from ASCEND-2. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2866–73.
Felip E, Orlov Sergey, Park Keunchil, Chong-Jen Yu, Tsai Chun-Ming, Nishio Makoto, Dols Manuel Cobo, et al. ASCEND-3: a single-arm, open-label, multicenter phase II study of ceritinib in ALKi-naïve adult patients (pts) with ALK-rearranged (ALK+) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(15 Suppl):8060.
Katayama R, Sakashita T, Yanagitani N, Ninomiya H, Horiike A, Friboulet L, et al. P-glycoprotein mediates ceritinib resistance in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. EBioMedicine. 2016;3:54–66.
Sakamoto H, Tsukaguchi T, Hiroshima S, Kodama T, Kobayashi T, Fukami TA, et al. CH5424802, a selective ALK inhibitor capable of blocking the resistant gatekeeper mutant. Cancer Cell. 2011;19(5):679–90.
Peters S, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Gadgeel S, Ahn JS, Kim DW, et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(9):829–38.
Ou SH, Ahn JS, De Petris L, Govindan R, Yang JC, Hughes B, et al. Alectinib in crizotinib-refractory ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase ii global study. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(7):661–8.
Shaw AT, Gandhi L, Gadgeel S, Riely GJ, Cetnar J, West H, et al. Alectinib in ALK-positive, crizotinib-resistant, non-small-cell lung cancer: a single-group, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(2):234–42.
Tamura T, Kiura K, Seto T, Nakagawa K, Maemondo M, Inoue A, et al. Three-year follow-up of an alectinib phase I/II study in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: AF-001JP. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(14):1515–21.
Hida T, Nokihara H, Kondo M, Kim YH, Azuma K, Seto T, et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017;390(10089):29–39.
Ou SH, Klempner SJ, Azada MC, Rausei-Mills V, Duma C. Radiation necrosis presenting as pseudoprogression (PsP) during alectinib treatment of previously radiated brain metastases in ALK-positive NSCLC: Implications for disease assessment and management. Lung Cancer. 2015;88(3):355–9.
Gainor JF, Sherman CA, Willoughby K, Logan J, Kennedy E, Brastianos PK, et al. Alectinib salvages CNS relapses in ALK-positive lung cancer patients previously treated with crizotinib and ceritinib. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10(2):232–6.
Huang WS, Liu S, Zou D, Thomas M, Wang Y, Zhou T, et al. Discovery of brigatinib (AP26113), a phosphine oxide-containing, potent, orally active inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase. J Med Chem. 2016;59(10):4948–64.
Zhang S, Anjum R, Squillace R, Nadworny S, Zhou T, Keats J, et al. The potent ALK inhibitor brigatinib (AP26113) overcomes mechanisms of resistance to first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors in preclinical models. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(22):5527–38.
Kim DW, Tiseo M, Ahn MJ, Reckamp KL, Hansen KH, Kim SW, et al. Brigatinib in patients with crizotinib-refractory anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomized, multicenter phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(22):2490–8.
Johnson TW, Richardson PF, Bailey S, Brooun A, Burke BJ, Collins MR, et al. Discovery of (10R)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2H-8,4-(m etheno)pyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]-benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile (PF-06463922), a macrocyclic inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) with preclinical brain exposure and broad-spectrum potency against ALK-resistant mutations. J Med Chem. 2014;57(11):4720–44.
Collier TL, Normandin MD, Stephenson NA, Livni E, Liang SH, Wooten DW, et al. Synthesis and preliminary PET imaging of 11C and 18F isotopologues of the ROS1/ALK inhibitor lorlatinib. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15761.
Shaw AT, Felip E, Bauer TM, Besse B, Navarro A, Postel-Vinay S, et al. Lorlatinib in non-small-cell lung cancer with ALK or ROS1 rearrangement: an international, multicentre, open-label, single-arm first-in-man phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(12):1590–9.
Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Perez-Gracia JL, Han JY, et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;387(10027):1540–50.
Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, Crino L, Eberhardt WE, Poddubskaya E, et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(2):123–35.
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR, Steins M, Ready NE, et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(17):1627–39.
Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, Park K, Ciardiello F, von Pawel J, et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10066):255–65.
Louveau A, Smirnov I, Keyes TJ, Eccles JD, Rouhani SJ, Peske JD, et al. Structural and functional features of central nervous system lymphatic vessels. Nature. 2015;523(7560):337–41.
Aspelund A, Antila S, Proulx ST, Karlsen TV, Karaman S, Detmar M, et al. A dural lymphatic vascular system that drains brain interstitial fluid and macromolecules. J Exp Med. 2015;212(7):991–9.
Berghoff AS, Preusser M. The inflammatory microenvironment in brain metastases: potential treatment target? Chin Clin Oncol. 2015;4(2):21.
Pukrop T, Dehghani F, Chuang HN, Lohaus R, Bayanga K, Heermann S, et al. Microglia promote colonization of brain tissue by breast cancer cells in a Wnt-dependent way. Glia. 2010;58(12):1477–89.
Ransohoff RM, Engelhardt B. The anatomical and cellular basis of immune surveillance in the central nervous system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12(9):623–35.
Kivisakk P, Tucky B, Wei T, Campbell JJ, Ransohoff RM. Human cerebrospinal fluid contains CD4+ memory T cells expressing gut- or skin-specific trafficking determinants: relevance for immunotherapy. BMC Immunol. 2006;7:14.
Le DT, Uram JN, Wang H, Bartlett BR, Kemberling H, Eyring AD, et al. PD-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(26):2509–20.
Berghoff AS, Fuchs E, Ricken G, Mlecnik B, Bindea G, Spanberger T, et al. Density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes correlates with extent of brain edema and overall survival time in patients with brain metastases. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5(1):e1057388.
Berghoff AS, Kiesel B, Widhalm G, Rajky O, Ricken G, Wohrer A, et al. Programmed death ligand 1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2015;17(8):1064–75.
Berghoff AS, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILS) and PD-l1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases (BM) and matched primary tumors (PT). Ann Oncol. 2014;25(Suppl 4):iv465–6.
Rizvi NA, Hellmann MD, Snyder A, Kvistborg P, Makarov V, Havel JJ, et al. Cancer immunology. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science. 2015;348(6230):124–8.
Goldberg SB, Gettinger SN, Mahajan A, Chiang AC, Herbst RS, Sznol M, et al. Pembrolizumab for patients with melanoma or non-small-cell lung cancer and untreated brain metastases: early analysis of a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(7):976–83.
Rizvi NA, Mazieres J, Planchard D, Stinchcombe TE, Dy GK, Antonia SJ, et al. Activity and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, for patients with advanced, refractory squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 063): a phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(3):257–65.
Lukas RV, Gandhi M, O’Hear C, Hu S, Lai C, Patel JD. Safety and efficacy analyses of atezolizumab in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with or without baseline brain metastases. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(Suppl 2):ii28–51.
Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, Vicente D, Murakami S, Hui R, et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(20):1919–29.
Iuchi T, Shingyoji M, Sakaida T, Hatano K, Nagano O, Itakura M, et al. Phase II trial of gefitinib alone without radiation therapy for Japanese patients with brain metastases from EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2013;82(2):282–7.
Zeng YD, Zhang L, Liao H, Liang Y, Xu F, Liu JL, et al. Gefitinib alone or with concomitant whole brain radiotherapy for patients with brain metastasis from non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(3):909–14.
Park SJ, Kim HT, Lee DH, Kim KP, Kim SW, Suh C, et al. Efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for brain metastasis in nonsmall cell lung cancer patients harboring either exon 19 or 21 mutation. Lung Cancer. 2012;77(3):556–60.
Porta R, Sanchez-Torres JM, Paz-Ares L, Massuti B, Reguart N, Mayo C, et al. Brain metastases from lung cancer responding to erlotinib: the importance of EGFR mutation. Eur Respir J. 2011;37(3):624–31.
Kim JE, Lee DH, Choi Y, Yoon DH, Kim SW, Suh C, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors as a first-line therapy for neversmokers with adenocarcinoma of the lung having asymptomatic synchronous brain metastasis. Lung Cancer. 2009;65(3):351–4.
Kim DW, Mehra R, Tan DS, Felip E, Chow LQ, Camidge DR, et al. Activity and safety of ceritinib in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-1): updated results from the multicentre, open-label, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(4):452–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Grainne M. O’Kane is supported by the Division of Medical Oncology/Hematology, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, and Natasha B. Leighl is supported by the Princess Margaret Cancer Foundation OSI Pharmaceuticals Foundation Chair in Cancer New Drug Development. No external funding support was provided for this review.
Conflict of Interest
Grainne M. O’Kane and Natasha B. Leighl declare that they have no conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this review.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Kane, G.M., Leighl, N.B. Systemic Therapy of Lung Cancer CNS Metastases Using Molecularly Targeted Agents and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. CNS Drugs 32, 527–542 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-018-0526-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-018-0526-4